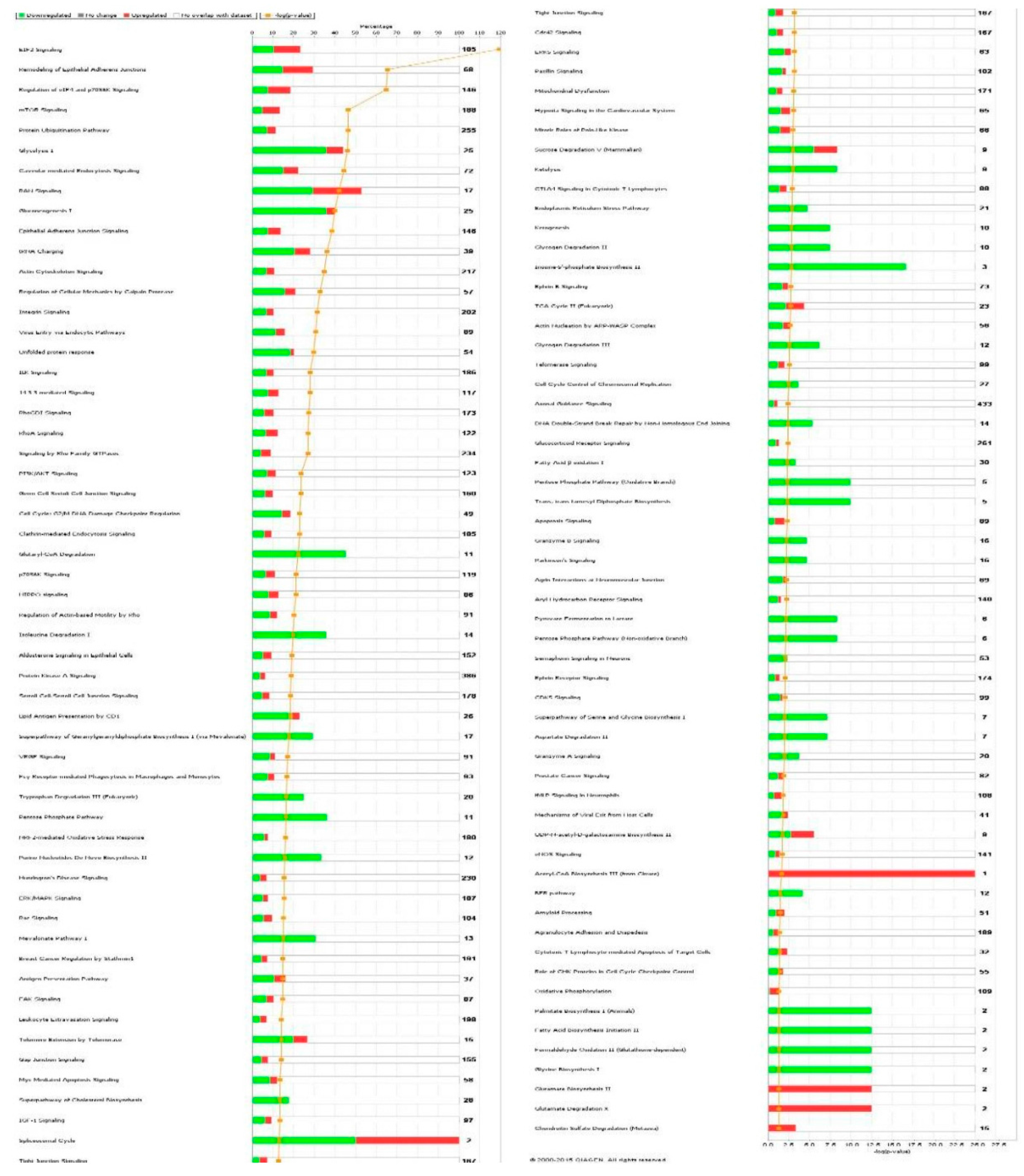
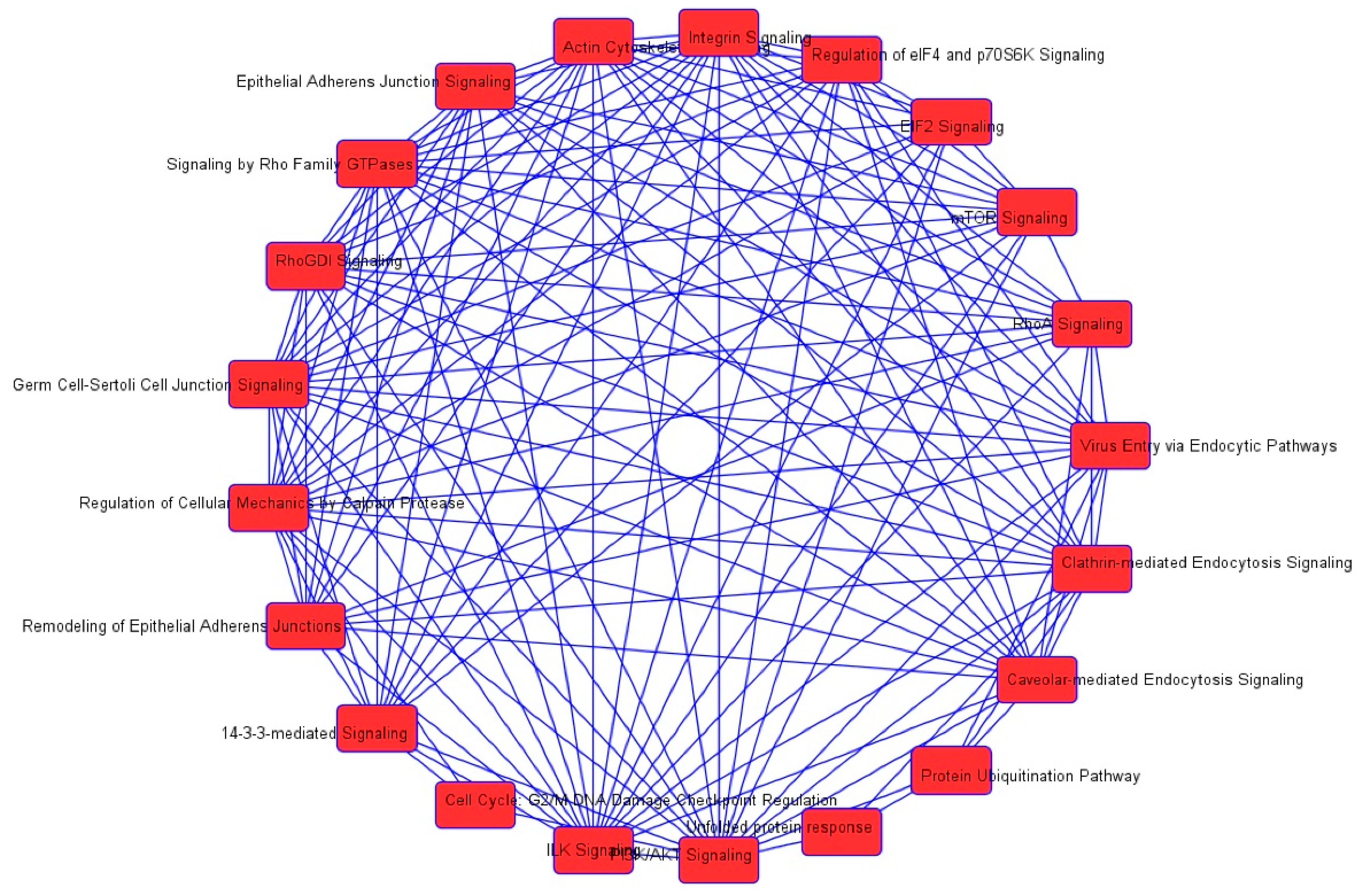
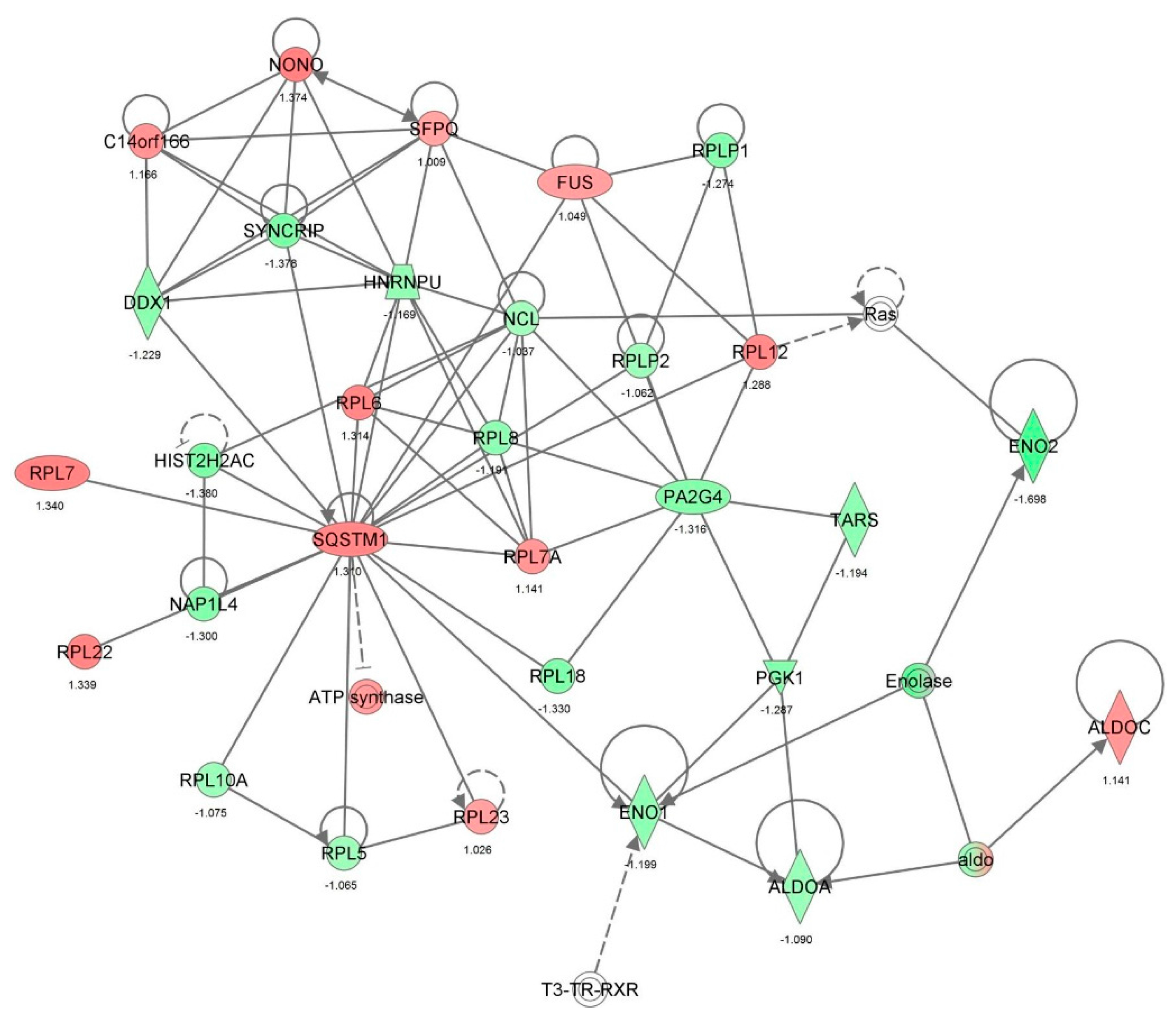
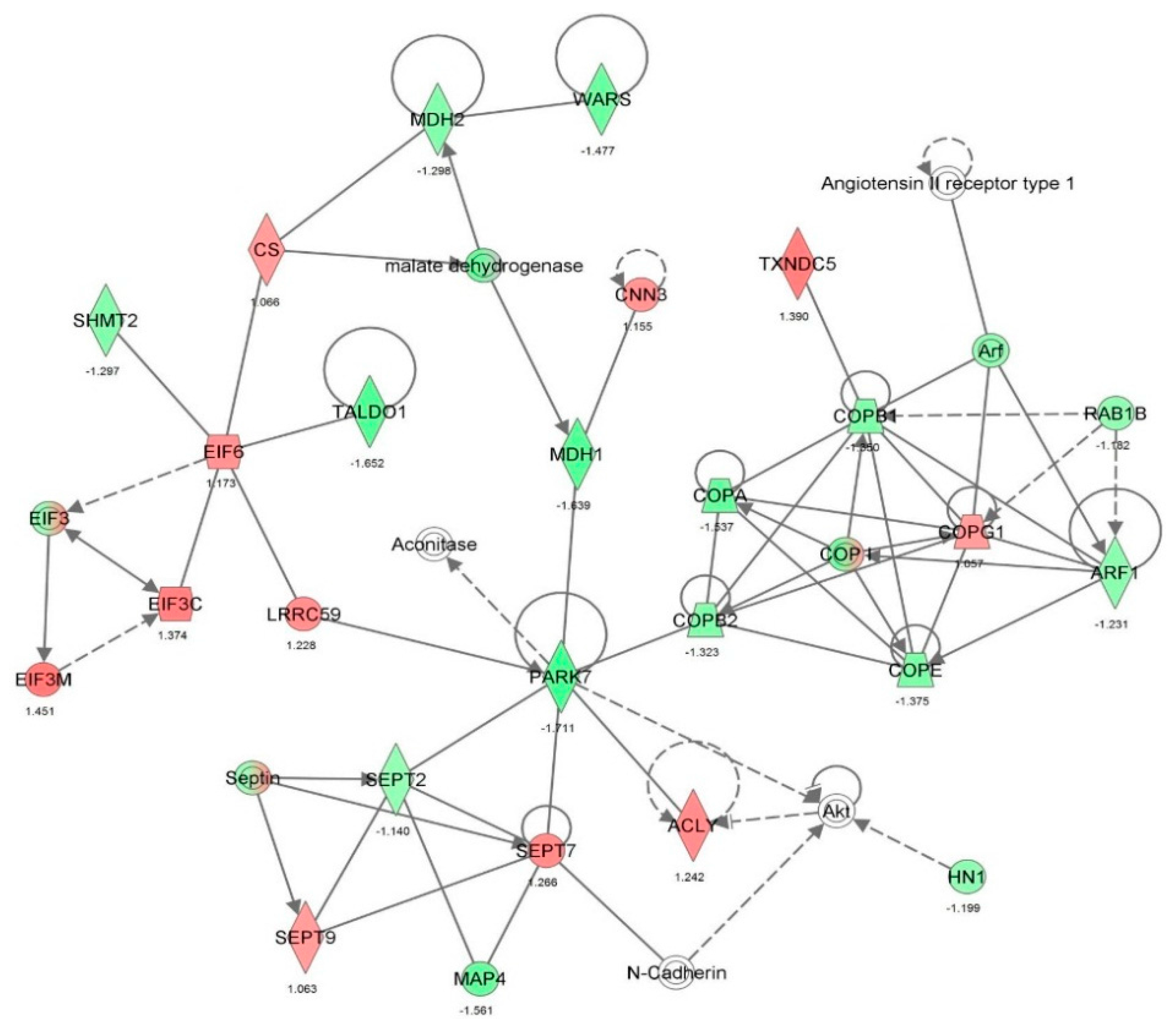
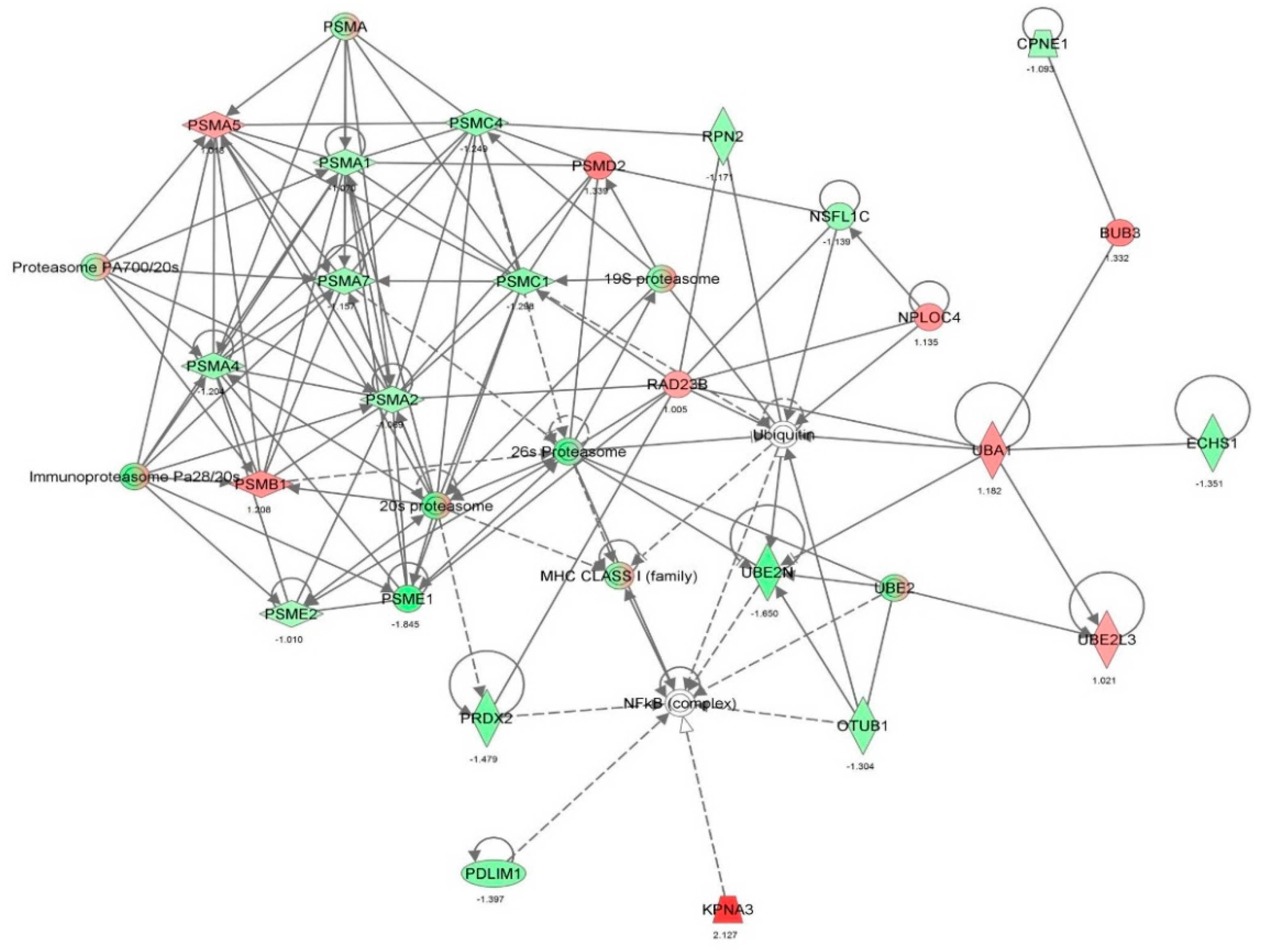
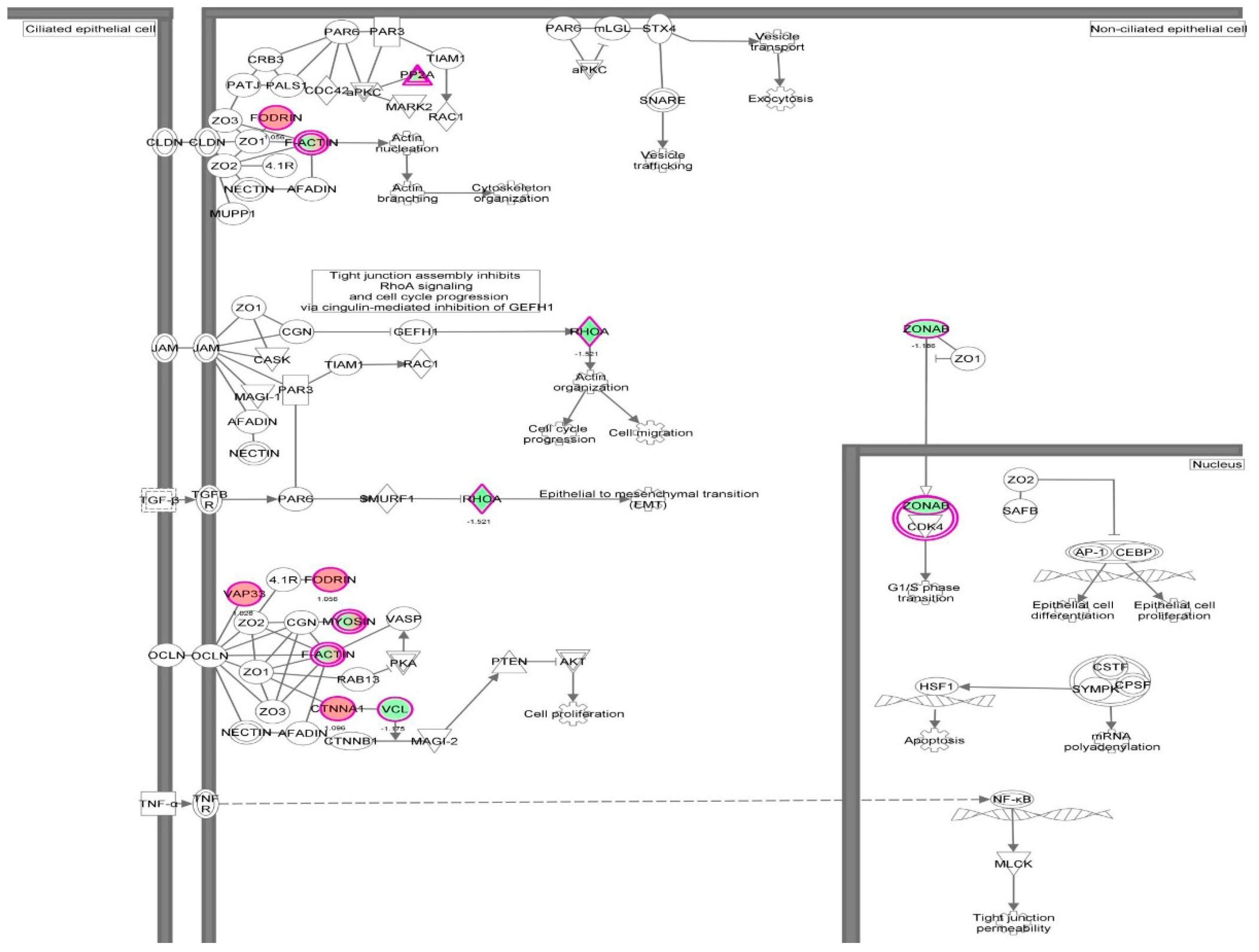
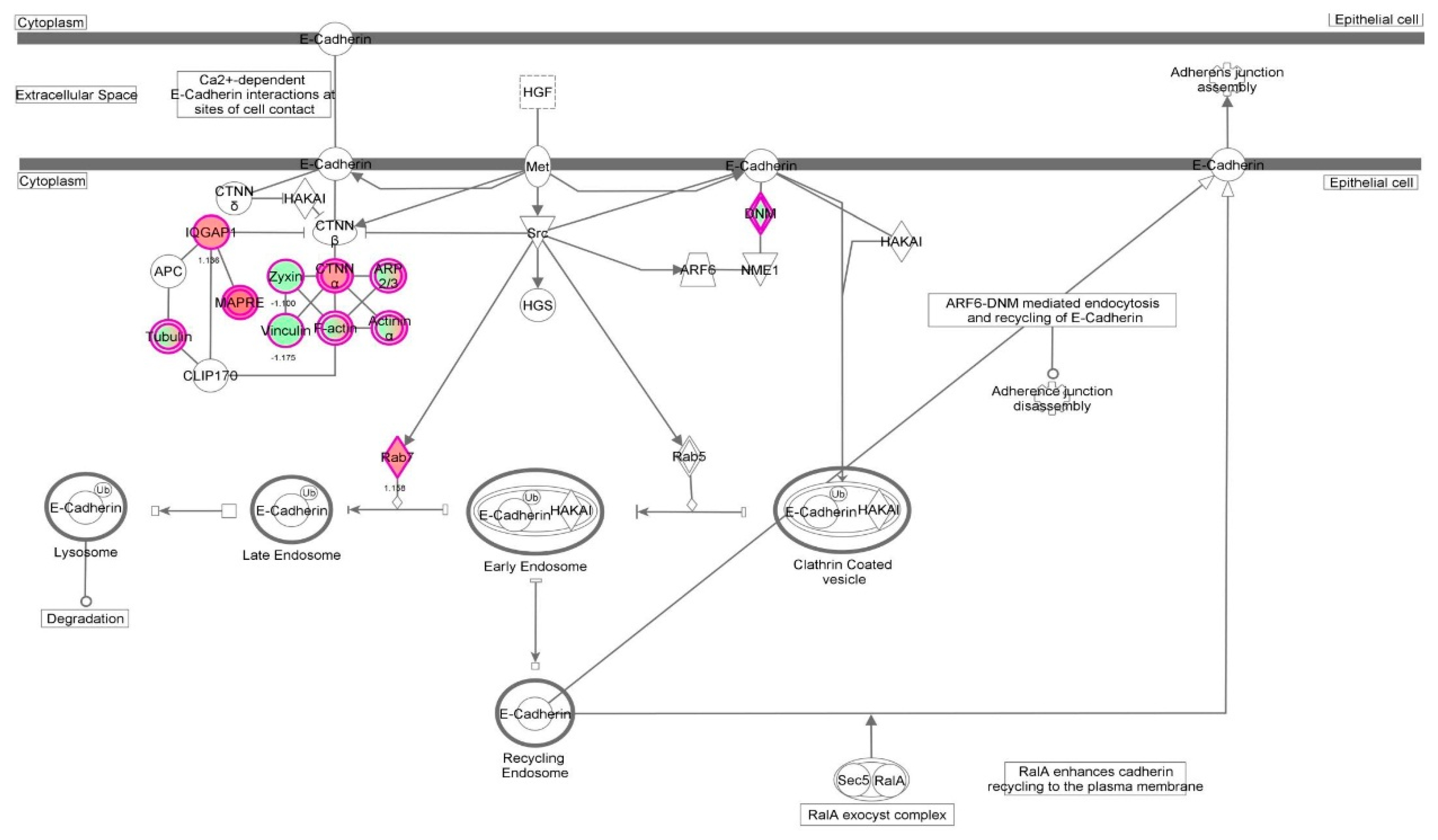
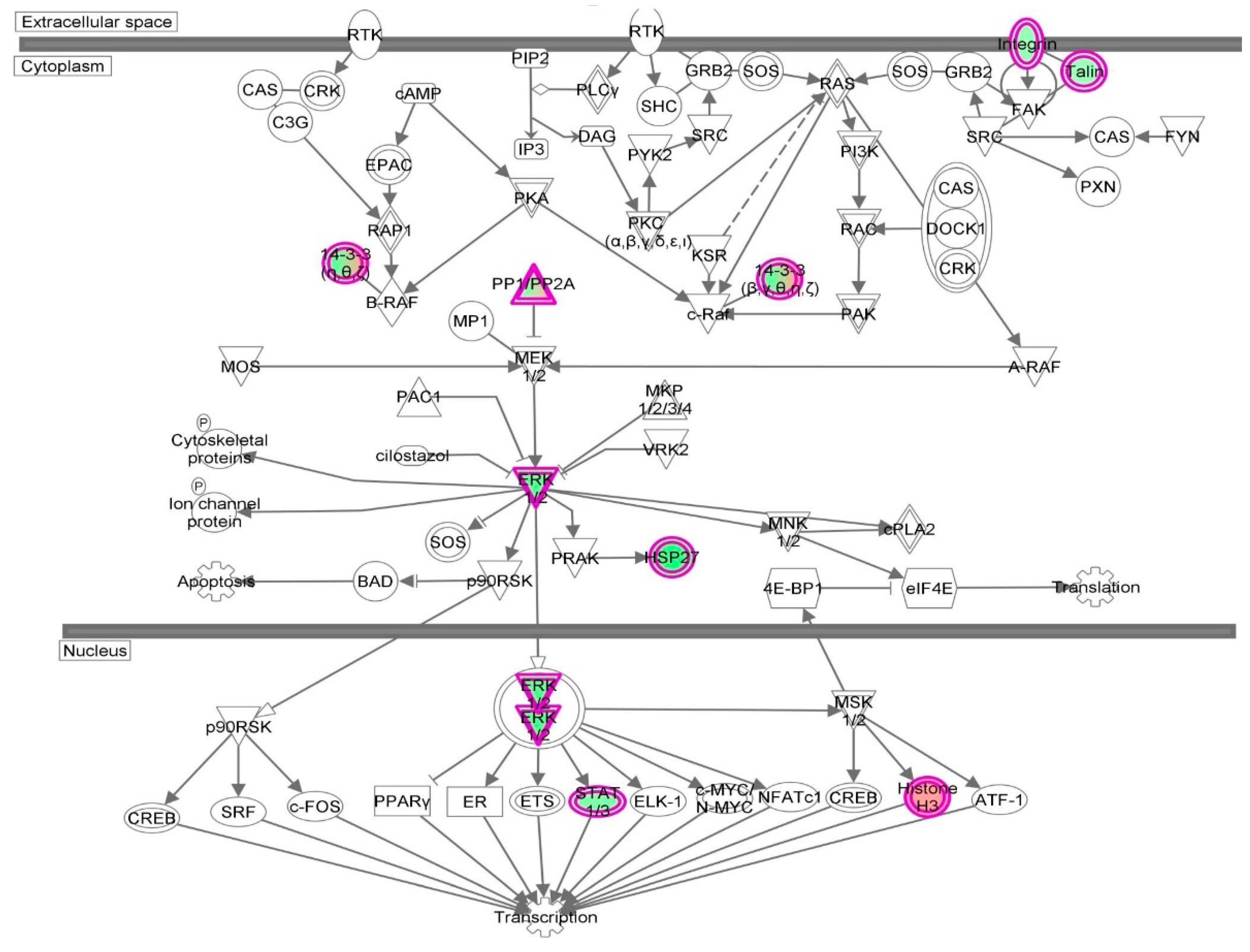
| Cell death and survival | Cell death | 2.14 × 10−35 | 0.626 | AARS, ACAT1, ACLY, ACTN4, AHSA1, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP2B1, APEX1, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, B2M, BASP1, BSG, BTF3, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CANX, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC4, CSE1L, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DNAJA1, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EHD1, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF4G1, EIF5A, EIF6, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, FUS, G6PD, GAPDH, GLO1, GLUD1, GML, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, HADHA, HDGF, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPK, HSD17B10, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KPNB1, KRT18, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LONP1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MCM7, MDH1, MSN, MVP, MYH9, NCL, | 232 |
| | | | | NPM1, NUMA1, OTUB1, P4HB, PA2G4, PAFAH1B2, PARK7, PCBP2, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDIA3, PDXK, PEA15, PEBP1, PHB2, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PPIA, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX4, PRDX5, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMB1, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PSME2, PTGES3, PTMA, QARS, RAD23B, RAN, RANBP1, RBM3, RHOA, RPL10, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPSA, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SND1, SOD1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TNC, TPM3, TPP1, TRIM28, TUBB, TUBB6, TUFM, TXNDC5, UBA1, UBE2L3, UBE2N, UCHL1, VAPA, VCL, VCP, VDAC1, VDAC2, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
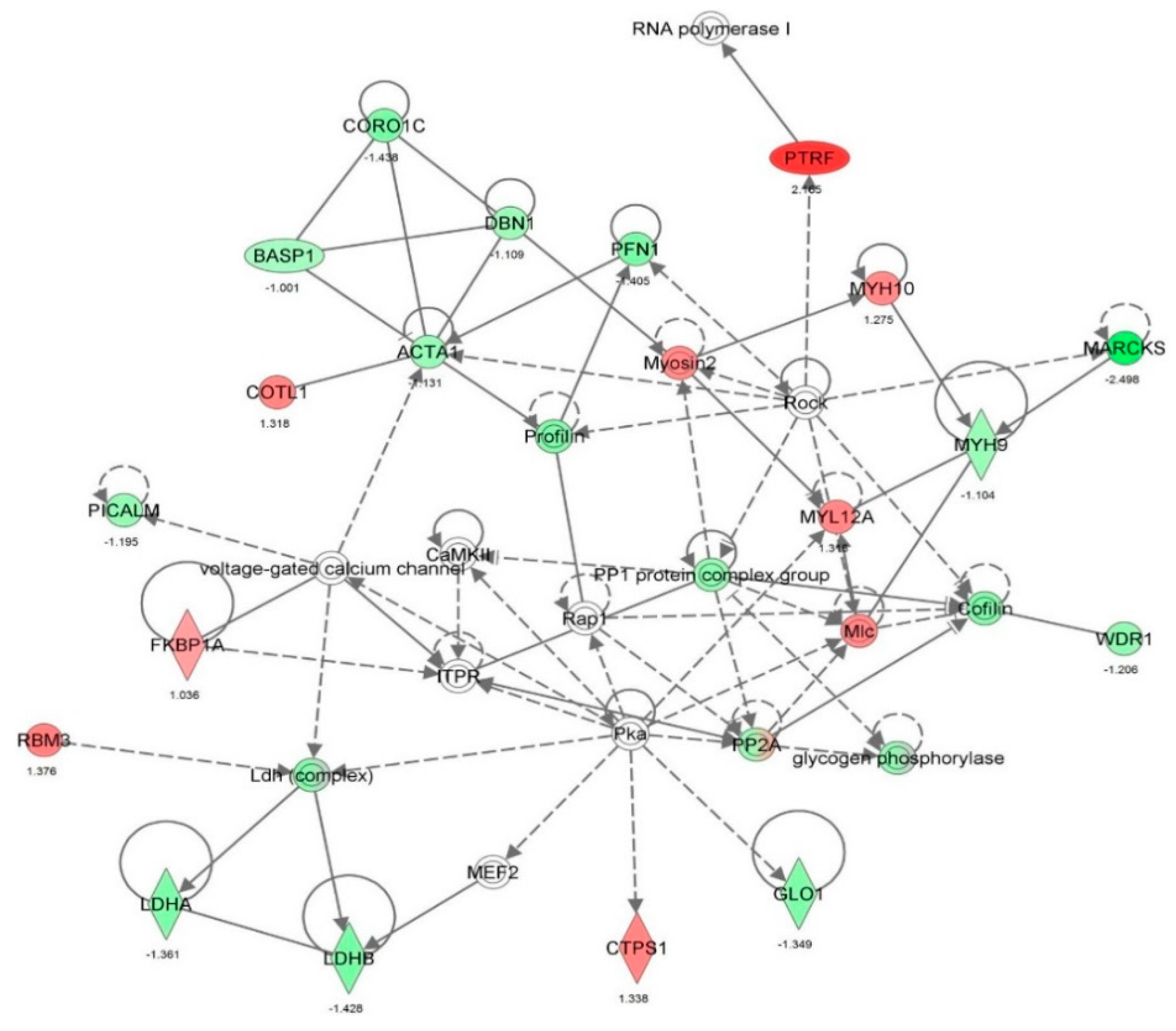
| Cellular growth and proliferation | Proliferation of cells | 5.39 × 10−34 | −1.530 | AARS, ACAT1, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, AHCY, AHNAK, AHSA1, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, BUB3, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZA1, CAST, CAV1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT5, CCT7, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC1, CLTC, COPE, CSE1L, CSRP1, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX3X, DDX5, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNM1L, DPY30, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF5A, EIF6, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, FN1, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GAPDH, GML, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HDGF, HEXB, HINT1, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPR, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPB1, HSPD1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO7, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LONP1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MCM3, MCM4, MCM7, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NPM1, NUMA1, PA2G4, PARK7, PCNA, PDCD6, PDIA3, PDXK, PEA15, PEBP1, PFKP, PFN1, PGK1, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLS3, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX4, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMA4, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PSME2, PTBP1, PTGES3, PTMA, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RBM3, RHOA, RNH1, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPSA, RTN4, S100A6, SAE1, SEPT9, SERPINH1, SET, SFN, SFPQ, SHMT2, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SND1, SNX3, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, SURF4, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TPM3, TRIM28, TUBB, TUBB4B, TXLNA, TXNDC5, UBA1, UBE2L3, UBE2N, UCHL1, VAPA, VCL, VCP, VDAC1, VIM, WARS, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAG, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 242 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis | 8.59 × 10−31 | 0.054 | AARS, ACLY, ACTN4, AHSA1, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, APEX1, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, B2M, BASP1, BSG, BTF3, C1QBP, CALR, CANX, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, CCT2, CCT4, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC4, CSE1L, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DNAJA1, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EHD1, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF4G1, EIF5A, EIF6, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, FUS, G6PD, GAPDH, GLO1, GLUD1, GML, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, HDGF, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HLA-B, | 192 |
| | | | | HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPK, HSD17B10, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, ILF3, IMMT, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT18, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MDH1, MSN, MVP, NCL, NPM1, NUMA1, OTUB1, P4HB, PA2G4, PAFAH1B2, PARK7, PCBP2, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDIA3, PDXK, PEA15, PEBP1, PHB2, PKM, PPIA, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX4, PRDX5, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMB1, PTMA, QARS, RAD23B, RANBP1, RBM3, RHOA, RPL10, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SERPINH1, SET, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SND1, SOD1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TNC, TRIM28, TXNDC5, UBA1, UCHL1, VCL, VCP, VDAC1, VDAC2, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAQ, YWHAZ | |
| Cell death and survival | Necrosis | 1.65 × 10−30 | 1.232 | AARS, ACAT1, ACLY, AHSA1, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA2, AP2B1, APEX1, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, B2M, BSG, CALR, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CLIC4, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DDX3X, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF6, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, FUS, G6PD, GAPDH, GLO1, GLUD1, GML, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, HADHA, HDGF, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPK, HSD17B10, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, ILF2, IMMT, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KPNB1, KRT18, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LONP1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MCM7, MDH1, MSN, MVP, NCL, NPM1, OTUB1, P4HB, PA2G4, PARK7, PCBP2, PCNA, PDIA3, PEA15, PEBP1, PKM, PLEC, PPIA, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMB1, PSMD2, PTMA, RAD23B, RAN, RBM3, RHOA, RPL10, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPSA, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SFN, SFPQ, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SND1, SOD1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TPP1, TRIM28, TUBB, TUBB6, TUFM, UBA1, UBE2L3, UCHL1, VAPA, VCP, VDAC1, VDAC2, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 188 |
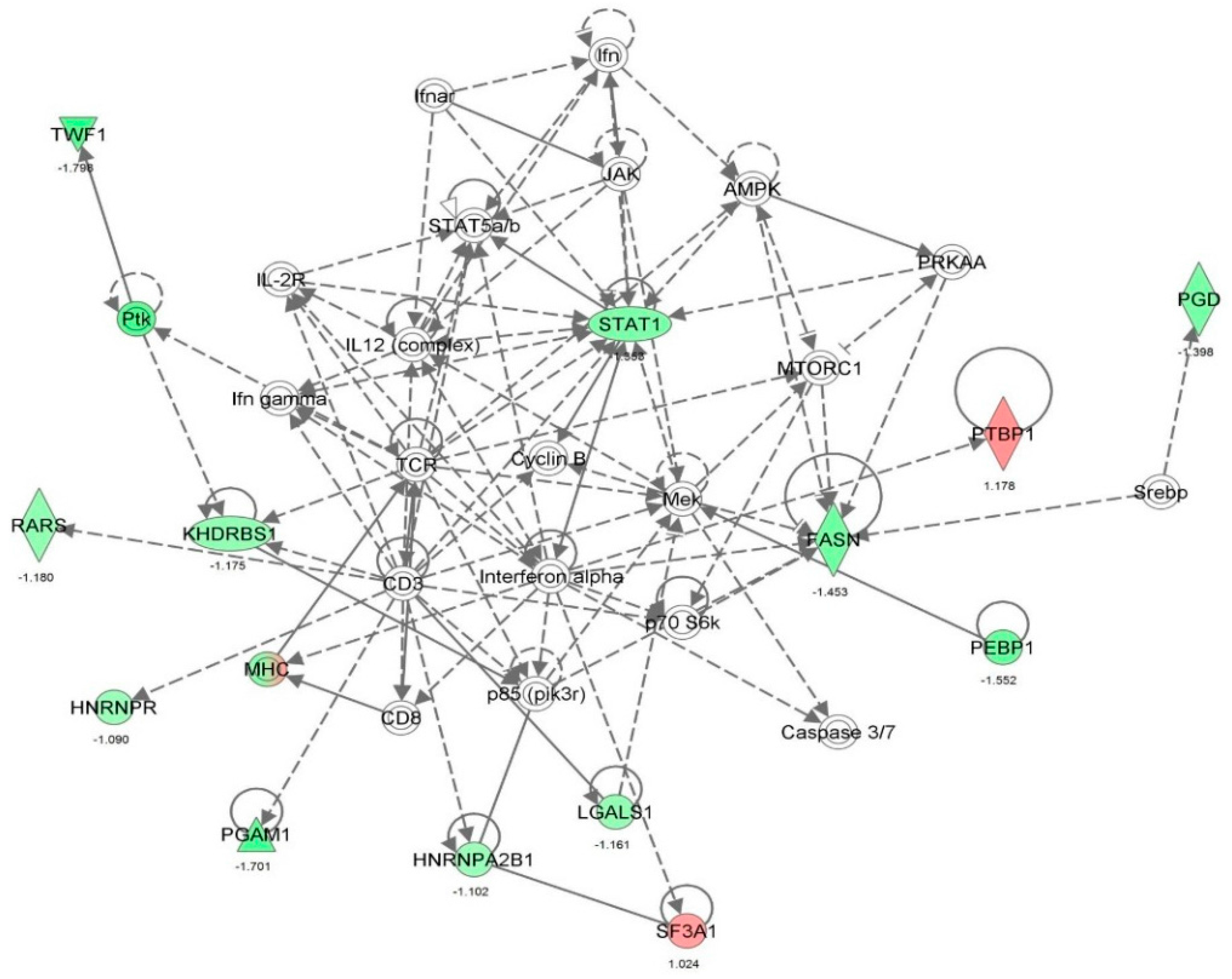
| Infectious disease | Viral infection | 2.33 × 10−30 | −1.968 | ACTN1, ACTR2, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, ANXA6, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARF1, ARPC1B, ATP5B, B2M, BSG, BTF3, C14orf166, CAV1, CCT2, CD44, CLIC4, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, CSE1L, CTSB, DDX3X, DDX5, DDX6, DHX9, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNM1L, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF3C, EIF3I, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, G3BP1, GANAB, GAPDH, GML, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPK, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA9, HSPD1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF3, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KPNB1, KRT18, KRT8, LGALS1, LMNA, LONP1, MAP4, MAPK1, MVP, NCL, NPM1, PCBP2, PDIA3, PDIA6, PDXK, PGM1, PICALM, PLIN3, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PSMD2, PSME2, PTGES3, PYGL, RAB11A, RAB1B, RAB7A, RAN, RANBP1, RHOA, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5, RPS10, RPS27A, RPS5, RPSA, SAE1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, | 142 |
| | | | | SNRPD3, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, SUPT16H, TAGLN2, TALDO1, TFRC, TKT, TMPO, TUBB, TUBB4B, TWF1, UAP1, UBE2L3, UQCRC1, XPO1, YBX1, ZYX | |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of tumor cell lines | 1.13 × 10−27 | 0.949 | AHSA1, AKR1B1, ANXA2, APEX1, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, B2M, CALR, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAST, CAV1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DDX3X, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EIF2S1, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNB, FN1, G6PD, GAPDH, GLO1, GML, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, HINT1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPK, HSP90AB1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, IGF2R, ILF2, IMMT, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KPNB1, KRT18, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LONP1, MAPK1, MCM7, MSN, MVP, NCL, NPM1, OTUB1, P4HB, PA2G4, PARK7, PCBP2, PCNA, PEA15, PEBP1, PKM, PPIA, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMD2, PTMA, RAD23B, RHOA, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, RTN4, S100A6, SF3A1, SFN, SFPQ, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SND1, SOD1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STMN1, STOML2, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TRIM28, TUBB6, TUFM, UBE2L3, UCHL1, VCP, VDAC1, VDAC2, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAZ | 131 |
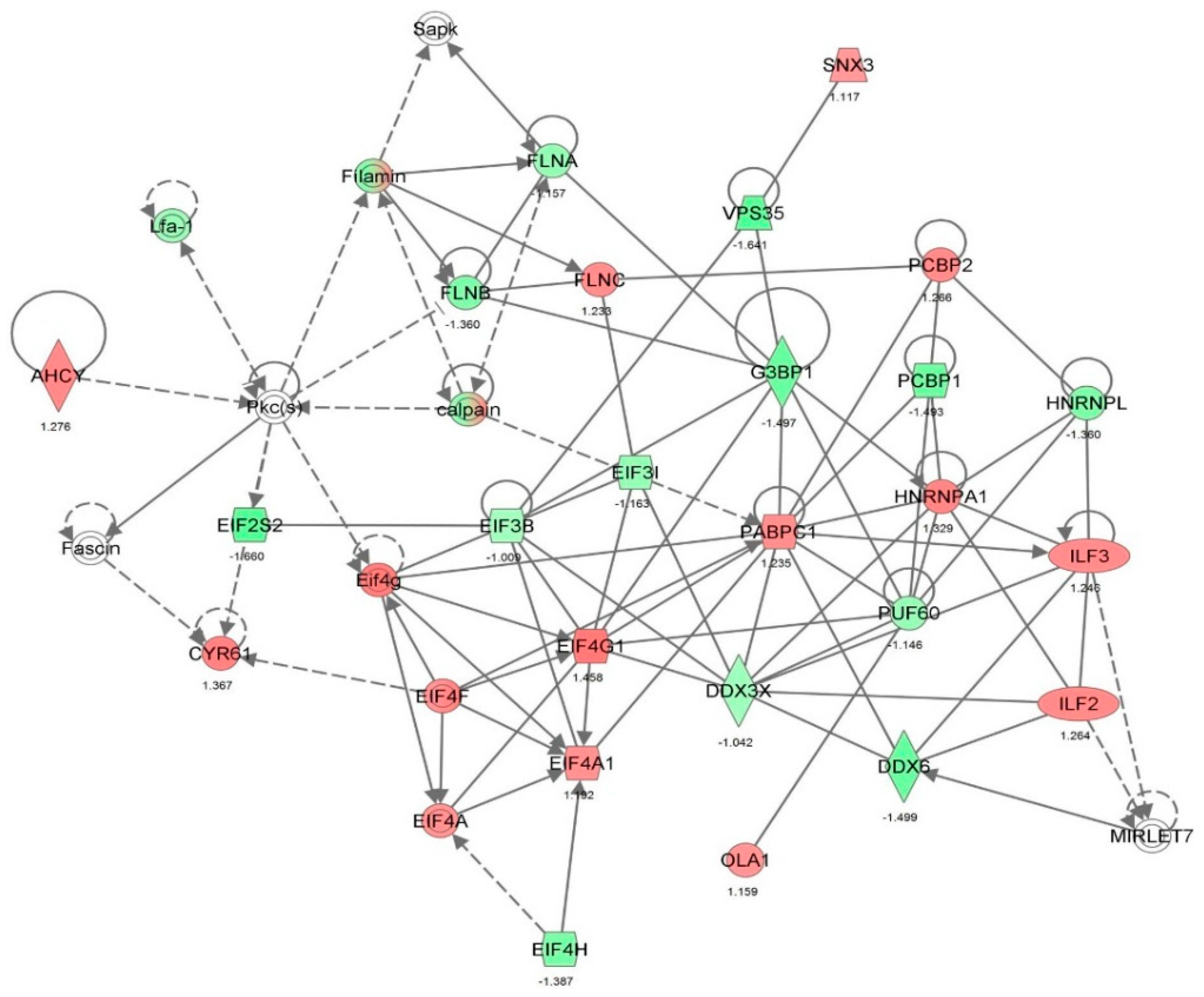
| Protein synthesis | Translation | 6.09 × 10−25 | 0.792 | APEX1, CALR, CAPRIN1, DDX3X, DDX6, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EIF5A, EPRS, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPK, HSPA5, HSPB1, ILF3, ITGB1, MARS, NACA, NCL, PABPC1, PCBP1, PPP1CA, PTBP1, RBM3, RPL23, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, SYNCRIP, TUFM, WARS, YBX1 | 47 |
| Protein synthesis | Translation of protein | 2.00 × 10−23 | 0.860 | APEX1, CALR, CAPRIN1, DDX3X, DDX6, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EIF5A, EPRS, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPK, HSPA5, HSPB1, ILF3, ITGB1, MARS, NACA, NCL, PABPC1, PCBP1, PPP1CA, PTBP1, RBM3, RPL23, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, SYNCRIP, WARS, YBX1 | 45 |
| Protein synthesis | Expression of protein | 2.95 × 10−22 | 0.229 | ANXA1, APEX1, CALR, CAPRIN1, CAV1, DDX3X, DDX6, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EIF5A, EPRS, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPK, HSPA5, HSPB1, ILF3, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, MARS, NACA, NCL, PABPC1, PCBP1, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PTBP1, RBM3, RPL23, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, SOD1, SYNCRIP, WARS, YBX1 | 50 |
| Protein synthesis | Synthesis of protein | 3.25 × 10−22 | −0.265 | ANXA1, APEX1, CALR, CAPRIN1, CAV1, DDX3X, DDX6, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EIF5A, EIF6, EPRS, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPK, HSPA5, HSPB1, ILF3, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, MAPK1, MARS, NACA, NCL, NPM1, PABPC1, PARK7, PCBP1, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PTBP1, RBM3, RPL23, RPL5, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, SOD1, STIP1, SYNCRIP, TUFM, WARS, YBX1 | 58 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of tumor cell lines | 3.17 × 10−21 | 0.816 | AHSA1, AKR1B1, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, B2M, CALR, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAST, CAV1, CCT2, CCT4, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FLNB, FN1, G6PD, GAPDH, GLO1, GML, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HINT1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPK, HSP90AB1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, IGF2R, IMMT, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT18, LGALS1, LMNB1, MAPK1, MSN, MVP, NCL, NPM1, OTUB1, P4HB, PA2G4, PARK7, PCBP2, PCNA, PEA15, PEBP1, PPIA, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PTMA, RAD23B, RHOA, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, RTN4, S100A6, SFN, SFPQ, SLC25A5, SND1, SOD1, SSRP1, STAT1, | 102 |
| | | | | STMN1, STOML2, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TRIM28, UCHL1, VCP, VDAC1, VDAC2, XPO1, XRCC5, YBX1, YWHAE, YWHAZ | |
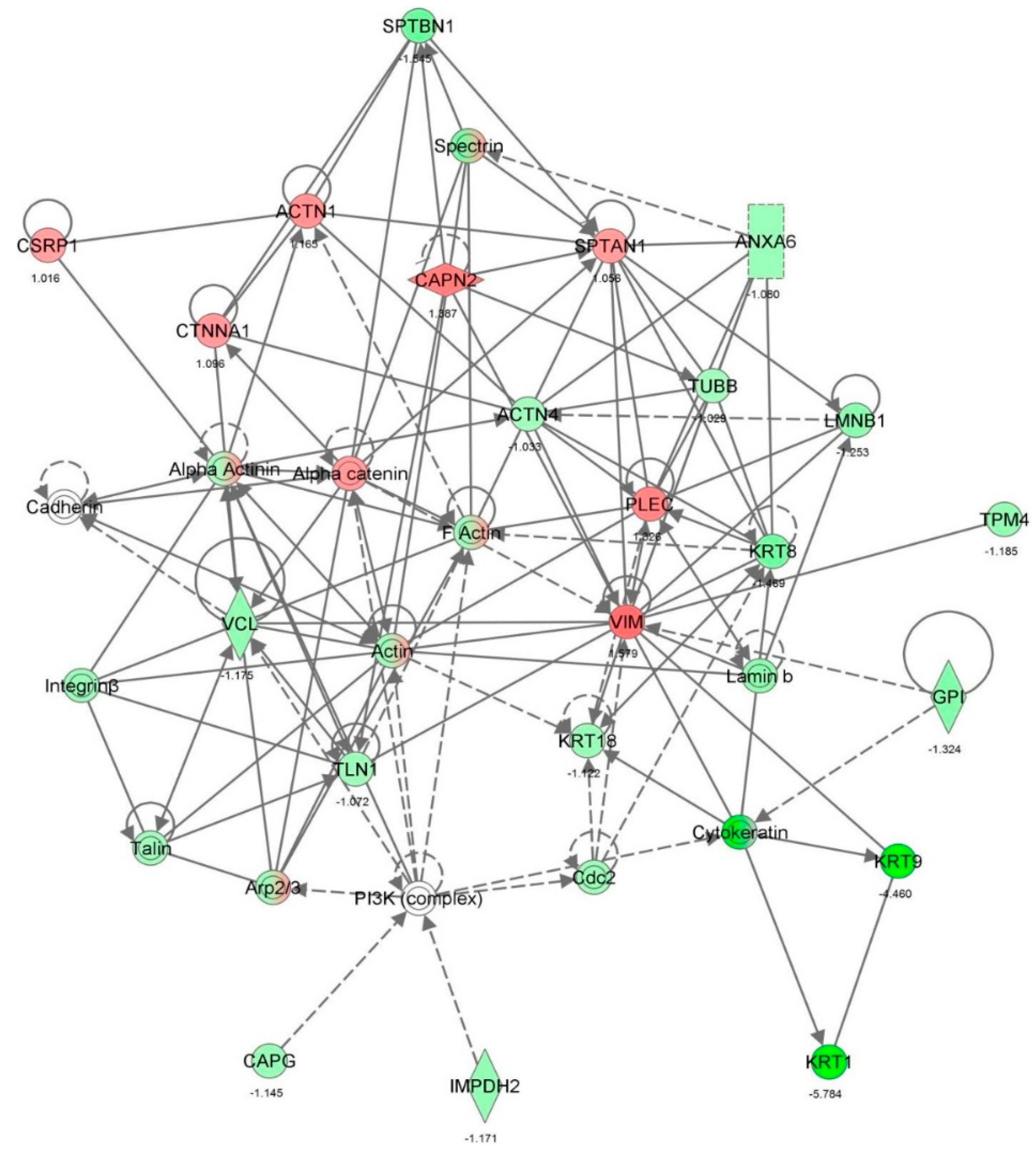
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Organization of cytoplasm | 4.80 × 10−20 | −1.198 | ACTG1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, BASP1, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CKAP4, CLTC, COPB2, CORO1C, CSRP1, CTTN, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FASN, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GAPDH, GDI1, HDGF, HEXB, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSPB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KIF5B, KPNB1, KRT18, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, LONP1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NNMT, NPLOC4, NSFL1C, NUMA1, PARK7, PCM1, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLS3, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, PRKDC, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RHOA, RRBP1, RTN4, SEPT2, SEPT7, SEPT9, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, SURF4, TLN1, TMOD3, TNC, TPM3, TPP1, TUBB, TWF2, UCHL1, VAPA, VCL, VIM, XPO1, YBX1, YWHAH | 116 |
| Protein synthesis | Metabolism of protein | 8.33 × 10−20 | 0.064 | ANXA1, APEX1, CALR, CANX, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, COPG1, CSTB, CTSB, DDX3X, DDX6, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EIF5A, EIF6, EPRS, FLNA, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HEXB, HNRNPK, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, ILF3, IPO9, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, LONP1, MAPK1, MARS, MYH9, NACA, NCL, NPEPPS, NPM1, PABPC1, PARK7, PCBP1, PDIA3, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PSMC4, PSMD2, PTBP1, RBM3, RPL23, RPL5, RPS24, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, SNX3, SOD1, SQSTM1, STIP1, SYNCRIP, TPP1, TUFM, UBE2L3, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VCP, WARS, XPO1, YBX1 | 87 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Mammary tumor | 1.12 × 10−19 | 1.847 | AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ALYREF, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, ATP5A1, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, CBX3, CCT3, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CTTN, CYR61, DDX5, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ETFA, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, FUS, GCN1L1, GLO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HDLBP, HLA-A, HLA-B, HNRNPA1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPD1, ILF3, ITGB1, KHSRP, KPNA2, KRT18, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LGALS1, LMNA, LONP1, MAPRE1, MARS, MCM4, MCM6, MYH10, MYH9, NAP1L4, NCL, NPEPPS, P4HB, PAFAH1B2, PCNA, PDCD6, PFN1, PGK1, PGM1, PKM, PLEC, PRDX1, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PTBP1, PTRF, RANBP1, RHOA, RPL4, RPL6, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, RPS4X, S100A6, SF3B1, SFPQ, SHMT2, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SOD1, STAT1, STIP1, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TCP1, TLN1, TNC, TPI1, TUBA1B, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, UBA1, UCHL1, VCL, VDAC2, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC5, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 119 |
| Dermatological diseases and conditions | Psoriasis | 2.52 × 10−19 | | ANXA1, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, ARPC1B, C1QBP, CALR, CAV1, CBX3, CCT5, CFL1, COPB2, CSTB, CTSB, CYB5R3, DBN1, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF5A, EIF6, FASN, FKBP1A, FN1, GAPDH, GARS, GSTP1, H2AFY, HSPA5, HSPA8, KPNA2, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, LGALS1, MARCKS, OTUB1, P4HB, PCBP2, PCMT1, PCNA, PGAM1, PGD, PKM, PPP2CA, PSME2, PTRF, RAN, RANBP1, SERBP1, SFN, SLC25A5, SPTAN1, STAT1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TNC, TUBB, TWF1, UBE2N, VDAC1, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAQ | 63 |
| Infectious disease | Infection of cells | 2.88 × 10−19 | −2.041 | ACTR2, ANXA2, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARF1, ARPC1B, ATP5B, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, CCT2, CD44, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, CTSB, DDX3X, DHX9, DNAJA2, EIF3I, FN1, G3BP1, | 78 |
| | | | | GANAB, GML, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPK, HNRNPU, HSPA5, HSPA9, IFITM3, IGF2R, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, KRT18, MAP4, PCBP2, PDIA3, PDIA6, PGM1, PICALM, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PSME2, PTGES3, RAB1B, RANBP1, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, STAT1, STIP1, TAGLN2, TFRC, TWF1, UAP1, UBE2L3, UQCRC1, XPO1, YBX1, ZYX | |
| Infectious disease | Replication of virus | 5.92 × 10−19 | −0.358 | ANXA5, ANXA6, ATP5B, B2M, BTF3, C14orf166, CAV1, CLIC4, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, CSE1L, DDX3X, DDX5, DDX6, DHX9, DNAJA1, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF3C, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, G3BP1, HMGB1, HNRNPM, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IFITM3, ILF3, KPNB1, KRT8, LONP1, MAPK1, MVP, NCL, NPM1, PCBP2, PLIN3, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PSMA1, PSMD2, RAB11A, RPS10, RPS27A, RPS5, RPSA, SAE1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SSRP1, STAT1, TMPO, TUBB, XPO1, YBX1 | 62 |
| Neurological disease | Progressive motor neuropathy | 9.90 × 10−19 | | ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, CAPN2, CAPZB, CCT2, COPE, CSE1L, CYR61, DBI, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENO2, EZR, FASN, FUS, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-B, HN1, HNRNPA1, HSPA5, HSPB1, IMPDH2, LDHA, LDHB, MAP1B, MAPK1, MDH1, NNMT, PARK7, PCNA, PDIA3, PEBP1, PFKP, PFN1, PGK1, PRDX2, PSMC1, PTGES3, RAN, RHOA, RPL3, RPL5, RPS3A, RPS4X, RTN4, S100A6, SLC25A6, SOD1, STMN1, TFRC, TUBA1B, UCHL1, VCP, VIM, VPS35 | 58 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Organization of cytoskeleton | 1.01 × 10−18 | −1.190 | ACTG1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, BASP1, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CKAP4, COPB2, CORO1C, CSRP1, CTTN, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FASN, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GAPDH, GDI1, HDGF, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSPB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KIF5B, KPNB1, KRT18, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NNMT, NUMA1, PCM1, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLS3, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, PRKDC, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RHOA, RRBP1, RTN4, SEPT2, SEPT7, SEPT9, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STIP1, STMN1, TLN1, TMOD3, TNC, TPM3, TUBB, TWF2, UCHL1, VAPA, VCL, VIM, XPO1, YBX1, YWHAH | 107 |
| Post-translational modification, protein folding | Folding of protein | 1.21 × 10−18 | 0.988 | AARS, AIP, B2M, CALR, CANX, CCT4, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, ERP29, FKBP1A, FKBP4, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPB1, HSPD1, P4HB, PDIA6, PPIA, PRDX4, RAB7A, TBCA, TCP1 | 24 |
| Neurological disease, psychological disorders | Disorder of basal ganglia | 2.74 × 10−18 | | ACAT1, AHCY, ANXA2, B2M, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, COPE, CSE1L, CYC1, DDX1, DNAJA1, EEF1A1, EIF4G1, ENO2, FKBP4, GAPDH, GPI, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADH, HINT1, HLA-B, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPB1, LAMB1, LDHA, LDHB, MAP1B, MDH1, MYL12A, NPM1, PARK7, PCMT1, PCNA, PDE6H, PDLIM1, PEBP1, PFN1, PGK1, PKM, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, PSMC1, PSME1, PTGES3, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RPL3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPSA, RTN4, SDHA, SLC25A6, SOD1, STMN1, TPI1, TPM3, TUBA1B, TUBB4B, UCHL1, UQCRC1, VIM, VPS35, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 74 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Microtubule dynamics | 4.81 × 10−18 | −0.705 | ACTG1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, ARPC2, BASP1, BSG, C1QBP, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CKAP4, COPB2, CSRP1, CTTN, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FASN, FKBP4, FLNA, FN1, GAPDH, GDI1, HDGF, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSPB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KIF5B, KPNB1, KRT18, LAMB1, LASP1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NNMT, NUMA1, PCM1, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RHOA, RRBP1, RTN4, SEPT2, SEPT7, SEPT9, SOD1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STIP1, STMN1, TLN1, TNC, TPM3, TUBB, TWF2, UCHL1, VAPA, VCL, VIM, XPO1, YBX1, YWHAH | 95 |
| Infectious disease | Replication of RNA virus | 4.87 × 10−18 | −0.056 | ANXA5, ANXA6, B2M, BTF3, C14orf166, CAV1, CLIC4, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, CSE1L, DDX3X, DDX5, DDX6, DHX9, DNAJA1, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF3C, FASN, FDPS, G3BP1, HMGB1, HNRNPM, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSPD1, IFITM3, ILF3, KPNB1, LONP1, MAPK1, MVP, NCL, NPM1, PCBP2, PLIN3, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PSMA1, PSMD2, RAB11A, RPS10, RPS27A, RPS5, RPSA, SAE1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, STAT1, TMPO, TUBB, XPO1, YBX1 | 57 |
| Infectious disease | Infection by RNA virus | 7.40 × 10−18 | −2.209 | ACTR2, ANXA1, ANXA2, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARF1, ARPC1B, ATP5B, B2M, BSG, CCT2, CD44, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, CTSB, DDX3X, DHX9, DNAJA2, EIF3I, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GANAB, GML, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPK, HNRNPU, HSPA5, HSPA9, IFITM3, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, MAP4, PCBP2, PDIA3, PDIA6, PGM1, PICALM, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PSME2, PTGES3, RAB1B, RANBP1, RHOA, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, STAT1, STIP1, TAGLN2, TFRC, TWF1, UAP1, UBE2L3, UQCRC1, XPO1, YBX1, ZYX | 79 |
| Neurological disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Neuromuscular disease | 2.20 × 10−17 | | ACAT1, AHCY, ANXA1, ANXA2, B2M, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CD44, COPE, CSE1L, CYC1, DDX1, DNAJA1, EEF1A1, EIF4G1, ENO2, FKBP1A, FKBP4, GAPDH, GPI, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADH, HINT1, HLA-B, HNRNPA1, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPB1, IMPDH2, LAMB1, LDHA, LDHB, MAP1B, MDH1, MYL12A, NPM1, PARK7, PCMT1, PCNA, PDE6H, PDIA3, PDLIM1, PEBP1, PFN1, PGK1, PKM, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, PSMC1, PSME1, PTGES3, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RPL3, RPL5, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPSA, RTN4, SDHA, SLC25A6, SOD1, STMN1, TPI1, TPM3, TUBA1B, UCHL1, UQCRC1, VIM, VPS35, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 78 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Breast cancer | 6.17 × 10−17 | | AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, ATP5A1, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, CBX3, CCT3, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, DDX5, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ETFA, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, FUS, GCN1L1, GLO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HNRNPA1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, ILF3, ITGB1, KHSRP, KPNA2, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LGALS1, LMNA, LONP1, MAPRE1, MARS, MCM6, MYH10, MYH9, NAP1L4, NCL, NPEPPS, P4HB, PAFAH1B2, PCNA, PDCD6, PFN1, PGK1, PGM1, PKM, PLEC, PRDX1, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PTBP1, PTRF, RANBP1, RPL4, RPL6, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, S100A6, SF3B1, SFPQ, SHMT2, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SOD1, STAT1, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TCP1, TLN1, TNC, TPI1, TUBA1B, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, UBA1, VCL, VDAC2, WDR1, XPO1, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 108 |
| Neurological disease | Movement disorders | 1.91 × 10−16 | 0.283 | ACAT1, AHCY, ANXA2, B2M, BASP1, CANX, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, COPE, CSE1L, CSTB, CTSA, CTSB, CYC1, DDX1, DNAJA1, EEF1A1, EEF2, EIF4G1, ENO2, FDPS, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FUS, GAPDH, GPI, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADH, HEXB, HINT1, HLA-B, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPB1, IGF2R, LAMB1, LDHA, LDHB, LMNA, MAP1B, MDH1, MYL12A, NPM1, PARK7, PCMT1, PCNA, PDE6H, PDLIM1, PEBP1, PFN1, PGK1, PKM, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, PSMC1, PSME1, PTGES3, RAB11A, RAN, RANBP1, RPL3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPSA, RTN4, SDHA, SLC25A6, SOD1, SQSTM1, STMN1, TPI1, TPM3, TPP1, TUBA1B, TUBB4B, UCHL1, UQCRC1, VIM, VPS35, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 87 |
| Cancer | Breast or ovarian cancer | 2.54 × 10−16 | | AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, ATIC, ATP5A1, B2M, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, CBX3, CCT3, CCT5, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, DDX5, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ETFA, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, FUS, GAPDH, GCN1L1, GLO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HN1, HNRNPA1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, ILF3, ITGB1, KHSRP, KPNA2, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LGALS1, LMNA, LONP1, MAPRE1, MARS, MCM6, MYH10, MYH9, NAP1L4, NCL, NPEPPS, P4HB, PAFAH1B2, PCNA, PDCD6, PDIA3, PEA15, PFN1, PGK1, PGM1, PKM, PLEC, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PTBP1, PTRF, RANBP1, RPL4, RPL6, RPLP0, RPS24, RPS3, S100A6, SF3B1, SFPQ, SHMT2, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SOD1, SSRP1, STAT1, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TCP1, TLN1, TNC, TPI1, TUBA1B, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, UBA1, VCL, VDAC2, VIM, WDR1, XPO1, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 118 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement | 4.44 × 10−15 | −1.559 | ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC1B, ARPC2, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC4, CORO1C, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DBN1, DDX3X, DNAJA1, DPYSL2, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FASN, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, G6PD, GDI1, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, HARS, HDGF, HLA-A, HMGB1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, ILF3, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MCM3, MCM7, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NCL, NPM1, PA2G4, PARK7, PDCD6, PEBP1, PFN1, PHB2, PKM, PLEC, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRMT5, PTMA, RHOA, RNH1, RPSA, RTN4, S100A6, SEPT7, SEPT9, SERPINH1, SFN, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TAGLN2, TARS, TLN1, TMOD3, TNC, TPM3, VCL, VCP, VIM, WARS, YBX1, YWHAE, YWHAZ, ZYX | 132 |
| Dermatological diseases and conditions | Chronic psoriasis | 5.65 × 10−15 | | C1QBP, CCT5, COPB2, CSTB, CTSB, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF5A, GARS, GSTP1, HSPA8, KPNA2, KPNB1, MARCKS, PCMT1, PGAM1, PGD, PKM, PPP2CA, PSME2, RANBP1, SLC25A5, STAT1, TAGLN, TWF1, UBE2N | 26 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Metabolism of nucleoside triphosphate | 1.02 × 10−14 | −2.160 | ACLY, ALDOA, ANXA1, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, ATP5B, ATP5H, CAV1, CCT8, CDK1, CTPS1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, G3BP1, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSPA8, HSPD1, LONP1, MCM7, MYH10, MYH9, NNMT, OLA1, PKM, PSMC1, PSMC4, SLC25A5, SOD1, VCP, VDAC1 | 35 |
| Neurological disease, psychological disorders, skeletal and muscular disorders | Parkinson’s disease | 1.16 × 10−14 | | ANXA2, CAPZB, COPE, CSE1L, EEF1A1, EIF4G1, ENO2, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-B, HSPB1, LDHA, LDHB, MAP1B, MDH1, PARK7, PCNA, PEBP1, PGK1, PRDX2, PSMC1, PTGES3, RAN, RPL3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RTN4, SLC25A6, SOD1, STMN1, TUBA1B, UCHL1, VIM, VPS35 | 34 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation | Proliferation of tumor cell lines | 3.28 × 10−14 | −0.292 | ACAT1, ACLY, ACTN4, AHSA1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, APEX1, ARF1, BSG, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DDX5, DYNC1H1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF3C, EIF4A1, EIF5A, EZR, FASN, FLNA, FN1, FUS, G6PD, GAPDH, GNB2L1, H2AFY, HDGF, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, IGF2R, ILF3, IMMT, IPO7, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KPNA2, KRT8, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MCM7, NASP, NCL, NPM1, NUMA1, PA2G4, PCNA, PDIA3, PEBP1, PFKP, PFN1, PKM, PPP2R1A, PRDX2, PRKCSH, PRMT5, PSMA4, PTBP1, PTMA, RAN, RHOA, S100A6, SEPT9, SET, SFN, SFPQ, SLC25A6, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, STAT1, STMN1, TAGLN2, TCP1, TFRC, TRIM28, TUBB, UBA1, UCHL1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YWHAG, YWHAQ | 101 |
| Molecular transport, protein trafficking | Transport of protein | 3.57 × 10−14 | 0.362 | AP1B1, ARF1, CALR, CAV1, CFL1, CSE1L, CTSA, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, EHD1, EIF5A, ERP29, GDI2, HSPA9, IGF2R, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, KPNA2, KPNB1, MAP1B, MYH9, NPM1, PDCD6, PDIA3, PICALM, RAB11A, RAB7A, RAN, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, TNPO1, VAPA, XPO1, YWHAH | 37 |
| Immunological disease | Allergy | 7.01 × 10−14 | | AHCY, AHNAK, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA5, CAPG, CAPN1, CAPZB, CD44, CFL1, CNN3, CPNE1, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, GAPDH, H3F3A/H3F3B, HN1, HNRNPR, HSPA5, IDI1, KRT1, LGALS1, MSN, MYH9, P4HB, PDIA3, PHGDH, PPIA, PRDX1, STAT1, TFRC, TKT, TPI1, TPM3, TUBB, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, XRCC6, ZYX | 44 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of tumor cell lines | 7.21 × 10−14 | 0.345 | ACTN4, ANXA1, ANXA2, ARF1, ARPC1B, ARPC2, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CAP1, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DPYSL2, ENAH, EZR, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GDI1, GNB2L1, GPI, HDGF, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, ILF3, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LASP1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NCL, PA2G4, PEBP1, PHB2, PPIA, PRDX2, PRMT5, RHOA, SEPT9, SFN, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TAGLN2, TLN1, TNC, TPM3, VCL, VCP, VIM, YBX1, ZYX | 67 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell survival | 1.06 × 10−13 | −1.997 | ACLY, ANXA5, AP2B1, APEX1, ATP5H, B2M, CALR, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, COPB2, CSE1L, CTSB, CYR61, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF3C, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EZR, FLNA, FN1, GLUD1, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HDGF, HINT1, HMGB1, HNRNPU, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LDHA, LMNA, MAPK1, MVP, P4HB, PARK7, PCNA, PDIA3, PEA15, PKM, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMA4, PSMA7, PSMC4, RAB11A, RHOA, RPL27, RPSA, S100A6, SET, SF3A1, SFN, SHMT2, SND1, SNRPD1, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TCP1, TRIM28, TUBB, TXNDC5, UCHL1, VCL, VCP, VDAC1, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, YBX1, YWHAZ | 96 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of cells | 1.22 × 10−13 | −2.069 | ACTN4, ACTR3, AHCY, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC4, CORO1C, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DBN1, DDX3X, DPYSL2, EHD1, EZR, FASN, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, G6PD, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, HARS, HDGF, HLA-A, HMGB1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, ILF3, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MCM3, MCM7, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NCL, NPM1, PA2G4, PARK7, PDCD6, PFN1, PHB2, PKM, PLEC, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRMT5, PTMA, RHOA, RNH1, RPSA, RTN4, S100A6, SEPT7, SFN, SOD1, STAT1, STMN1, TARS, TLN1, TMOD3, TNC, TPM3, VCL, VCP, VIM, WARS, YBX1, YWHAE, YWHAZ, ZYX | 119 |
| Gene expression, protein synthesis | Translation of mRNA | 2.07 × 10−13 | 1.632 | CALR, CAPRIN1, DDX3X, EEF1B2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EPRS, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HSPB1, ILF3, NACA, PPP1CA, RBM3, RPL23, RPS24, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RRBP1, SYNCRIP, WARS | 27 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Respiratory system tumor | 3.89 × 10−13 | 0.316 | ACLY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ALYREF, ANXA1, ANXA2, APEX1, ATIC, B2M, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CYR61, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NCL, NSFL1C, PABPC1, PCNA, PDCD6, PFKP, PKM, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRPF19, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1, SFN, SHMT2, SND1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TNC, TPI1, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM, YWHAE, ZYX | 79 |
| Cancer | Malignant neoplasm of thorax | 4.70 × 10−13 | 0.949 | ACLY, AHNAK, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA2, APEX1, ATIC, B2M, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CYR61, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NCL, NSFL1C, PABPC1, PCNA, PDCD6, PFKP, PKM, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRPF19, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1, SHMT2, SND1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TPI1, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAE | 76 |
| Gene expression | Expression of mRNA | 6.12 × 10−13 | 0.865 | CALR, CAPRIN1, DDX3X, EEF1B2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4G1, EIF4H, EPRS, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HMGB1, HSPB1, ILF3, KHDRBS1, NACA, PFN1, PPP1CA, RBM3, RPL23, RPS24, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RRBP1, STAT1, SYNCRIP, WARS | 31 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of cellular protrusions | 6.14 × 10−13 | −0.837 | ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, ARPC2, BASP1, BSG, C1QBP, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CSRP1, CTTN, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FASN, FLNA, FN1, GDI1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSPB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KIF5B, LAMB1, LASP1, MAP1B, MARCKS, MSN, MYH10, NNMT, PCM1, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PLEC, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, RAB11A, RANBP1, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT2, SOD1, SPTBN1, STIP1, STMN1, TNC, TPM3, TWF2, UCHL1, VAPA, VCL, VIM, YWHAH | 70 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Lung tumor | 7.06 × 10−13 | 0.316 | ACLY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ALYREF, ANXA2, APEX1, ATIC, B2M, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CYR61, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NCL, NSFL1C, PABPC1, PCNA, PDCD6, PFKP, PKM, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRPF19, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1, SHMT2, SND1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TNC, TPI1, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM, YWHAE, ZYX | 77 |
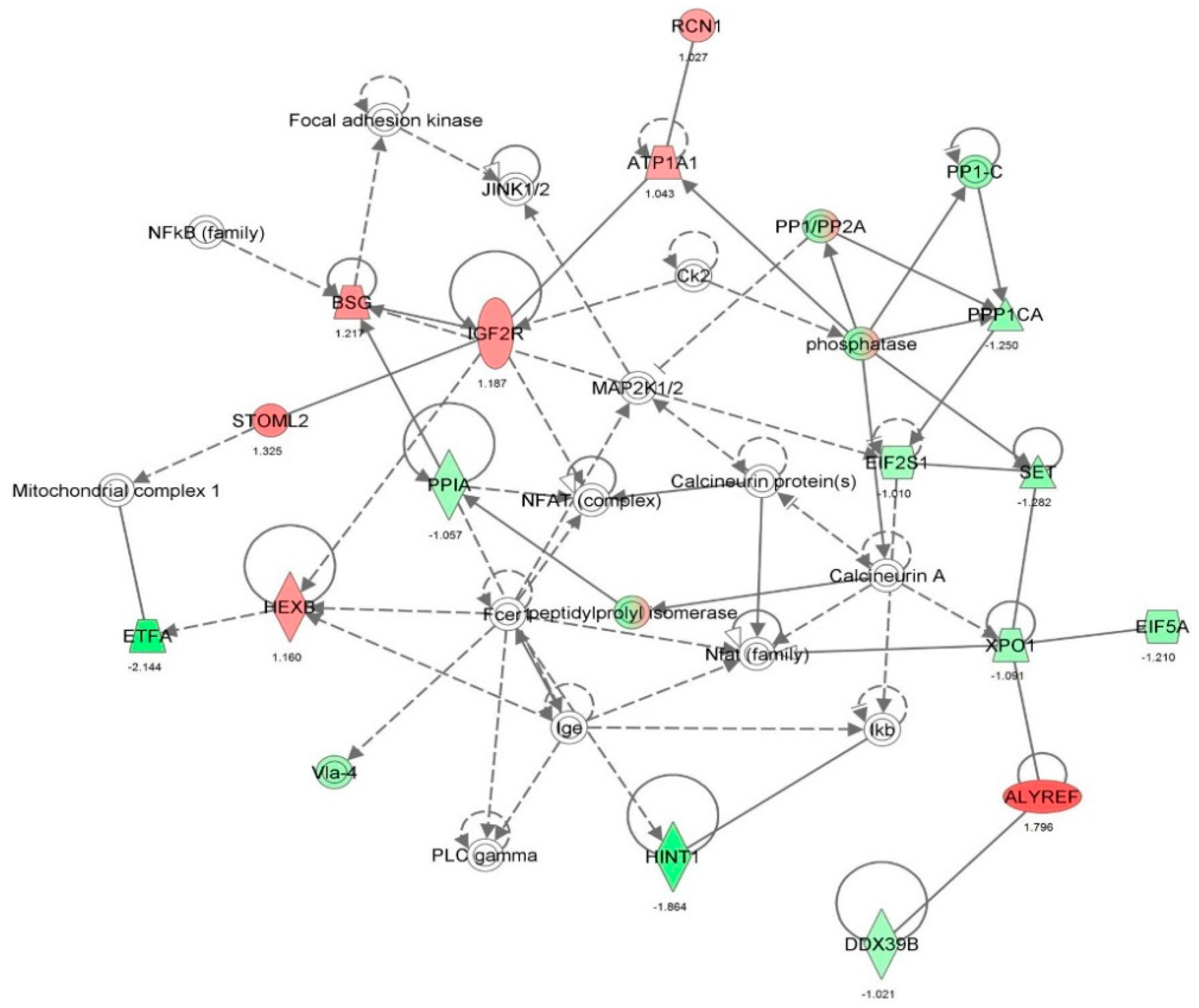
| Organismal survival | Organismal death | 9.82 × 10−13 | 2.742 | ACLY, ACTA1, ACTG1, ACTN4, AIP, ANXA1, APEX1, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, B2M, BSG, BUB3, C1QBP, CALR, CANX, CAP1, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC4, CSE1L, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DBI, DDX1, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EHD1, EIF2S1, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF6, ENAH, FASN, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUS, G6PD, GNAI2, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HEXB, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HYOU1, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KIF5B, KRT1, KRT8, LMNA, LMNB1, LRPPRC, MAP1B, MAPK1, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NASP, NPM1, NUMA1, PCNA, PDIA3, PEA15, PFN1, PHB2, PHGDH, PICALM, PLEC, PLS3, PPIA, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMC1, PSMC4, PTBP1, PTGES3, RAD23B, RHOA, RPL4, RPL6, RPSA, RTN4, SERPINH1, SF3B1, SHMT2, SOD1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, TFRC, TKT, TLN1, TPM3, TPP1, TRIM28, UBE2L3, UBE2N, VCL, VCP, VDAC1, VIM, WDR1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAE | 139 |
| Infectious disease, renal and urological disease | Infection of kidney cell lines | 1.19 × 10−12 | −1.281 | BSG, CTSB, GANAB, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HSPA5, IFITM3, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, KRT18, MAP4, PCBP2, PGM1, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PTGES3, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, TAGLN2, TFRC, UBE2L3, YBX1, ZYX | 34 |
| Inflammatory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Inclusion body myopathy | 2.03 × 10−12 | | CALR, CANX, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, PSMA2, PSMA4, SQSTM1, VCP | 10 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Lung cancer | 2.29 × 10−12 | 0.205 | ACLY, AHNAK, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA2, APEX1, ATIC, B2M, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CYR61, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NCL, NSFL1C, PABPC1, PCNA, PDCD6, PFKP, PKM, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRPF19, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1, SHMT2, SND1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TPI1, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM, YWHAE | 73 |
| Dermatological diseases and conditions, immunological disease, inflammatory disease, inflammatory response | Atopic dermatitis | 2.95 × 10−12 | | AHCY, AHNAK, ANXA1, ANXA5, CAPG, CAPZB, CD44, CFL1, CNN3, CPNE1, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, H3F3A/H3F3B, HN1, HNRNPR, IDI1, KRT1, LGALS1, MSN, PHGDH, STAT1, TPI1, TPM3, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, XRCC6, ZYX | 32 |
| Developmental disorder, hereditary disorder, skeletal and muscular disorders | Distal myopathy | 4.20 × 10−12 | | CALR, CANX, FLNC, HSP90B1, HSPA5, MATR3, PSMA2, PSMA4, SQSTM1, VCP | 10 |
| RNA post-transcriptional modification | Processing of RNA | 4.45 × 10−12 | 0.640 | AARS, AHNAK, C1QBP, DDX39B, DDX5, FUS, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, LOC102724594/U2AF1, NPM1, PABPC1, PCBP1, PRPF19, PTBP1, RBM3, RPL5, RPL7, RPS15, RPS24, RPS7, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SNRPD1, SYNCRIP, U2AF2 | 34 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism | Metabolism of nucleic acid component or derivative | 7.96 × 10-12 | −1.213 | ACLY, AHCY, ALDOA, ANXA1, ATIC, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, ATP5B, ATP5H, CAV1, CCT8, CDK1, CS, CTPS1, DBI, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, DPYSL2, FASN, FDPS, G3BP1, G6PD, GMPS, GNAI2, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSPA8, HSPD1, IMPDH2, LONP1, MAPK1, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MYH10, MYH9, NNMT, OLA1, PGK1, PKM, PPA1, PSMC1, PSMC4, SET, SLC25A5, SOD1, TALDO1, UAP1, VCP, VDAC1 | 54 |
| Infectious disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Infection of embryonic cell lines | 1.06 × 10-11 | −1.045 | BSG, GANAB, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HSPA5, IFITM3, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, MAP4, PCBP2, PGM1, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PTGES3, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, TAGLN2, TFRC, UBE2L3, YBX1, ZYX | 32 |
| Infectious disease | Infection of epithelial cell lines | 1.06 × 10-11 | −1.045 | BSG, GANAB, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HSPA5, IFITM3, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, MAP4, PCBP2, PGM1, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PTGES3, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, TAGLN2, TFRC, UBE2L3, YBX1, ZYX | 32 |
| Cellular movement | Invasion of cells | 1.64 × 10-11 | −0.711 | ACAT1, AHCY, ANXA1, ANXA2, APEX1, ARHGDIA, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CAP1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, ENAH, EZR, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, HDGF, HDLBP, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, ILF3, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KRT8, LASP1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, NPM1, OTUB1, PA2G4, PARK7, PEBP1, PICALM, PKM, PTGES3, RHOA, RNH1, RPSA, S100A6, SEPT9, SQSTM1, STMN1, TAGLN, TAGLN2, VCP, VIM, YWHAQ | 63 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell viability | 3.09 × 10-11 | −1.538 | ACLY, ANXA5, AP2B1, APEX1, ATP5H, B2M, CALR, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, COPB2, CTSB, CYR61, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, EEF2, EIF3C, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EZR, FLNA, FN1, GLUD1, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HDGF, HINT1, HMGB1, HNRNPU, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IGF2R, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LDHA, LMNA, MAPK1, MVP, P4HB, PARK7, PCNA, PDIA3, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMA4, PSMC4, RAB11A, RHOA, RPL27, RPSA, S100A6, SF3A1, SFN, SHMT2, SND1, SNRPD1, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TCP1, TRIM28, TXNDC5, UCHL1, VCP, VDAC1, XPO1, XRCC5, YBX1, YWHAZ | 85 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Cervical tumor | 3.68 × 10-11 | | ACTR3, ALYREF, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, ATIC, CTSB, ENO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPB1, KRT1, KRT9, MAP4, MCM7, RPS12, TAGLN, TFRC, TPM2, TPM3, TUBB, TUBB4B, XPO1, YWHAE | 31 |
| Developmental disorder, hereditary disorder, inflammatory disease, neurological disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Nonaka myopathy | 4.55 × 10-11 | | CALR, CANX, HSP90B1, HSPA5, PSMA2, PSMA4, SQSTM1, VCP | 8 |
| Dermatological diseases and conditions, inflammatory disease, inflammatory response | Dermatitis | 5.49 × 10-11 | | AHCY, AHNAK, ANXA1, ANXA5, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, CALR, CAPG, CAPZB, CD44, CFL1, CNN3, CPNE1, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HN1, HNRNPR, IDI1, KRT1, LGALS1, MSN, PHGDH, SFN, STAT1, TPI1, TPM3, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, XRCC6, ZYX | 41 |
| Infectious disease | Replication of influenza A virus | 6.00 × 10-11 | −0.322 | ANXA6, B2M, C14orf166, CLIC4, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, CSE1L, EEF1A1, EIF3C, FDPS, HSP90AA1, HSPD1, IFITM3, ILF3, KPNB1, LONP1, MAPK1, PSMA1, PSMD2, RPS10, RPS27A, RPS5, RPSA, SAE1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, STAT1, TUBB, XPO1 | 32 |
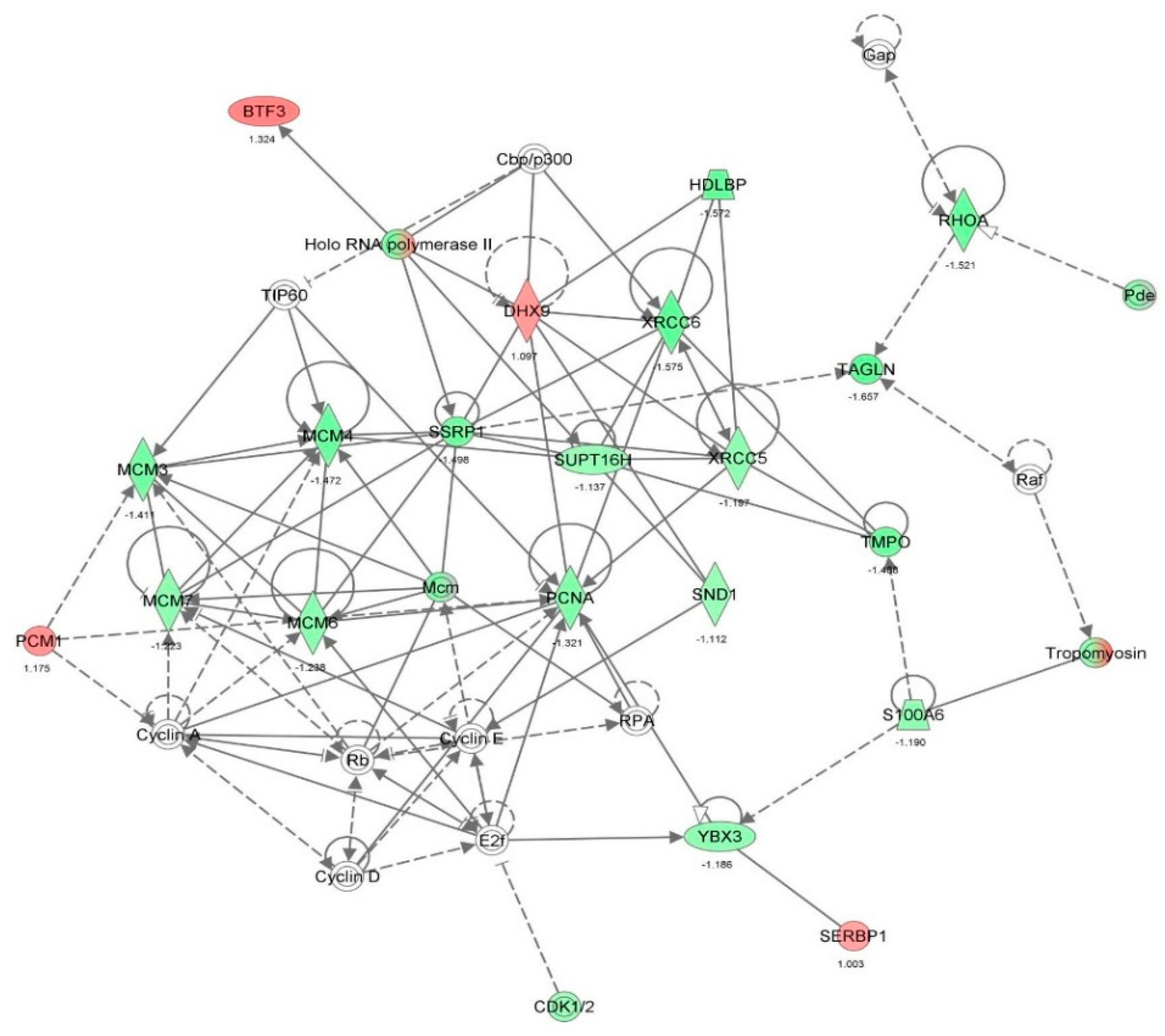
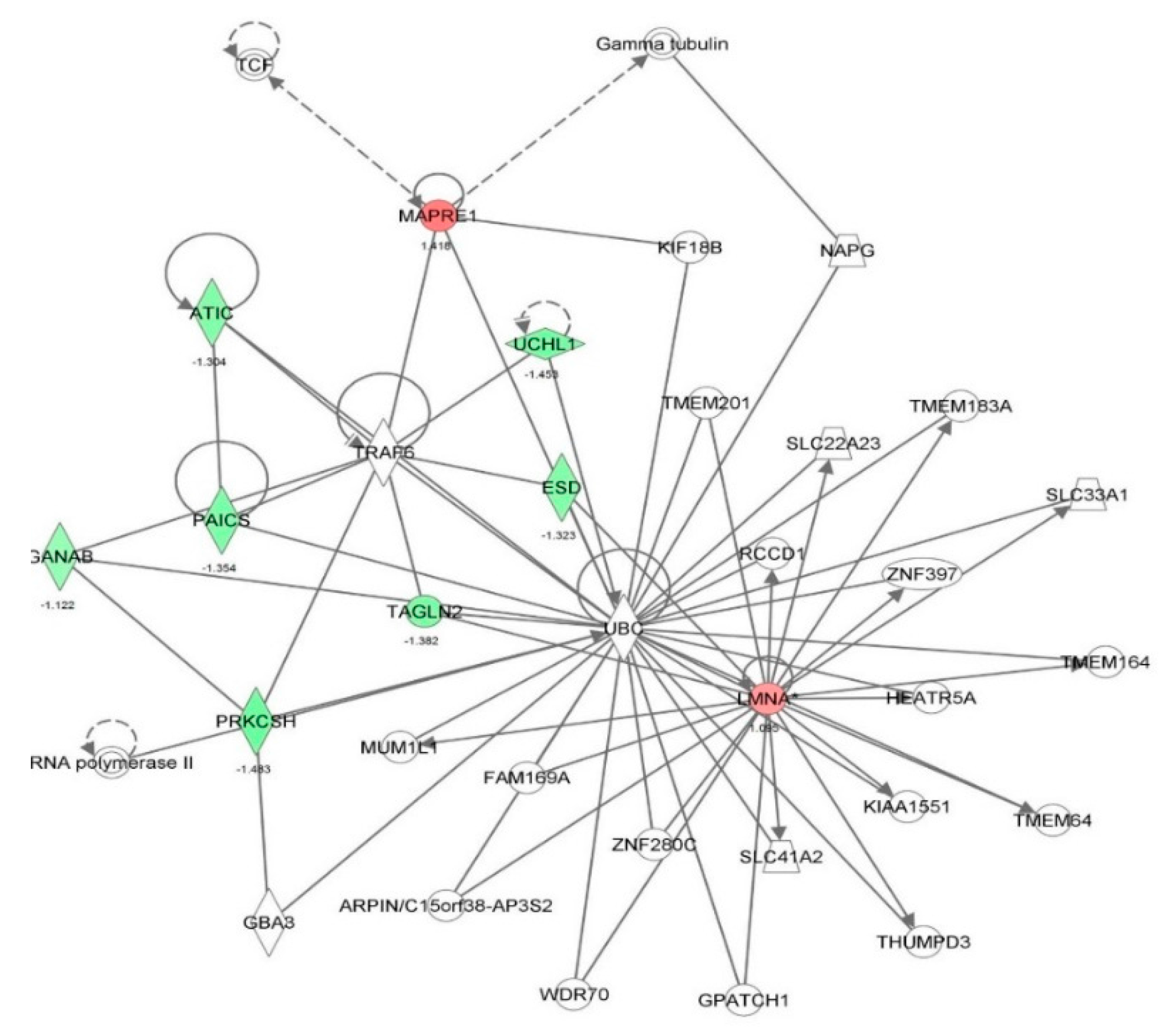
| Cell cycle | M phase | 6.05 × 10-11 | −0.578 | ACTN4, BUB3, CAP1, CAPN2, CDK1, CFL1, FLNA, FN1, GNAI2, ITGB1, LMNA, MAPRE1, MCM4, MCM7, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NPM1, NUMA1, PFN1, RAB11A, RHOA, SEPT2, SEPT7, SEPT9, SSRP1, XRCC5, YBX1 | 28 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair, energy production, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Catabolism of ATP | 7.68 × 10-11 | | ACLY, ANXA1, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, ATP5B, ATP5H, CCT8, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, G3BP1, HSP90AA1, HSPA8, LONP1, MCM7, MYH10, MYH9, OLA1, PSMC1, PSMC4, VCP | 23 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of neuroblastoma cell lines | 1.35 × 10-10 | −1.206 | ATP5A1, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAST, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, ENO1, FKBP1A, GAPDH, HSPA8, ITGB1, PARK7, PEBP1, PRDX2, S100A6, SOD1, SQSTM1, TCP1, YWHAE | 24 |
| Hematological disease, immunological disease, inflammatory disease, inflammatory response, respiratory disease | Allergic pulmonary eosinophilia | 1.55 × 10-10 | | ALDOA, ENO1, GAPDH, HSPA5, MYH9, P4HB, PDIA3, PRDX1, TKT, TPI1, TUBB | 11 |
| Cell morphology | Cell spreading | 1.72 × 10-10 | −0.739 | CAP1, CAPN2, CAST, CD44, CYR61, EHD1, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GNB2L1, IGF2R, IPO9, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAP4, MAPK1, MARCKS, PFN1, PTBP1, RHOA, RRBP1, RTN4, TLN1, TNC, UCHL1, VCL, VIM, YWHAZ, ZYX | 30 |
| Skeletal and muscular disorders | Myopathy | 1.81 × 10-10 | −2.236 | AARS, ACTA1, AHNAK, ATP1A1, BUB3, CALR, CANX, CAST, DYNC1H1, ECHS1, FKBP1A, FLNC, FN1, GARS, HARS, HEXB, HINT1, HLA-A, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPB1, ITGB1, LMNA, LRPPRC, MATR3, PLEC, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PSMA2, PSMA4, RAB7A, RHOA, SDHA, SOD1, SQSTM1, STMN1, TPM2, TPM3, TUBB, TUBB4B, UBA1, VCL, VCP | 46 |
| Molecular transport, protein trafficking | Internalization of protein | 2.17 × 10-10 | 1.900 | AP1B1, AP2B1, CAP1, CFL1, CLTC, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, KPNA2, KPNB1, PDIA3, RAN, RHOA, SPTBN1, XPO1 | 17 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of cervical cancer cell lines | 2.24 × 10-10 | −0.340 | ATP1A1, CALR, CCT4, CDK1, CTSB, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EZR, FLNB, HNRNPK, IMMT, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, KRT18, LMNA, MAPK1, MSN, PCBP2, PKM, PPIA, PPP2R1A, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRPF19, PTMA, RPS24, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, TCP1, UCHL1, VCP, VDAC1, YWHAH | 34 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, connective tissue development and function | Proliferation of fibroblast cell lines | 2.34 × 10-10 | −0.983 | ACAT1, AKR1B1, ALDOA, APEX1, ATIC, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, CLTC, DDX3X, DPY30, EEF1D, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF6, FN1, G6PD, GNAI2, GNB2L1, HDGF, HINT1, HMGB1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, LMNA, MAPK1, NPM1, PRPF19, PSMA4, PTMA, RHOA, S100A6, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, TFRC, TPM3, XRCC6 | 39 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Stage 1-2 non-small cell lung cancer | 2.36 × 10-10 | | ANXA2, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1 | 12 |
| Immunological disease | Immediate hypersensitivity | 2.58 × 10-10 | | AHCY, AHNAK, ANXA1, ANXA5, CAPG, CAPZB, CD44, CFL1, CNN3, CPNE1, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, H3F3A/H3F3B, HN1, HNRNPR, IDI1, KRT1, LGALS1, MSN, PHGDH, PPIA, STAT1, TPI1, TPM3, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, XRCC6, ZYX | 33 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Metabolism of DNA | 2.73 × 10-10 | −1.611 | APEX1, BSG, CACYBP, CALR, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CDK1, DHX9, ENO1, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HSD17B10, HSPB1, KPNA2, KRT8, LMNA, MAPK1, MCM7, NAP1L1, NASP, NCL, NPM1, PCM1, PCNA, PEA15, PFN1, PPIA, RAN, RHOA, SET, SOD1, SSRP1, STAT1, SUPT16H, TMPO, XRCC5, XRCC6 | 38 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Organization of organelle | 3.33 × 10-10 | −1.732 | ALDOA, ANXA2, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CLTC, CTNNA1, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, ENAH, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, GAPDH, H3F3A/H3F3B, HEXB, ITGB1, KRT18, KRT9, LMNA, LONP1, MAPRE1, MSN, MYH9, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, PARK7, PCM1, PLS3, RHOA, RRBP1, SERPINH1, SOD1, SPTBN1, STOML2, SURF4, TPP1, TUBB, VCL, VIM | 44 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Carcinoma in lung | 3.34 × 10-10 | 0.555 | AHNAK, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA2, APEX1, ATIC, B2M, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENO1, ENO2, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, ITGB1, LDHA, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NSFL1C, PABPC1, PCNA, PDCD6, PFKP, PKM, PPIA, PRDX1, PRPF19, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1, STAT1, STMN1, TPI1, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM, YWHAE | 61 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Metabolism of nucleotide | 4.07 × 10-10 | −1.647 | ACLY, ALDOA, ANXA1, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, ATP5B, ATP5H, CAV1, CCT8, CDK1, CTPS1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, FASN, FDPS, G3BP1, G6PD, GMPS, GNAI2, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSPA8, HSPD1, IMPDH2, LONP1, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MYH10, MYH9, NNMT, OLA1, PKM, PPA1, PSMC1, PSMC4, SET, SLC25A5, SOD1, TALDO1, VCP, VDAC1 | 46 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Hydrolysis of nucleotide | 4.19 × 10-10 | −1.306 | ATP1A1, CALR, CCT4, CCT5, CDK1, DNM1L, GNAI2, HMGB1, HSPA5, HSPD1, IPO5, MAPK1, RAB7A, RAN, RANBP1, RHOA, STMN1, UBA1, XPO1 | 19 |
| Infectious disease | HIV infection | 4.22 × 10-10 | −1.958 | ANXA2, ARF1, ATP5B, B2M, CCT2, CD44, DDX3X, DHX9, DNAJA2, FDPS, FN1, GANAB, GML, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPU, IMPDH2, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, MAP4, PDIA3, PDIA6, PGM1, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PSME2, PTGES3, RAB1B, RANBP1, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, STIP1, TAGLN2, TFRC, TWF1, UAP1, UBE2L3, UQCRC1, XPO1, YBX1, ZYX | 55 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Metabolism of purine nucleotide | 4.60 × 10-10 | | ACLY, ANXA1, ATP1A1, ATP5A1, ATP5B, ATP5H, CCT8, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, G3BP1, G6PD, HSP90AA1, HSPA8, LONP1, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MYH10, MYH9, OLA1, PSMC1, PSMC4, VCP | 26 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Non-small cell lung cancer | 4.91 × 10-10 | | AHNAK, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA2, APEX1, ATIC, B2M, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, DHX9, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FN1, G3BP1, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, ITGB1, LDHA, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NSFL1C, PABPC1, PCNA, PFKP, PKM, PPIA, PRDX1, PRPF19, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1, STAT1, STMN1, TPI1, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM | 58 |
| Immunological disease | Hypersensitive reaction | 5.39 × 10-10 | 0.404 | AHCY, AHNAK, ANXA1, ANXA5, CALR, CAPG, CAPZB, CD44, CFL1, CNN3, CPNE1, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, GARS, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HN1, HNRNPR, IDI1, KRT1, LGALS1, MSN, PHGDH, PPIA, PSME2, SOD1, STAT1, TPI1, TPM3, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, XRCC6, ZYX | 39 |
| Cancer, endocrine system disorders, organismal injury and abnormalities | Benign cold thyroid nodule | 1.09 × 10-9 | | ANXA5, CALR, CTSB, GSTP1, HSP90AB1, PARK7, PRDX2, PRDX5 | 8 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Cervical cancer | 1.13 × 10-9 | | ACTR3, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, ATIC, CTSB, ENO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPB1, KRT1, KRT9, MAP4, MCM7, RPS12, TAGLN, TFRC, TPM2, TPM3, TUBB, TUBB4B, XPO1, YWHAE | 28 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Organization of filaments | 1.22 × 10-9 | −1.929 | ALDOA, ANXA2, CFL1, DBN1, DPYSL2, ENAH, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, GAPDH, ITGB1, KRT18, KRT9, MAPRE1, MSN, NUMA1, PCM1, PLS3, RHOA, RRBP1, SERPINH1, SOD1, TUBB, VIM | 24 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Pulmonary metastasis | 1.30 × 10-9 | | ATIC, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, YWHAE | 13 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Stabilization of filaments | 1.55 × 10-9 | −0.454 | CFL1, COPB2, CTTN, DNM1L, DPYSL2, FLNA, IQGAP1, KRT18, KRT8, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPRE1, NUMA1, PKM, RHOA, SEPT7, STMN1 | 17 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic lung carcinoma | 1.60 × 10-9 | | ATIC, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, YWHAE | 12 |
| Cancer | Metastasis | 1.88 × 10-9 | −1.645 | ANXA1, ANXA5, ATIC, B2M, C1QBP, CAPG, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, ENAH, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUS, GNB2L1, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HYOU1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KRT18, KRT8, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYL12A, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, RHOA, RNH1, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SND1, SQSTM1, STAT1, TUBB, TUBB4B, UBE2N, VIM, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 55 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of tumor cell lines | 1.96 × 10-9 | −0.054 | ACTN4, ANXA1, ANXA2, ARF1, ARPC2, BSG, C1QBP, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CSE1L, CTTN, CYR61, DPYSL2, EZR, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GNB2L1, HDGF, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, ILF3, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LASP1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NCL, PHB2, PRDX2, PRMT5, RHOA, SFN, STAT1, STMN1, TNC, TPM3, VCP, VIM, ZYX | 50 |
| Cell morphology, connective tissue development and function | Cell spreading of fibroblast cell lines | 2.05 × 10-9 | 0.201 | CAST, EHD1, FLNA, FLNC, FN1, GNB2L1, IPO9, ITGB1, PTBP1, RTN4, VCL, VIM | 12 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic lung cancer | 2.05 × 10-9 | | ATIC, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, YWHAE | 12 |
| Gene expression | Expression of RNA | 2.21 × 10-9 | 1.310 | ACTR2, ACTR3, ALYREF, BASP1, BTF3, C14orf166, C1QBP, CALR, CAND1, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CBX3, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4G1, EIF4H, ENO1, EPRS, EZR, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUBP3, GAPDH, GLO1, GNB2L1, GSTP1, H2AFY, HDGF, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HSPA4, HSPA8, HSPB1, ILF2, ILF3, IQGAP1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, LGALS1, LMNA, LRPPRC, MAPK1, MATR3, MCM7, MSN, NACA, NONO, NPM1, OTUB1, PA2G4, PARK7, PCNA, PDLIM1, PEA15, PEBP1, PFN1, PHB2, PHGDH, PICALM, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PRKDC, PRMT5, PTGES3, PTMA, PTRF, RBM3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL6, RPS24, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RRBP1, SET, SFPQ, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TMPO, TNC, TRIM28, UBE2L3, VAPA, VIM, WARS, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ | 117 |
| Inflammatory response | Inflammation of organ | 2.36 × 10-9 | 0.481 | ACTN4, AHCY, AHNAK, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA5, ARHGDIA, ATP1A1, B2M, BSG, CALR, CAPG, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CNN3, CPNE1, CTSB, CYR61, DDX5, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FKBP4, FLNA, FUS, GAPDH, GNAI2, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HARS, HLA-A, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPR, HSP90B1, HSPA5, IDI1, IMPDH2, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, LGALS1, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, P4HB, PDIA3, PDLIM1, PHGDH, PPIA, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PSMB1, PSMD2, SFN, SOD1, STAT1, TKT, TPI1, TPM3, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, VIM, XRCC6, YBX1, ZYX | 74 |
| Embryonic development, organismal survival | Death of embryo | 2.51 × 10-9 | 0.942 | BSG, CAPN2, CAPNS1, EIF6, FASN, IMPDH2, KIF5B, LRPPRC, MAP1B, NASP, PCNA, PFN1, PHB2, PRPF19, PSMC4, RPSA, SF3B1, TKT, TPM3, VCP | 20 |
| Cell cycle | Cell cycle progression | 2.53 × 10-9 | −1.218 | BUB3, C1QBP, CALR, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CCT4, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CLTC, CSE1L, CYR61, DBI, DHX9, DYNC1H1, EIF6, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, GNB2L1, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HSPA8, HSPB1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, KRT18, KRT8, LMNA, MAP4, MAPK1, MARCKS, MCM7, MYH10, NASP, NPM1, NUMA1, PA2G4, PCM1, PCNA, PEBP1, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PRMT5, PTMA, RAN, RBM3, RHOA, RPS24, SEPT9, SFN, SFPQ, SSRP1, STAT1, STMN1, TCP1, TMPO, TNC, TUBB, VCP, XRCC6, YWHAB, YWHAE | 69 |
| Cell morphology | Morphology of cells | 2.61 × 10-9 | | ACTA1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ANXA1, ANXA2, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, B2M, BUB3, CALR, CAP1, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC4, CLTC, CSTB, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, DNAJA1, DNM1L, DPY30, DPYSL2, EHD1, EIF6, EZR, FASN, FLNA, FLNC, FN1, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADH, HADHA, HEXB, HLA-A, HMGB1, HSP90AA1 | 110 |
| | | | | HSP90B1, HSPA4, IGF2R, ILF3, IMPDH2, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KIF5B, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, LAMB1, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, MYH9, NPEPPS, NPM1, PAFAH1B2, PEA15, PEBP1, PLEC, PLIN3, PLS3, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKDC, PTBP1, RAB11A, RAD23B, RAN, RHOA, RPSA, RTN4, SEPT7, SEPT9, SERPINH1, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, STAT1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TALDO1, TFRC, TLN1, TMOD3, TNC, TPM3, TPP1, VCL, VIM, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YWHAG, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Stage 1 non-small-cell lung carcinoma | 2.83 × 10-9 | | B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, SERBP1 | 11 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, tissue development | Formation of filaments | 3.49 × 10-9 | −0.462 | ACTA1, ACTR3, ARF1, ARPC2, CAPN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CTTN, DPYSL2, FKBP4, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, HSPA5, HSPB1, ITGB1, KRT18, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, NPM1, PFN1, RHOA, SERPINH1, SOD1, STMN1, TCP1, TNC, TPM2, TUBB, TWF1, TWF2, VIM, ZYX | 36 |
| Infectious disease | Infection by HIV-1 | 4.09 × 10-9 | −1.626 | ARF1, ATP5B, CCT2, CD44, DDX3X, DHX9, DNAJA2, GANAB, GML, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPU, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNB1, MAP4, PDIA3, PDIA6, PGM1, PLOD2, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA5, PSMA7, PSMC4, PSME2, PTGES3, RAB1B, RANBP1, RNH1, RPL10A, RPL12, RPL18, SF3A1, SF3B1, SNRPD3, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, STIP1, TAGLN2, TWF1, UAP1, UBE2L3, UQCRC1, XPO1, YBX1, ZYX | 48 |
| Cancer | Malignant neoplasm of heart, mediastinum and pleura | 4.65 × 10-9 | 1.982 | ATIC, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, PRDX1, PRKDC, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, TUBB, TUBB4B, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAE | 19 |
| Cancer | Growth of tumor | 5.06 × 10-9 | −0.277 | ACLY, ACTN4, AHCY, AKR1B1, ANXA1, ANXA2, BSG, CACYBP, CALR, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CTSB, CTTN, CYR61, EEF1A1, EZR, FASN, FLNA, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HDGF, HMGB1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPD1, HYOU1, ILF3, ITGB1, LAMB1, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, NPM1, PARK7, PKM, PLEC, PPP2CA, RHOA, RPL22, RPS4X, S100A6, SET, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TNC, TXLNA, UCHL1, XRCC5, YBX1 | 54 |
| RNA post-transcriptional modification | Splicing of RNA | 5.23 × 10-9 | 0.239 | AHNAK, C1QBP, DDX39B, DDX5, FUS, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPM, KHSRP, NPM1, PRPF19, PTBP1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SNRPD1, SYNCRIP, U2AF2 | 20 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of connective tissue cells | 5.91 × 10-9 | −0.258 | CAPNS1, CD44, CDK1, CLIC4, CTSB, CYR61, DDX3X, DNM1L, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF6, ENO1, FKBP4, FLNA, FN1, FUS, GLO1, GPI, GSTP1, HINT1, HSPA5, HSPD1, IGF2R, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KRT18, KRT8, LMNA, MAP4, MAPK1, PARK7, PRKDC, RHOA, RPL10, SERPINH1, STAT1, STMN1, TPP1, UBA1, VCP, VIM, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 46 |
| Cancer, hematological disease | Blood tumor | 6.43 × 10-9 | 1.121 | ACTG1, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CSE1L, CYR61, DNM1L, EEF1A1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUS, G3BP1, GMPS, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HMGB1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, IQGAP1, KPNA2, KRT1, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, MARS, MYH10, NNMT, NONO, NPM1, PCNA, PDIA6, PICALM, PLOD2, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMA2, PSMB1, PSMD2, PSME1, RHOA, RPL3, RPL6, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, SF3B1, SHMT2, SNRPD3, SPTBN1, STIP1, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 78 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction | Binding of cells | 6.68 × 10-9 | −0.441 | ANXA2, ANXA5, BSG, C1QBP, CALR, CAV1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CKAP4, CYR61, DDX3X, FN1, HLA-A, HMGB1, HSPA5, IGF2R, ITGB1, KRT1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, NCL, PDIA3, PPP2CA, PRMT5, RHOA, RPSA, STIP1, STMN1, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TNC, VCL | 40 |
| Cancer, hematological disease | Hematologic cancer | 7.44 × 10-9 | 1.121 | ACTG1, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CSE1L, CYR61, DNM1L, EEF1A1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUS, G3BP1, GMPS, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HMGB1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, IQGAP1, KPNA2, KRT1, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, MARS, MYH10, NNMT, NONO, NPM1, PCNA, PDIA6, PICALM, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMA2, PSMB1, PSMD2, PSME1, RHOA, RPL3, RPL6, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, SF3B1, SHMT2, SNRPD3, SPTBN1, STIP1, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 77 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Development of cytoplasm | 8.43 × 10-9 | −0.761 | ACTR3, ANXA1, ARF1, ARPC2, CAPN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CORO1C, CTTN, DNM1L, DPYSL2, ERP29, FKBP4, FLNA, FN1, GDI1, GNAI2, GPI, HSPA8, IPO9, ITGB1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, NPM1, PARK7, PFN1, RHOA, STMN1, STOML2, TNC, TPM2, TUBB, TWF1, TWF2, ZYX | 38 |
| Neurological disease | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | 9.09 × 10-9 | | ANXA1, ANXA5, CAPN2, CCT2, CYR61, DBI, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, EZR, FASN, FUS, HN1, HNRNPA1, MAPK1, NNMT, PFKP, PFN1, RHOA, RTN4, S100A6, SOD1, TFRC, VCP, VIM | 24 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell viability of tumor Cell lines | 9.74 × 10-9 | −0.894 | APEX1, ATP5H, B2M, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, COPB2, DHX9, EEF2, EIF3C, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, FLNA, FN1, GLUD1, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HINT1, HMGB1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPB1, IGF2R, ITGB1, P4HB, PARK7, PCNA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMA4, PSMC4, RAB11A, RHOA, RPL27, RPSA, S100A6, SF3A1, SFN, SNRPD1, SOD1, SQSTM1, TCP1, TRIM28, VCP, XPO1, YBX1 | 53 |
| Hereditary disorder, neurological disease, psychological disorders, skeletal and muscular disorders | Huntington’s disease | 1.18 × 10-8 | | ACAT1, AHCY, B2M, BASP1, CAPNS1, CD44, CYC1, DDX1, DNAJA1, ENO2, FKBP4, GAPDH, GPI, HADH, HINT1, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPA8, LAMB1, LDHA, LDHB, MYL12A, NPM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDE6H, PDLIM1, PFN1, PGK1, PKM, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, PSME1, RAB11A, RANBP1, RPSA, SDHA, TPI1, TPM3, UCHL1, UQCRC1, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 45 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation | Proliferation of breast cancer cell lines | 1.19 × 10-8 | 0.389 | ANXA2, ARF1, C1QBP, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EIF3C, FN1, GNB2L1, HNRNPK, HSPA5, ILF3, ITGB1, KPNA2, KRT8, LGALS1, MAPK1, PDIA3, PFKP, PFN1, PPP2R1A, PRDX2, PTMA, SEPT9, SFN, SOD1, TRIM28, UBA1, YBX1, YWHAQ | 35 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | Glycolysis of cells | 1.30 × 10-8 | −1.474 | ALDOA, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, ENO1, ENO2, GAPDH, GPI, LDHA, PFKP, PGAM1, PGK1, PGM1, PKM, TPI1 | 15 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer | 1.31 × 10-8 | | ATIC, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A | 11 |
| Protein synthesis | Polymerization of protein | 1.44 × 10-8 | | ACAT1, AHNAK, ALDOC, ANXA2, ANXA5, ANXA6, ARPC2, CAV1, CTNNA1, CUTA, DNM1L, EEF1A1, EHD1, ENAH, HSD17B10, IMPDH2, LONP1, NPM1, PFKP, PFN1, PRKCSH, RHOA, SEPT2, SEPT7, SEPT9, SHMT2, SQSTM1, STOML2, TRIM28, VCP, YWHAB | 31 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of fibroblast cell lines | 1.61 × 10-8 | −0.361 | CAPNS1, CDK1, CLIC4, CTSB, CYR61, DDX3X, DNM1L, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF6, ENO1, FKBP4, FN1, FUS, GLO1, GPI, GSTP1, HINT1, HSPA5, HSPD1, ITGB1, KRT18, KRT8, MAPK1, PARK7, RHOA, RPL10, STAT1, STMN1, UBA1, VCP, VIM, YWHAZ | 36 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Organization of actin cytoskeleton | 2.12 × 10-8 | −1.937 | ACTR2, ALDOA, ARHGDIA, CALR, CAP1, CFL1, CORO1C, CSRP1, DBN1, DPYSL2, ENAH, EZR, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, ITGB1, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, PLS3, RAN, RHOA, SEPT2, SPTAN1, TLN1, TMOD3, TWF2 | 28 |
| Cancer | Malignant neoplasm of mediastinum | 2.27 × 10-8 | 1.982 | ATIC, B2M, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FN1, MYL12A, PPIA, PRDX1, PRKDC, RHOA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, TUBB4B, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAE | 18 |
| Metabolic disease | Amyloidosis | 2.45 × 10-8 | | ACLY, ATP5A1, B2M, CANX, CAPN1, CAST, CAV1, CDK1, CTSB, DHX9, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1G, EEF2, EIF2S1, EPRS, FDPS, G3BP1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPU, HSPA5, HSPD1, LGALS1, PCNA, PICALM, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMB1, PSMD2, RAN, SET, SOD1, STIP1, TAGLN, TUBB, UBXN4, UCHL1, VIM, VPS35, YWHAZ | 43 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Biosynthesis of purine ribonucleotide | 2.57 × 10-8 | −2.378 | ALDOA, ATP5A1, ATP5B, CAV1, CDK1, DNM1L, HMGB1, HSPD1, NNMT, PKM, PPA1, SLC25A5, SOD1, VCP, VDAC1 | 15 |
| Neurological disease | Neurological signs | 2.58 × 10-8 | | ACAT1, AHCY, B2M, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CYC1, DDX1, DNAJA1, ENO2, FKBP4, GAPDH, GPI, HADH, HINT1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPA8, LAMB1, LDHA, LDHB, MYL12A, NPM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDE6H, PDLIM1, PFN1, PGK1, PKM, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, PSME1, RAB11A, RANBP1, RPSA, SDHA, SOD1, TPI1, TPM3, UCHL1, UQCRC1, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 48 |
| Cancer | Epithelial cancer | 3.20 × 10-8 | −0.050 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, C1QBP, CACYBP, CAND1, CANX, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, ETFA, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS | 350 |
| | | | | NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAFAH1B2, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLOD2, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RANBP1, RARS, RHOA, RPL10, RPL12, RPL22, RPL27, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS11, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS27A, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TWF2, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| Cancer | Metastatic carcinoma | 3.23 × 10-8 | | ATIC, B2M, CSE1L, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FKBP1A, FN1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, TUBB, TUBB4B, YWHAE | 19 |
| Neurological disease | Dyskinesia | 3.44 × 10-8 | | ACAT1, AHCY, B2M, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CYC1, DDX1, DNAJA1, ENO2, FKBP4, GAPDH, GPI, HADH, HINT1, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPA8, LAMB1, LDHA, LDHB, MYL12A, NPM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDE6H, PDLIM1, PFN1, PGK1, PKM, PLOD2, PPIA, PRDX2, PSME1, RAB11A, RANBP1, RPSA, SDHA, TPI1, TPM3, UCHL1, UQCRC1, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 46 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Formation of cytoskeleton | 3.46 × 10-8 | −0.867 | ACTR3, ARF1, ARPC2, CAPN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CORO1C, CTTN, DPYSL2, ERP29, FKBP4, FLNA, FN1, GDI1, GNAI2, GPI, ITGB1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MAPRE1, NPM1, PFN1, RHOA, STMN1, TNC, TPM2, TUBB, TWF1, TWF2, ZYX | 32 |
| Inflammatory disease | Chronic inflammatory disorder | 3.62 × 10-8 | | ACLY, ACTA1, ACTN4, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARF1, ATIC, B2M, BSG, CALR, CAPG, CD59, COTL1, CTSB, DDX39B, DDX5, EEF1G, EEF2, ENO1, FDPS, FKBP1A, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HSP90B1, HSPA8, HSPD1, IMPDH2, KHSRP, KRT18, KRT8, LDHB, LGALS1, MAPRE1, MYL12A, NONO, P4HB, PCM1, PDIA3, PDLIM1, PGK1, PKM, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PSMB1, PSMD2, PTMA, RHOA, RPS24, RPS3, RPSA, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, TPM2, TRIM28, UCHL1, VARS, VIM | 62 |
| Cell morphology, connective tissue development and function | Shape change of fibroblast cell lines | 3.74 × 10-8 | −0.342 | CAST, EHD1, FLNA, FLNC, FN1, GNB2L1, IPO9, ITGB1, MARCKS, PTBP1, RHOA, RTN4, VCL, VIM | 14 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of lamellipodia | 3.90 × 10-8 | 0.308 | ACTN4, ACTR3, ARPC2, BSG, C1QBP, CAP1, CAPZB, CD44, CFL1, CYR61, DNM1L, EZR, FN1, HSP90AA1, HSPB1, LASP1, RHOA, TWF2, VCL | 19 |
| Cell cycle, cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular movement | Elongation of filaments | 4.03 × 10-8 | −1.000 | ACTN4, CAP1, FN1, MAPRE1, PFN1, SEPT7, SEPT9 | 7 |
| Cell death and survival | Neuronal cell death | 4.08 × 10-8 | 0.202 | AARS, AP2B1, CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAST, CDK1, CTSB, DNM1L, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, G6PD, GAPDH, GLUD1, GPI, HDGF, HMGB1, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, ITGB1, LDHA, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, NPM1, P4HB, PARK7, PDIA3, PEA15, PRDX2, RHOA, RPS3, SDHA, SET, SOD1, STAT1, STIP1, TCP1, UCHL1, VAPA, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAB, YWHAZ | 49 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular assembly and organization, tissue development | Quantity of focal adhesions | 4.08 × 10-8 | 1.463 | CAPNS1, CAV1, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, GNB2L1, ITGB1, MYH9, RHOA, SPTAN1 | 10 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | Glycolysis | 4.46 × 10-8 | −1.946 | ALDOA, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, DNM1L, ENO1, ENO2, GAPDH, GPI, LDHA, PFKP, PGAM1, PGK1, PGM1, PKM, TPI1 | 16 |
| RNA post-transcriptional modification | Processing of mRNA | 4.53 × 10-8 | −0.128 | C1QBP, DDX39B, DDX5, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPM, KHDRBS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, NPM1, PABPC1, PCBP1, PRPF19, PTBP1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SNRPD1, U2AF2 | 20 |
| Molecular transport | Transport of molecule | 4.60 × 10-8 | −1.226 | ACAT2, ALYREF, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, AP1B1, ARF1, ATP1A1, ATP5B, B2M, BSG, CALR, CANX, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CLIC1, CLIC4, CPNE1, CSE1L, CTSA, DDX39B, DDX3X, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EHD1, EIF5A, ERP29, FKBP4, FN1, FUS, GDI2, GNAI2, HNRNPA2B1, HSPA8, HSPA9, IGF2R, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNB1, KRT8, LASP1, LGALS1, MAP1B, MYH9, NPM1, P4HB, PDCD6, PDIA3, PDIA4, PEA15, PICALM, PLIN3, PPIA, RAB11A, RAB7A, RAN, RHOA, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SEC13, SEPT2, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STOML2, TFRC, TNPO1, U2AF2, VAPA, VDAC1, XPO1, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAH, YWHAZ | 89 |
| Cellular development | Differentiation of cells | 4.66 × 10-8 | −1.742 | ACLY, ACTR3, ALYREF, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CAND1, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CD44, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC1, CLIC4, CLTC, CSRP1, CTSB, CYR61, DBN1, DDX5, DHX9, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EIF5A, ENO1, EZR, FASN, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GAPDH, GLO1, GNB2L1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPD1, IARS, IGF2R, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KRT1, KRT8, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LONP1, MAP1B, MAPK1, NAP1L1, NNMT, NPEPPS, NPM1, PA2G4, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PPIA, PPP1CA, PRDX2, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, RHOA, RNH1, RPL22, RPS11, RPS15, RPS3A, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, SFN, SFPQ, SND1, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TFRC, TLN1, TNC, TPM2, TPM4, VIM, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAG, YWHAQ | 115 |
| Cancer | Neoplasia of epithelial tissue | 4.68 × 10-8 | 0.453 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHNAK, AIP, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CAND1, CANX, CAPG, CAPN2, CAPRIN1, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61 | 355 |
| | | | | DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, ETFA, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAFAH1B2, PAICS, PARK7, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLOD2, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RANBP1, RARS, RHOA, RPL10, RPL12, RPL21, RPL22, RPL27, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS11, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS27A, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TWF2, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| Hereditary disorder, skeletal and muscular disorders | Autosomal recessive myopathy | 4.96 × 10-8 | | AHNAK, CALR, CANX, FN1, HINT1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, ITGB1, LMNA, PLEC, PSMA2, PSMA4, SQSTM1, VCP | 14 |
| Infectious disease | Infection of tumor cell lines | 5.02 × 10-8 | −1.728 | ACTR2, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARF1, ARPC1B, ATP5B, CCT2, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, DDX3X, DNAJA2, EIF3I, G3BP1, GML, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HNRNPU, HSPA9, IFITM3, IGF2R, MAP4, PDIA3, PDIA6, PICALM, PSME2, RAB1B, RANBP1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, STAT1, STIP1, TFRC, TWF1, UAP1, UQCRC1, XPO1 | 40 |
| Cancer | Abdominal neoplasm | 5.10 × 10-8 | −1.025 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALYREF, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, CACYBP, CALR, CAND1, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DDX6, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2 | 350 |
| | | | | DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GAPDH, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSD17B10, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCNA, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PSMA1, PSMA7, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RAN, RANBP1, RARS, RBM3, RHOA, RPL12, RPL22, RPL27, RPL4, RPL5, RPL6, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS12, RPS15, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SHMT2, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM3, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB8, TWF1, TWF2, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| RNA post-transcriptional modification | Splicing of mRNA | 5.56 × 10-8 | 0.239 | C1QBP, DDX39B, DDX5, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPM, NPM1, PRPF19, PTBP1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SNRPD1, U2AF2 | 15 |
| Cell morphology | Shape of cells | 7.25 × 10-8 | | ACTN4, CAPN1, FLNA, GPI, IGF2R, ITGB1, MYH10, RHOA, TPM3 | 9 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of plasma membrane projections | 7.91 × 10-8 | −0.331 | ACTR3, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EHD1, EZR, GDI1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, KIF5B, LAMB1, MAP1B, MSN, MYH10, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT2, SOD1, SPTBN1, STIP1, STMN1, TNC, UCHL1, VAPA, VIM, YWHAH | 43 |
| Cell cycle, cellular movement | Cytokinesis | 8.89 × 10-8 | −0.943 | ACTN4, CAP1, CFL1, FN1, GNAI2, ITGB1, LMNA, MAPRE1, MSN, MYH10, MYH9, NPM1, PFN1, RAB11A, RHOA, SEPT2, SEPT7, SEPT9, SSRP1, YBX1 | 20 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of breast cancer cell lines | 1.01 × 10-7 | 0.407 | ANXA1, ANXA2, ARF1, ARPC1B, CAPN2, CAV1, CSE1L, CTTN, ENAH, FLNA, FN1, GNB2L1, GPI, ILF3, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LASP1, MAPK1, MYH9, RHOA, SEPT9, SFN, VIM | 25 |
| Post-translational modification, protein folding | Refolding of protein | 1.08 × 10-7 | | B2M, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, FKBP1A, HSP90AA1, HSPA8, HSPD1 | 7 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell viability of myeloma cell lines | 1.08 × 10-7 | −0.376 | COPB2, EIF3C, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, HSP90B1, PSMA1, PSMA4, PSMC4, RAB11A, RPL27, SF3A1, SOD1, XPO1 | 13 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular function and maintenance, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Neuritogenesis | 1.09 × 10-7 | −0.401 | ACTR3, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EHD1, EZR, GDI1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, LAMB1, MAP1B, MSN, MYH10, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT2, SOD1, SPTBN1, STIP1, STMN1, TNC, UCHL1, VAPA, VIM, YWHAH | 42 |
| Free radical scavenging | Synthesis of reactive oxygen species | 1.15 × 10-7 | −0.019 | AKR1B1, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, CAV1, CD44, CLIC1, CTTN, CYR61, DNM1L, FN1, G6PD, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, HSPA9, HSPB1, IMMT, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LDHA, LONP1, MAPK1, PARK7, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, RHOA, S100A6, SOD1, SQSTM1, TAGLN, TFRC, VDAC1, YWHAZ | 37 |
| Free radical scavenging | Metabolism of reactive oxygen species | 1.17 × 10-7 | −0.644 | AKR1B1, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, CAV1, CD44, CLIC1, CTTN, CYR61, DNM1L, FN1, G6PD, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, HSPA9, HSPB1, IMMT, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LDHA, LONP1, MAPK1, PARK7, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, RHOA, S100A6, SOD1, SQSTM1, TAGLN, TFRC, VDAC1, YWHAZ | 38 |
| Cancer | Breast or colorectal cancer | 1.22 × 10-7 | 0.555 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTN1, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, ATIC, ATP5A1, B2M, BSG, C1QBP, CACYBP, CAPG, CAPN2, CAV1, CBX3, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CD44, CDK1, COPA, COPB2, CSE1L, CTSB, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX3X, DDX5, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJC8, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ESYT1, ETFA, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GARS, GCN1L1, GLO1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HDGF, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HLA-B, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH3, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IPO7, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LONP1, LRPPRC, MAP1B, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MDH1, MDH2, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NCL, NNMT, NPEPPS, OLA1, P4HB, PAFAH1B2, PAICS, PCBP1, PCNA, PDCD6, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PSMA7, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PYGB, RANBP1, RARS, RHOA, RPL4, RPL5, RPL6, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS24, RPS3, RTN4, S100A6, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3B1, SFPQ, SHMT2, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SOD1, SPTAN1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM4, TUBA1B, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, UBA1, VCL, VDAC2, VIM, VPS35, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC6, YBX1, YWHAE, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 223 |
| Cellular function and maintenance | Endocytosis | 1.22 × 10-7 | −0.427 | ACTN4, ANXA5, ANXA6, ATP5B, CANX, CAP1, CAV1, CD44, CLTC, CORO1C, CTTN, DPYSL2, EHD1, EZR, GNB2L1, HNRNPK, HSPA8, HSPA9, HYOU1, IGF2R, IQGAP1, ITGB1, MAP1B, NCL, PICALM, RAB7A, RHOA, SFPQ, TLN1 | 29 |
| Neurological disease, psychological disorders | Dementia | 1.30 × 10-7 | | ACLY, ATP5A1, CANX, CAPN1, CAV1, CDK1, CTSB, DHX9, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1G, EEF2, EIF2S1, EPRS, FDPS, G3BP1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPU, HSPA5, HSPD1, LGALS1, PARK7, PCNA, PICALM, PRDX1, PRKDC, RAN, SET, SOD1, STIP1, TAGLN, TUBB, UBXN4, UCHL1, VCP, VIM, VPS35, YWHAZ | 41 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer | 1.39 × 10-7 | | AHNAK, ALDOA, ALDOC, ATIC, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, DHX9, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENO1, EZR, G3BP1, GPI, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, IMPDH2, LDHA, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, NACA, NSFL1C, PCNA, PFKP, PKM, PRDX1, PRPF19, SERBP1, TPI1, TUBB4B | 36 |
| Skeletal and muscular disorders | Caveolinopathy | 1.42 × 10-7 | | ACTA1, AHNAK, CALR, CANX, FLNC, HSP90B1, HSPA5, LMNA, MATR3, PSMA2, PSMA4, SQSTM1, VCL, VCP | 14 |
| Cellular movement | Invasion of tumor cell lines | 1.49 × 10-7 | −0.733 | ACAT1, ANXA1, APEX1, ARHGDIA, BSG, CALR, CAP1, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, ENAH, EZR, FN1, GNB2L1, GPI, HDGF, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, ILF3, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KRT8, LGALS1, MAPK1, MARCKS, PA2G4, PEBP1, PKM, PTGES3, RHOA, RPSA, S100A6, SEPT9, SQSTM1, STMN1, TAGLN, TAGLN2, VCP, VIM, YWHAQ | 43 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of connective tissue cells | 1.54 × 10-7 | −0.391 | CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CYR61, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FLNB, FN1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, IGF2R, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10, PLEC, STMN1, VCL, ZYX | 22 |
| Cancer | Follicular adenoma | 1.67 × 10-7 | | ANXA5, CALR, CTSB, GSTP1, HSP90AB1, PARK7, PRDX2 | 7 |
| Neurological disease, psychological disorders | Tauopathy | 1.70 × 10-7 | | ACLY, ATP5A1, CANX, CAPN1, CAV1, CDK1, CTSB, DHX9, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1G, EEF2, EIF2S1, EPRS, FDPS, G3BP1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPU, HSPA5, HSPD1, LGALS1, PARK7, PCNA, PICALM, PRDX1, PRKDC, RAN, SET, SOD1, STIP1, TAGLN, TUBB, TUBB4B, UBXN4, UCHL1, VIM, VPS35, YWHAZ | 41 |
| Cancer | Metastatic malignant solid tumor | 1.70 × 10-7 | | ATIC, B2M, CAV1, CSE1L, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FKBP1A, FN1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, MYL12A, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, TUBB, TUBB4B, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 21 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of central nervous system cells | 1.85 × 10-7 | 0.374 | CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, CDK1, DNM1L, FUS, GAPDH, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, MAP1B, MAPK1, NPM1, P4HB, PARK7, PEA15, RHOA, RPS3, SOD1, STIP1, TCP1, VAPA, YWHAB | 26 |
| Molecular transport, protein trafficking | Import of protein | 2.01 × 10-7 | 0.816 | CFL1, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, KPNA2, KPNB1, PDIA3, RAN, SPTBN1, XPO1 | 12 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Synthesis of purine nucleotide | 2.04 × 10-7 | −2.561 | ALDOA, ATP5A1, ATP5B, CAV1, CDK1, DNM1L, FASN, G6PD, GMPS, HMGB1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, NNMT, PKM, PPA1, SLC25A5, SOD1, VCP, VDAC1 | 19 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities | Lymphatic neoplasia | 2.22 × 10-7 | 0.882 | ACTG1, ANXA1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CD44, CFL1, CSE1L, CYR61, DNM1L, EEF1A1, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, GMPS, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KRT1, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, MARS, MYH10, NNMT, NPM1, PICALM, PLOD2, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMB1, PSMD2, PSME1, RHOA, RPL10, RPL3, RPL6, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, SF3B1, SHMT2, SNRPD3, SPTBN1, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 66 |
| Energy production, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Synthesis of ATP | 2.47 × 10-7 | −2.160 | ALDOA, ATP5B, CAV1, CDK1, DNM1L, HMGB1, HSPD1, NNMT, PKM, SLC25A5, SOD1, VCP, VDAC1 | 13 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular function and maintenance, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Morphogenesis of neurites | 2.71 × 10-7 | −0.815 | ACTR3, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EHD1, EZR, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, LAMB1, MAP1B, MYH10, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT2, SOD1, TNC, VAPA, YWHAH | 32 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of neurons | 2.84 × 10-7 | 1.726 | AARS, CAPN1, CAPRIN1, CAST, CDK1, CTSB, DNM1L, FN1, G6PD, GAPDH, GLUD1, GPI, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, NPM1, P4HB, PARK7, PEA15, PRDX2, RHOA, RPS3, SET, SOD1, STAT1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAB | 34 |
| Nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Biosynthesis of nucleoside triphosphate | 2.93 × 10-7 | −2.160 | ALDOA, ATP5B, CAV1, CDK1, CTPS1, DNM1L, HMGB1, HSPD1, NNMT, PKM, SLC25A5, SOD1, VCP, VDAC1 | 14 |
| Cellular development, skeletal and muscular system development and function, tissue development | Differentiation of osteoblasts | 3.01 × 10-7 | −1.093 | ALYREF, ATP5B, CAPNS1, CLIC1, CLTC, CYR61, DDX5, DHX9, FASN, FN1, GNB2L1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HNRNPU, IARS, MAPK1, RPS11, RPS15, RRBP1, SND1, STAT1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TNC, TPM4, VIM | 25 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular movement, hematological system development and function, immune cell trafficking, tissue development | Detachment of granulocytes | 3.22 × 10-7 | 0.254 | ANXA1, ANXA5, ITGB1, RHOA | 4 |
| Cellular movement, connective tissue development and function | Cell movement of fibroblasts | 3.30 × 10-7 | −0.142 | CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CYR61, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FLNB, FN1, HMGB1, IGF2R, ITGB1, MAPK1, MYH10, PLEC, STMN1, VCL, ZYX | 19 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities | Lymphoid cancer | 3.34 × 10-7 | 0.818 | ACTG1, ANXA1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CD44, CFL1, CSE1L, CYR61, DNM1L, EEF1A1, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, GMPS, GNB2L1, GSTP1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, IMPDH2, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KRT1, LDHA, LGALS1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, MARS, MYH10, NNMT, NPM1, PICALM, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMB1, PSMD2, PSME1, RHOA, RPL3, RPL6, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, SF3B1, SHMT2, SNRPD3, SPTBN1, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 64 |
| Metabolic disease, neurological disease, psychological disorders | Alzheimer’s disease | 3.37 × 10-7 | | ACLY, ATP5A1, CANX, CAPN1, CAV1, CDK1, CTSB, DHX9, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EEF1G, EEF2, EIF2S1, EPRS, FDPS, G3BP1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPU, HSPA5, HSPD1, LGALS1, PCNA, PICALM, PRDX1, PRKDC, RAN, SET, SOD1, STIP1, TAGLN, TUBB, UBXN4, UCHL1, VIM, VPS35, YWHAZ | 39 |
| Cancer, tumor morphology | Invasion of tumor | 3.40 × 10-7 | −1.402 | AHCY, ANXA2, BSG, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, CTSB, CTTN, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, HDLBP, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HSPA5, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, PARK7, RHOA, VIM | 23 |
| Hereditary disorder, neurological disease | Autosomal dominant neuropathy | 4.17 × 10-7 | | AARS, DYNC1H1, FUS, GARS, HSPB1, HSPD1, RAB7A, SOD1, UCHL1 | 9 |
| Gene expression | Binding of DNA | 4.32 × 10-7 | −1.045 | ALYREF, APEX1, CALR, CAV1, CDK1, CFL1, FN1, GAPDH, GNB2L1, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, LGALS1, LMNA, MAPK1, NCL, NPM1, PCNA, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX4, PRKDC, RHOA, SET, SFPQ, SND1, SOD1, STAT1, TAGLN, TRIM28, UBE2N, XRCC5, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAZ | 38 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Adhesion of connective tissue cells | 5.10 × 10-7 | −1.487 | ANXA2, CALR, CD44, CYR61, FN1, IGF2R, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, MAPK1, PLEC, RHOA, RPL22, TLN1, TNC, VCL, ZYX | 17 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of fibrosarcoma cell lines | 5.20 × 10-7 | −1.621 | ARPC2, CTTN, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, GPI, HNRNPK, TPM3 | 9 |
| Lipid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Binding of lipid | 5.48 × 10-7 | 0.823 | ANXA2, DNAJA1, FKBP4, FN1, HMGB1, HSP90AB1, MAP4, PTGES3, RPSA, SFN, STIP1, STMN1 | 12 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Double-stranded DNA break repair | 5.75 × 10-7 | 0.116 | CDK1, DDX1, FUS, KPNA2, NPM1, OTUB1, PCNA, PRKDC, PRPF19, TRIM28, UBE2N, VCP, XRCC5, XRCC6 | 14 |
| Cell signaling, DNA replication, recombination, and repair, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Hydrolysis of GTP | 5.79 × 10-7 | −1.580 | CALR, CDK1, DNM1L, GNAI2, IPO5, RAB7A, RAN, RANBP1, RHOA, STMN1, XPO1 | 11 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of breast cancer Cell lines | 6.10 × 10-7 | −0.856 | ARHGDIA, B2M, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, FASN, FN1, HINT1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, KPNA2, KRT18, MAPK1, PEA15, PEBP1, PRKDC, RHOA, SLC25A6, SND1, SSRP1, STAT1, STMN1, TFRC, VCP | 27 |
| Connective tissue disorders, skeletal and muscular disorders | Arthropathy | 7.25 × 10-7 | −0.277 | ACLY, ACTA1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARF1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CAPN2, CD44, CD59, CTSB, DDX39B, EEF1G, EEF2, ENO1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPD1, KHSRP, LDHB, LGALS1, MAPRE1, MYL12A, NONO, PCM1, PDIA3, PGK1, PHB2, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PTMA, RPS24, RPS3, RPSA, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, TPM2, TRIM28, TUBB, TUBB4B, UBA1, VARS, VIM | 59 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, hepatic system disease | Cholangiocarcinoma | 7.33 × 10-7 | | ANXA1, ANXA2, GNB2L1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, PGK1, PKM, RPL4, RPLP0, VIM | 10 |
| Endocrine system disorders, gastrointestinal disease, immunological disease, inflammatory disease | Autoimmune pancreatitis | 7.47 × 10-7 | | CALR, CAPG, COTL1, P4HB, PKM, PRDX2, UCHL1 | 7 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular compromise | Formation of cytoplasmic inclusions | 7.50 × 10-7 | | FUS, KRT18, KRT8, SOD1, SQSTM1, UCHL1 | 6 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of colon cancer Cell lines | 7.75 × 10-7 | 1.899 | AHSA1, CAPN2, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, FASN, GSTP1, HINT1, HSPD1, IGF2R, ITGB1, KRT18, LMNA, PARK7, PPIA, RHOA, SFN, SFPQ, SQSTM1, STAT1, VCP, XRCC5, YWHAE, YWHAH | 24 |
| Cancer | Abdominal cancer | 8.21 × 10-7 | −0.593 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, CACYBP, CALR, CAND1, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GAPDH, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCNA, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PSMA1, PSMA7, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RAN, RANBP1, RARS, RBM3, RHOA, RPL12, RPL22, RPL4, RPL5, RPL6, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SHMT2, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM3, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB8, TWF2, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | 342 |
| Drug metabolism, endocrine system development and function, lipid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Binding of progesterone | 8.87 × 10-7 | −0.277 | DNAJA1, FKBP4, HSP90AB1, PTGES3, STIP1 | 5 |
| Connective tissue disorders, inflammatory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Arthritis | 8.98 × 10-7 | −0.277 | ACLY, ACTA1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARF1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CAPN2, CD44, CD59, CTSB, DDX39B, EEF1G, EEF2, ENO1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPD1, KHSRP, LDHB, LGALS1, MAPRE1, MYL12A, NONO, PCM1, PDIA3, PGK1, PHB2, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PTMA, RPS24, RPS3, RPSA, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, TPM2, TRIM28, TUBB, TUBB4B, VARS, VIM | 58 |
| Cellular compromise, cellular function and maintenance | Endoplasmic reticulum stress response | 9.28 × 10-7 | 1.069 | AARS, CALR, CTSB, DNAJA1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPD1, HYOU1, SERPINH1, SLC38A2, SQSTM1, UCHL1, VCP | 15 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of cerebral cortex cells | 9.41 × 10-7 | 1.181 | CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, CDK1, FUS, GAPDH, HMGB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, MAP1B, P4HB, PARK7, PEA15, RPS3, SOD1, STIP1, TCP1, VAPA, YWHAB | 21 |
| Connective tissue disorders, immunological disease, inflammatory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Rheumatoid arthritis | 9.82 × 10-7 | | ACLY, ACTA1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARF1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CTSB, DDX39B, EEF1G, EEF2, ENO1, FDPS, FKBP1A, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HSP90B1, HSPA8, HSPD1, KHSRP, LDHB, LGALS1, MAPRE1, MYL12A, NONO, PCM1, PDIA3, PGK1, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PTMA, RPS24, RPS3, RPSA, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, TPM2, TRIM28, VARS, VIM | 46 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Bundling of microtubules | 1.03 × 10-6 | 0.218 | DNM1L, MAP1B, MAPRE1, NUMA1, RRBP1, SEPT9, SSRP1 | 7 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of breast cancer Cell lines | 1.21 × 10-6 | 0.280 | ANXA1, ANXA2, ARF1, CAPN2, CAV1, CSE1L, CTTN, FLNA, FN1, GNB2L1, ILF3, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, KRT8, LASP1, MAPK1, MYH9, RHOA, SFN, VIM | 21 |
| Cellular compromise | Collapse of intermediate filaments | 1.58 × 10-6 | | KRT18, KRT8, PLEC, RHOA | 4 |
| Connective tissue disorders, inflammatory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Rheumatic disease | 1.66 × 10-6 | −0.277 | ACLY, ACTA1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARF1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CAPN2, CD44, CD59, CTSA, CTSB, DDX39B, EEF1G, EEF2, ENO1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPD1, KHSRP, LDHB, LGALS1, MAPRE1, MYL12A, NONO, PCM1, PDIA3, PGK1, PHB2, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PTMA, RHOA, RPS24, RPS3, RPSA, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, TPM2, TRIM28, TUBB, TUBB4B, UBE2L3, VARS, VIM | 62 |
| Organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Adenomyosis | 1.67 × 10-6 | | ALDOA, ANXA2, DDX6, GPI, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LDHA, MYH10, PRDX5, VDAC1 | 10 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair, energy production, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Hydrolysis of ATP | 1.72 × 10-6 | −0.164 | ATP1A1, CCT4, CCT5, CDK1, HMGB1, HSPA5, HSPD1, MAPK1, UBA1 | 9 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Detachment of blood cells | 1.74 × 10-6 | 0.293 | ANXA1, ANXA5, FN1, ITGB1, RHOA | 5 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of muscle cells | 1.79 × 10-6 | 1.087 | ALDOA, CALR, CAPN1, CAV1, CYR61, EEF1A1, EEF1D, GAPDH, GNAI2, HADHA, HLA-B, HMGB1, HSPB1, HSPD1, LMNA, MAPK1, MDH1, NCL, PARK7, PLEC, PSMB1, RBM3, RHOA, RPSA, S100A6, STAT1, ZYX | 27 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Adhesion of tumor cell lines | 1.86 × 10-6 | −0.235 | ANXA1, ANXA2, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CYR61, ERP29, FLNA, FN1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, ITGB1, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH9, PTGES3, RHOA, RPSA, UCHL1, VCL, ZYX | 23 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, cellular movement | Migration of endothelial cells | 1.90 × 10-6 | −2.222 | ANXA2, CAV1, CYR61, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, G6PD, HMGB1, HSP90AB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, IGF2R, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MARCKS, NCL, PDCD6, PKM, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT7, TARS, VIM, WARS, YWHAZ | 26 |
| Cancer, cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, tumor morphology | Proliferation of tumor cells | 2.04 × 10-6 | −1.588 | ACLY, ACTN4, AHCY, AKR1B1, ANXA1, ANXA2, BSG, CACYBP, CAV1, CD44, CTSB, CYR61, EEF1A1, EZR, FASN, FN1, HDGF, HMGB1, HSPA5, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, NPM1, PARK7, PPP2CA, RHOA, RPS4X, S100A6, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TXLNA, UCHL1, XRCC5 | 34 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Binding of zona pellucida | 2.10 × 10-6 | | CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, TCP1 | 8 |
| Cellular function and maintenance | Engulfment of cells | 2.23 × 10-6 | −0.600 | ACTN4, ANXA1, ANXA5, CALR, CAPG, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, CLTC, CORO1C, EHD1, EZR, FN1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, HYOU1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MYH9, NCL, NPM1, PFN1, PICALM, RAB7A, RHOA, SFPQ, SNX3, VIM | 30 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Non small cell lung adenocarcinoma | 2.24 × 10-6 | | AHNAK, ALDOA, ALDOC, ATIC, CAPRIN1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, DHX9, EEF1B2, EIF4A1, ENO1, EZR, G3BP1, GPI, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, IMPDH2, LDHA, LOC102724594/U2AF1, MAP4, MSN, MYH9, NACA, NSFL1C, PCNA, PFKP, PKM, PRDX1, PRPF19, SERBP1, TPI1, TUBB4B | 33 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Peripheral t-cell lymphoma | 2.47 × 10-6 | | CYR61, FN1, NNMT, PSMB1, PSMD2, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 9 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of brain | 2.52 × 10-6 | 0.904 | CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, CDK1, DNM1L, FUS, GAPDH, HMGB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, MAP1B, P4HB, PARK7, PEA15, RPS3, SDHA, SOD1, STAT1, STIP1, TCP1, VAPA, YWHAB | 24 |
| Cancer | Metastatic cancer | 2.58 × 10-6 | | ATIC, B2M, CAPG, CAV1, CSE1L, DPYSL2, EEF1A1, EIF4A1, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, KRT18, MYL12A, PLOD2, PPIA, RPL27, RPL7, RPS11, RPS27A, STAT1, TUBB, TUBB4B, YWHAE | 27 |
| Free radical scavenging | Production of reactive oxygen species | 2.60 × 10-6 | 0.372 | AKR1B1, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, CAV1, CD44, CTTN, DNM1L, FN1, G6PD, GNB2L1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSP90AB1, HSPA9, IMMT, LDHA, LONP1, MAPK1, PARK7, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, RHOA, SOD1, SQSTM1, TAGLN, VDAC1, YWHAZ | 28 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of fibrosarcoma cell lines | 2.60 × 10-6 | −1.394 | ARPC2, CTTN, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, HNRNPK, TPM3 | 8 |
| Cellular growth and proliferation | Outgrowth of cells | 2.75 × 10-6 | −0.580 | APEX1, BASP1, CDK1, CYR61, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, FKBP4, FN1, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, MYH9, NPM1, PDIA3, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SLC25A5, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, TNC, VAPA, VIM, YWHAZ | 32 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease | Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia | 2.79 × 10-6 | | ANXA2, ANXA6, CAV1, CDK1, FASN, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, G3BP1, KPNA2, NONO, PCNA, PPP2CA, PSMB1, PSMD2, STIP1, XRCC6, YWHAE | 18 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Upper gastrointestinal tract tumor | 2.84 × 10-6 | | AKR1B1, ALYREF, ANXA1, ATIC, BSG, CANX, CAV1, CD44, COPB2, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTTN, DDX39B, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HDGF, HINT1, HLA-B, HNRNPH1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, IGF2R, IPO5, LGALS1, NPM1, P4HB, PA2G4, PCNA, PLOD2, PPP1CA, RAN, RHOA, RPL10, RPL22, SFN, TAGLN, TNC, TUBB, TUBB4B, XRCC5 | 46 |
| Molecular transport, RNA trafficking | Transport of RNA | 3.04 × 10-6 | −1.969 | ALYREF, DDX39B, DDX3X, EIF5A, FUS, HNRNPA2B1, KHDRBS1, RAN, U2AF2, XPO1 | 10 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease | Plasma cell dyscrasia | 3.09 × 10-6 | | ANXA2, ANXA6, CAV1, CDK1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUS, G3BP1, HLA-A, KPNA2, NONO, PCNA, PDIA6, PPP2CA, PSMA2, PSMB1, PSMD2, STIP1, VIM, XRCC6, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 25 |
| Cell cycle | Arrest in interphase | 3.10 × 10-6 | | ANXA2, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, LGALS1, LMNA, MAPK1, MCM7, PDCD6, PPP1CA, PRKDC, PTGES3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL5, RPL7A, SFN, SPTAN1, STAT1, TCP1, TFRC, TMPO, YWHAG | 30 |
| Cell signaling, post-translational modification, protein synthesis | Actin capping of filament barbed ends | 3.12 × 10-6 | | CAPG, CAPZA1, CAPZB, TWF1, TWF2 | 5 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of bone cancer cell lines | 3.21 × 10-6 | −1.584 | ACTN4, CAPN2, CAV1, CTSB, FN1, STMN1, TLN1, VCP | 8 |
| Hematological system development and function, inflammatory response, tissue development | Aggregation of blood platelets | 3.42 × 10-6 | −0.977 | ACTG1, AKR1B1, CAPN1, CAST, CLIC1, CSRP1, FLNA, GNAI2, HSPB1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH9, MYL12A, P4HB, PDIA3, TLN1, VCL | 18 |
| Cancer | Cancer | 3.45 × 10-6 | −1.084 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, ANXA6, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CAND1, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPRIN1, CAPZA1, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC1, CLTC, CNN3, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB | 406 |
| | | | | CTTN, CUTA, CYB5R3, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EHD1, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, ETFA, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GAPDH, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI1, GDI2, GLO1, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPR, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAFAH1B2, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDE6H, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDIA6, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMA2, PSMA7, PSMB1, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PSME1, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RAN, RANBP1, RARS, RBM3, RCN1, RHOA, RNH1, RPL10, RPL12, RPL22, RPL27, RPL3, RPL4, RPL5, RPL6, RPL7, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS11, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS27A, RPS3, RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SHMT2, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SLC38A2, SND1, SNRPD3, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TAGLN2, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM3, TPM4, TUBA1B, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TWF2, TXLNA, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, UQCRC1, VARS, VAT1, VCL, VCP, VDAC2, VIM, VPS35, WARS, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| Cell morphology | Blebbing | 3.47 × 10-6 | 0.053 | CTTN, DPYSL2, EZR, HSPB1, LMNA, LMNB1, MARCKS, RHOA, SPTAN1 | 9 |
| Hereditary disorder, neurological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities, skeletal and muscular disorders | Charcot-Marie-tooth disease type 2 | 3.75 × 10-6 | | AARS, DYNC1H1, GARS, HSPB1, LMNA, RAB7A | 6 |
| Endocrine system development and function, small molecule biochemistry | Binding of hormone | 3.75 × 10-6 | 0.250 | DNAJA1, FKBP4, HSP90AB1, PTGES3, SFN, STIP1 | 6 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Classic Hodgkin disease | 3.75 × 10-6 | | FKBP1A, LGALS1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 6 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Stabilization of microtubules | 3.80 × 10-6 | 0.247 | COPB2, DNM1L, DPYSL2, IQGAP1, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPRE1, NUMA1, PKM, RHOA, SEPT7, STMN1 | 12 |
| Cell morphology, cellular function and maintenance | Transmembrane potential of mitochondria | 4.05 × 10-6 | −0.508 | ANXA6, B2M, CLIC1, CLIC4, HSPA4, HSPB1, HSPD1, IMMT, LDHA, LGALS1, LONP1, PARK7, PHB2, SLC25A6, SOD1, STOML2, VCP, VDAC1, YWHAE | 19 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Digestive organ tumor | 4.26 × 10-6 | −0.321 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALYREF, ANXA1, ANXA2, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BSG, CACYBP, CANX, CAPG, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB2, COPG1, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCNA, PDIA4, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PSMA7, PSMC1, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RAN, RANBP1, RARS, RHOA, RPL10, RPL12, RPL22, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7A, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB8, TWF2, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAZ | 297 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, tissue development | Polymerization of filaments | 4.45 × 10-6 | 0.934 | ACTR3, ARPC2, CAPZB, CAV1, CFL1, FKBP4, MAP1B, MAPRE1, PFN1, RHOA, STMN1, TUBB, TWF1, TWF2 | 14 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Growth of neurites | 4.55 × 10-6 | −1.344 | APEX1, BASP1, CAV1, CDK1, CSRP1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, FKBP4, FN1, HMGB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, MYH9, PDIA3, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT9, SLC25A5, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, TNC, VAPA, VCL, VIM, YWHAZ | 33 |
| Hematological disease | Blood protein disorder | 4.60 × 10-6 | | ANXA2, ANXA6, ARHGDIA, B2M, CAV1, CDK1, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUS, G3BP1, HLA-A, KPNA2, NONO, PCNA, PDIA6, PPP2CA, PSMA2, PSMB1, PSMD2, STIP1, VIM, XRCC6, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 27 |
| Hereditary disorder | Autosomal dominant disease | 4.66 × 10-6 | | AARS, ACTA1, ACTG1, ACTN4, AHNAK, CAV1, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EEF2, EIF4G1, FKBP1A, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUS, GARS, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HSPB1, HSPD1, KRT1, KRT9, LMNA, LMNB1, MYH9, PARK7, RAB7A, SOD1, STAT1, TNC, TPM2, TPM3, UCHL1, VCP, VPS35 | 35 |
| Cancer, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Lymphatic node tumor | 4.71 × 10-6 | 0.000 | ANXA1, ATIC, B2M, CSE1L, CYR61, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, LONP1, NNMT, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMB1, PSMD2, RHOA, RPS2, SF3B1, SHMT2, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, XPO1, XRCC5, YWHAZ | 33 |
| Molecular transport | Nuclear export | 4.97 × 10-6 | | ALYREF, CALR, CSE1L, DDX39B, EIF5A, HNRNPA1, HSPA9, KHDRBS1, NPM1, RAN, XPO1 | 11 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of colon cancer cell lines | 5.12 × 10-6 | 1.294 | AHSA1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, FASN, GSTP1, HINT1, HSPD1, IGF2R, ITGB1, KRT18, PARK7, PPIA, RHOA, SFN, SFPQ, STAT1, VCP, XRCC5, YWHAE | 20 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of pericytes | 5.37 × 10-6 | −0.928 | CD44, FN1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10 | 7 |
| Molecular transport, protein synthesis, protein trafficking | Localization of protein | 5.46 × 10-6 | −0.324 | APEX1, ARHGDIA, BTF3, C1QBP, CAV1, CUTA, FKBP1A, FKBP4, GNB2L1, HLA-A, HYOU1, ITGB1, NPM1, PICALM, SEPT2, SQSTM1, TFRC | 17 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of connective tissue cells | 5.46 × 10-6 | 0.420 | CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CYR61, EHD1, FLNB, FN1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10, PLEC, STMN1, VCL, ZYX | 17 |
| Hereditary disorder, skeletal and muscular disorders | Autosomal dominant myopathy | 6.79 × 10-6 | | AARS, AHNAK, DYNC1H1, GARS, HSPB1, LMNA, RAB7A | 7 |
| Neurological disease | Lower motor neuron disease | 6.79 × 10-6 | | DYNC1H1, GARS, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HSPB1, UBA1, VCP | 7 |
| Cancer, endocrine system disorders | Thyroid adenoma | 6.79 × 10-6 | | ANXA5, CALR, CTSB, GSTP1, HSP90AB1, PARK7, PRDX2 | 7 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of cervical cancer cell lines | 7.05 × 10-6 | −0.772 | CCT4, CDK1, CTSB, DNM1L, DYNC1H1, EZR, FLNB, HNRNPK, IMMT, KHDRBS1, MAPK1, MSN, PCBP2, PPIA, PRKDC, PRPF19, PTMA, RPS24, STAT1, TCP1, UCHL1, VDAC1 | 22 |
| Cell morphology | Shape change of tumor cell lines | 7.13 × 10-6 | −1.937 | ANXA5, CAP1, CAPN2, DPYSL2, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, ITGB1, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH9, PFN1, RHOA, TNC, UCHL1 | 15 |
| Energy production, molecular transport, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Concentration of ATP | 7.22 × 10-6 | −1.019 | ALDOA, ATP5B, CAV1, DNM1L, ENO1, HSD17B10, KRT8, LDHA, LRPPRC, PKM, SQSTM1, STOML2, VDAC1 | 13 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of brain cells | 7.42 × 10-6 | 1.086 | CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, CDK1, DNM1L, FUS, GAPDH, HMGB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, HYOU1, MAP1B, P4HB, PARK7, PEA15, RPS3, SOD1, STIP1, TCP1, VAPA, YWHAB | 22 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Digestive tract cancer | 7.58 × 10-6 | 0.345 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ANXA1, ANXA2, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BSG, CACYBP, CANX, CAPG, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB2, COPG1, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCNA, PDIA4, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PSMA7, PSMC1, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RAN, RANBP1, RARS, RHOA, RPL10, RPL12, RPL22, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7A, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB8, TWF2, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAZ | 294 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Malignant neoplasm of digestive system | 7.58 × 10-6 | 0.345 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ANXA1, ANXA2, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BSG, CACYBP, CANX, CAPG, CAPN2, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CLIC1, CLTC, COPA, COPB2, COPG1, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1D, EEF2, EIF3I, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, | 294 |
| | | | | GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPRE1, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCNA, PDIA4, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PKM, PLEC, PLIN3, PLOD2, PLS3, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PSMA7, PSMC1, PSMD2, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RAN, RANBP1, RARS, RHOA, RPL10, RPL12, RPL22, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7A, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS2, RPS24, RPS4X, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SET, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB8, TWF2, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VARS, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAZ | |
| Molecular transport | Export of molecule | 7.90 × 10-6 | −1.118 | ALYREF, ANXA6, CALR, CSE1L, DDX39B, EIF5A, HSPA9, KHDRBS1, RAN, SEC13, U2AF2, XPO1, YWHAE | 13 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Quantity of filaments | 8.03 × 10-6 | −0.914 | CFL1, FN1, GNB2L1, KRT18, MAP1B, MAP4, MARCKS, PLEC, RHOA, SERPINH1, SPTAN1, STMN1, TMOD3, VIM | 14 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, reproductive system development and function | Binding of sperm | 8.32 × 10-6 | | CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, TCP1 | 8 |
| Connective tissue disorders, developmental disorder, metabolic disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Paget’s disease of bone | 8.37 × 10-6 | | FDPS, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, SQSTM1, VCP | 5 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma | 8.37 × 10-6 | | FKBP1A, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 5 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Relapsed classical hodgkin lymphoma | 8.37 × 10-6 | | FKBP1A, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 5 |
| Infectious disease | Infection of hepatoma cell lines | 8.85 × 10-6 | −0.425 | ACTR2, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARPC1B, CLTC, G3BP1, HMGB1, IFITM3, TFRC | 9 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Upper gastrointestinal tract cancer | 8.86 × 10-6 | | ANXA1, ATIC, BSG, CANX, CAV1, CD44, COPB2, CSTB, CTNNA1, CTTN, DDX39B, EZR, FASN, FKBP1A, FN1, FUS, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HDGF, HINT1, HLA-B, HNRNPH1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, IGF2R, IPO5, LGALS1, NPM1, P4HB, PA2G4, PLOD2, RAN, RHOA, RPL10, RPL22, SFN, TAGLN, TNC, TUBB, TUBB4B | 41 |
| Hematological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Myelodysplastic syndrome | 9.44 × 10-6 | | CALR, LOC102724594/U2AF1, NPM1, PDIA3, RPL3, RPL4, RPL5, RPL6, RPL7, RPLP0, RPLP1, RPS27A, RPS4X, SF3B1 | 14 |
| Cancer | Osteosarcoma | 9.56 × 10-6 | | CD44, FASN, FDPS, HINT1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, IMPDH2, PRDX1, STOML2, TUBB, TUBB4B | 12 |
| Cellular function and maintenance | Uptake of cells | 9.91 × 10-6 | 0.555 | C1QBP, CAV1, ITGB1, NCL, OTUB1, RHOA, RPSA, SNX3 | 8 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation | Proliferation of carcinoma Cell lines | 1.06 × 10-5 | −0.759 | ACLY, ANXA1, ANXA2, BSG, C1QBP, CAV1, CYR61, DYNC1H1, GAPDH, H2AFY, HMGB1, HNRNPA2B1, IGF2R, ITGB1, MAPK1, MAPRE1, PTBP1, S100A6, SET, SLC25A6, SOD1, STMN1, TRIM28, UCHL1 | 24 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of breast cancer Cell lines | 1.16 × 10-5 | −1.394 | ARHGDIA, B2M, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, FASN, FN1, HINT1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, KPNA2, KRT18, MAPK1, PEA15, PEBP1, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, VCP | 22 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, connective tissue development and function, tissue development | Adhesion of fibroblast Cell lines | 1.18 × 10-5 | −1.591 | CALR, CD44, CYR61, FN1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, MAPK1, RHOA, VCL | 9 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular compromise | Formation of cellular inclusion bodies | 1.21 × 10-5 | 0.246 | CTSB, DNAJA1, FUS, HSPA4, KRT18, KRT8, PSMC4, SOD1, SQSTM1, TCP1, UCHL1 | 11 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction | Binding of lymphoma cell lines | 1.31 × 10-5 | −0.881 | ANXA2, CD44, FN1, ITGB1, NCL, RHOA, TFRC | 7 |
| Organismal injury and abnormalities, renal and urological disease | Nephrosis | 1.35 × 10-5 | | ACTN4, ANXA1, ARHGDIA, CLTC, FKBP1A, IMPDH2, ITGB1, LAMB1, PDLIM1 | 9 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | CDKN2A positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 1.35 × 10-5 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1 | 3 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Advanced stage primary laryngeal cancer | 1.35 × 10-5 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1 | 3 |
| Gene expression | Binding of Y box | 1.35 × 10-5 | | APEX1, YBX1, YBX3 | 3 |
| Connective tissue disorders, developmental disorder, hereditary disorder, metabolic disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Familial Paget’s disease of bone | 1.35 × 10-5 | | HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, VCP | 3 |
| Cellular movement | Initiation of migration of fibrosarcoma cell lines | 1.35 × 10-5 | | FLNA, FLNB, FLNC | 3 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Locally advanced cervical cancer | 1.35 × 10-5 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1 | 3 |
| Cancer, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Node positive cervical cancer | 1.35 × 10-5 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1 | 3 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Outgrowth of neurites | 1.36 × 10-5 | −1.232 | APEX1, BASP1, CDK1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, FKBP4, FN1, HMGB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, MYH9, PDIA3, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SLC25A5, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, TNC, VAPA, VIM, YWHAZ | 29 |
| Cancer, tumor morphology | Invasion of malignant tumor | 1.38 × 10-5 | −2.111 | AHCY, BSG, CAPN2, CD44, CTSB, CTTN, EZR, FASN, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HSPA5, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, VIM | 15 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Quantity of cellular protrusions | 1.38 × 10-5 | 0.905 | ACTG1, ACTR2, ARPC2, BSG, CANX, CAPZB, CTTN, ENAH, EZR, FN1, MAP1B, MSN, SOD1, TLN1, TPM3 | 15 |
| Cell cycle | Interphase | 1.57 × 10-5 | 0.828 | ANXA2, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, DDX3X, FASN, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, GNB2L1, GPI, ITGB1, LGALS1, LMNA, MAPK1, MCM7, NASP, NPM1, PCNA, PDCD6, PEA15, PPP1CA, PRKDC, PTGES3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL5, RPL7A, SFN, SPTAN1, STAT1, TCP1, TFRC, TMPO, XRCC5, YWHAG, YWHAQ | 40 |
| Cell morphology, cellular function and maintenance | Repair of cells | 1.62 × 10-5 | 0.131 | APEX1, KPNA2, NPM1, OTUB1, PCNA, PRKDC, UBE2N, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1 | 10 |
| Protein synthesis | Oligomerization of protein | 1.63 × 10-5 | | ACAT1, AHNAK, ANXA5, ANXA6, CAV1, CTNNA1, CUTA, EEF1A1, EHD1, LONP1, NPM1, PRKCSH, SEPT7, SEPT9, SQSTM1, STOML2, TRIM28, VCP, YWHAB | 19 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of pericytes | 1.68 × 10-5 | −0.600 | CD44, FN1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, LGALS1, MYH10 | 6 |
| Cellular development, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Development of neurons | 1.85 × 10-5 | −0.428 | ACTR3, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, GDI1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, HSPB1, ITGB1, LAMB1, MAP1B, MSN, MYH10, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, PHGDH, PICALM, PPP2CA, PRKCSH, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT2, SOD1, SPTBN1, STIP1, STMN1, TNC, UCHL1, VAPA, VIM, YWHAG, YWHAH | 45 |
| Hereditary disorder, neurological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities, skeletal and muscular disorders | Autosomal dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 | 1.88 × 10-5 | | AARS, DYNC1H1, GARS, HSPB1, RAB7A | 5 |
| Cell morphology, hair and skin development and function | Cell spreading of epithelial cell lines | 1.88 × 10-5 | −1.446 | CYR61, FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, VIM | 5 |
| Cell morphology, cellular function and maintenance, DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Double-stranded DNA break repair of cells | 1.91 × 10-5 | 0.131 | KPNA2, NPM1, OTUB1, PCNA, PRKDC, UBE2N, XRCC5, XRCC6 | 8 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of central nervous system cells | 1.96 × 10-5 | −0.963 | CAPN1, CAST, CDK1, DNM1L, GAPDH, HSP90AA1, HSPA5, MAP1B, NPM1, P4HB, PEA15, RHOA, RPS3, SOD1, YWHAB | 15 |
| Cell cycle | Arrest in G1 phase | 1.97 × 10-5 | | CYR61, FASN, FKBP1A, FN1, ITGB1, LGALS1, LMNA, MAPK1, MCM7, PPP1CA, PRKDC, PTGES3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL5, RPL7A, SPTAN1, TFRC, TMPO, YWHAG | 20 |
| Cellular function and maintenance | Cellular homeostasis | 1.98 × 10-5 | 0.822 | AKR1B1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA6, ARF1, ATP1A1, B2M, BSG, CALR, CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, CAV1, CLIC1, CLIC4, CLTC, CTTN, CYR61, DNM1L, EEF1D, EIF2S1, EIF4G1, FKBP1A, FN1, GPI, H2AFY, HADH, HEXB, HMGB1, HNRNPL, HSP90AA1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, IGF2R, IMMT, ITGB1, KIF5B, KRT18, KRT8, LDHA, LGALS1, LONP1, MAPK1, PAFAH1B2, PARK7, PGM1, PHB2, PICALM, PPIA, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PRDX2, PRKDC, PSMD2, PYGL, RAB11A, RAB7A, RPL22, SEPT9, SERPINH1, SLC25A6, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STOML2, TFRC, TUFM, UBE2N, VCP, VDAC1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAE | 77 |
| Tissue development | Growth of connective tissue | 2.07 × 10-5 | 0.381 | ANXA2, ATIC, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CLTC, CTSB, CYR61, DDX5, DNM1L, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, GSTP1, HDGF, HNRNPA2B1, HSPB1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAPK1, MYH10, MYH9, NPM1, PA2G4, PGK1, PRDX4, PRKDC, PTGES3, RBM3, RHOA, SERPINH1, SFN, STAT1, STMN1, TPM3, VCL, YBX1 | 40 |
| Post-translational modification, protein folding | Folding maturation of protein | 2.09 × 10-5 | | AIP, CALR, FKBP1A, PRDX4 | 4 |
| Cellular movement | Invasion of breast cancer cell lines | 2.24 × 10-5 | 0.051 | BSG, CALR, CAV1, CD44, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, ENAH, EZR, FN1, HSP90AA1, ILF3, IQGAP1, KRT8, MAPK1, PTGES3, RHOA, SEPT9, STMN1 | 19 |
| Cellular function and maintenance, inflammatory response | Phagocytosis | 2.34 × 10-5 | −0.334 | ANXA1, ANXA5, CALR, CAPG, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, CLTC, CORO1C, EHD1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, ITGB1, MAPK1, MSN, MYH9, NPM1, PFN1, RAB7A, RHOA, SNX3, VIM | 22 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, connective tissue development and function, tissue development | Proliferation of fibroblasts | 2.34 × 10-5 | 0.428 | ANXA2, CAV1, CD44, DDX5, DNM1L, FN1, GPI, GSTP1, HDGF, HSPB1, ITGB1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAPK1, NPM1, PA2G4, PGK1, PRDX4, PRKDC, PTGES3, RBM3, RHOA, STAT1, VCL, YBX1 | 25 |
| Protein trafficking | Targeting of protein | 2.35 × 10-5 | | AIP, CALR, CSE1L, EIF5A, HSPA9, RAB7A, RAN, XPO1, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAQ, YWHAZ | 13 |
| Hematological system development and function, tissue development | Aggregation of blood cells | 2.36 × 10-5 | −1.292 | ACTG1, AKR1B1, CAPN1, CAST, CD44, CLIC1, CSRP1, FLNA, GNAI2, HSPB1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH9, MYL12A, P4HB, PDIA3, TLN1, VCL | 19 |
| Cellular movement, connective tissue development and function | Cell movement of fibroblast Cell lines | 2.39 × 10-5 | −0.697 | ACTR2, ACTR3, ARPC2, CD44, CLIC4, CTTN, DDX3X, EHD1, FN1, GPI, HMGB1, ITGB1, MAPRE1, NPM1, RHOA | 15 |
| Cellular development, tissue development | Differentiation of bone cells | 2.43 × 10-5 | −1.093 | ALYREF, ATP5B, CAPNS1, CLIC1, CLTC, CYR61, DDX5, DHX9, FASN, FN1, GLO1, GNB2L1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HNRNPU, IARS, MAPK1, RPS11, RPS15, RRBP1, SND1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, SYNCRIP, TFRC, TNC, TPM4, VIM | 28 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Lymphocytic cancer | 2.48 × 10-5 | 1.450 | ANXA1, ATIC, B2M, CD44, CSE1L, CYR61, FKBP1A, FN1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, IQGAP1, LGALS1, LONP1, NNMT, NPM1, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMB1, PSMD2, RHOA, RPS2, SF3B1, SHMT2, SPTBN1, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YWHAZ | 35 |
| Cancer, cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, tumor morphology | Proliferation of cancer cells | 2.63 × 10-5 | −1.887 | AHCY, AKR1B1, BSG, CACYBP, CAV1, CD44, CTSB, CYR61, EEF1A1, EZR, FASN, HDGF, HMGB1, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, NPM1, PPP2CA, RHOA, RPS4X, S100A6, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TXLNA, XRCC5 | 26 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction | Fusion of cells | 2.74 × 10-5 | 1.580 | ANXA1, ANXA5, CAPN2, CAV1, CD44, CTSB, FLNC, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH9, RHOA, SOD1, STAT1 | 13 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular function and maintenance, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Branching of neurons | 2.75 × 10-5 | −0.900 | ACTR3, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, MAP1B, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, RHOA, RTN4, SOD1 | 21 |
| Cell morphology | Cell spreading of tumor Cell lines | 2.96 × 10-5 | −1.711 | CAP1, CAPN2, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, ITGB1, MARCKS, PFN1, RHOA, TNC, UCHL1 | 11 |
| Dermatological diseases and conditions, immunological disease, inflammatory disease | Lichen planus | 2.96 × 10-5 | | B2M, CFL1, EEF1A1, EIF5A, ENO1, FKBP1A, HLA-A, HLA-B, IFITM3, PFN1, PSME2 | 11 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of vesicles | 3.07 × 10-5 | 0.707 | ANXA2, ANXA5, ARF1, CAST, CLTC, FLNA, IQGAP1, MARCKS, PICALM, RAB11A, RHOA, SNX3 | 12 |
| Immunological disease | Systemic autoimmune syndrome | 3.10 × 10-5 | | ACLY, ACTA1, ALDOA, ANXA1, ARF1, ATIC, B2M, CALR, CD44, CTSA, CTSB, DDX39B, EEF1G, EEF2, ENAH, ENO1, FDPS, FKBP1A, H3F3A/H3F3B, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA3, HSP90B1, HSPA8, HSPD1, KHSRP, LDHB, LGALS1, MAPRE1, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NONO, PCM1, PDIA3, PGK1, PGM1, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PTMA, RPS24, RPS3, RPSA, S100A6, SND1, STAT1, TFRC, TPM2, TRIM28, TUBB, UBE2L3, VARS, VIM | 57 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of filopodia | 3.11 × 10-5 | −2.546 | ACTN4, ACTR3, CAPNS1, CSRP1, CYR61, EEF1A1, ENAH, EZR, FN1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, MAP1B, MARCKS, RHOA, TNC | 15 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance, tissue development | Formation of focal adhesions | 3.12 × 10-5 | −2.245 | ACTN1, CAPN1, CAV1, CTTN, EHD1, EZR, FN1, GNAI2, GNB2L1, ITGB1, RHOA, STMN1, VCL, VIM | 14 |
| Cellular growth and proliferation, tissue development | Proliferation of connective tissue cells | 3.14 × 10-5 | 0.548 | ANXA2, ATIC, CAPNS1, CAV1, CD44, CLTC, CTSB, CYR61, DDX5, DNM1L, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, GSTP1, HDGF, HSPB1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, MAPK1, NPM1, PA2G4, PGK1, PRDX4, PRKDC, PTGES3, RBM3, RHOA, SERPINH1, SFN, STAT1, STMN1, TPM3, VCL, YBX1 | 37 |
| Hematological disease, immunological disease | Eosinophilia | 3.45 × 10-5 | | ALDOA, ENO1, GAPDH, HLA-A, HLA-B, HSPA5, MYH9, P4HB, PDIA3, PRDX1, TKT, TPI1, TUBB | 13 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Organization of actin filaments | 3.56 × 10-5 | −1.633 | ALDOA, CFL1, DBN1, DPYSL2, ENAH, FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, MSN, PLS3, RHOA | 11 |
| Cancer | Benign neoplasia | 3.63 × 10-5 | 1.591 | ACAT1, AIP, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, CALR, CD44, CTSB, CYR61, DBN1, DDX5, DDX6, FKBP1A, GSTP1, HINT1, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, IFITM3, IQGAP1, KPNA3, LGALS1, MAPK1, MDH1, MYH10, NPEPPS, PARK7, PCNA, PEA15, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, RPL27, RPS15, SF3A1, SPTBN1, TNC, TWF1, VCP, ZYX | 41 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Oral cancer | 3.66 × 10-5 | | ANXA1, ATIC, BSG, EZR, FASN, FN1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, LGALS1, NPM1, PLOD2, RPL10, TAGLN, TNC, TUBB, TUBB4B | 18 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of lymphoma Cell lines | 3.67 × 10-5 | 1.961 | ANXA2, ARHGDIA, CD59, EZR, GLO1, HNRNPA1, HSPB1, LGALS1, LMNB1, LONP1, MAPK1, MSN, NCL, RAD23B, RPLP0, YWHAG, YWHAZ | 17 |
| Cell cycle, cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular movement | Elongation of actin filaments | 3.68 × 10-5 | −1.969 | ACTN4, CAP1, FN1, PFN1 | 4 |
| Infectious disease | Infection by Marburg virus | 3.68 × 10-5 | −0.000 | HSPA5, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5 | 4 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism, nucleic acid metabolism | Pentose shunt of monosaccharide | 3.68 × 10-5 | | G6PD, PGD, TALDO1, TKT | 4 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Non-Hodgkin’s disease | 3.72 × 10-5 | | ANXA1, ATIC, B2M, CSE1L, CYR61, FKBP1A, FN1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, IQGAP1, LONP1, NNMT, PRDX1, PRKDC, PSMB1, PSMD2, RHOA, RPS2, SF3B1, SHMT2, STMN1, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TXLNA, UQCRC1, XPO1, XRCC5, YWHAZ | 30 |
| Organismal injury and abnormalities | Nodule | 3.73 × 10-5 | | ANXA5, CALR, CTSB, GSTP1, HMGB1, HSP90AB1, PARK7, PRDX2, PRDX5 | 9 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell death of cortical neurons | 3.77 × 10-5 | 0.671 | CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, CDK1, FUS, GAPDH, HMGB1, HSPA5, HSPB1, HSPD1, MAP1B, PARK7, PEA15, TCP1, YWHAB | 15 |
| Cell morphology, connective tissue development and function | Morphology of fibroblast cell lines | 3.85 × 10-5 | | CAV1, CTTN, DPY30, FN1, KRT18, KRT8, MARCKS, PTBP1, RHOA, RTN4 | 10 |
| Infectious disease | Replication of flaviviridae | 3.85 × 10-5 | −0.905 | DDX3X, DDX6, DNAJA1, FASN, G3BP1, HMGB1, IFITM3, MVP, PPIA, YBX1 | 10 |
| Cell death and survival | Cell viability of neuroblastoma cell lines | 3.96 × 10-5 | 0.537 | APEX1, HSP90AB1, HSPB1, P4HB, S100A6, SOD1, SQSTM1, VCP | 8 |
| Cellular compromise | Stress response of cells | 4.00 × 10-5 | 0.174 | CALR, CTSB, DNAJA1, HNRNPA1, HSD17B10, HSP90B1, HSPA5, PRDX1, SLC38A2, SOD1, SQSTM1, VCP, YBX1 | 13 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Laryngeal tumor | 4.00 × 10-5 | | ANXA1, CD44, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 7 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | DNA damage | 4.01 × 10-5 | 1.228 | CALR, FN1, G6PD, GNAI2, GSTP1, HSPB1, LONP1, NPM1, PARK7, PDIA3, PRDX1, PRKDC, SOD1, SQSTM1, XRCC5, YWHAE | 16 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Proliferation of neuronal cells | 4.31 × 10-5 | −1.654 | APEX1, B2M, BASP1, CAV1, CDK1, CFL1, CSRP1, CTNNA1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, FKBP4, FN1, HMGB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAP1B, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, MYH9, PDIA3, RAB11A, RHOA, RTN4, SEPT9, SLC25A5, SNX3, SOD1, SPTBN1, TNC, VAPA, VCL, VIM, YWHAZ | 36 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of hepatic stellate cells | 4.34 × 10-5 | −0.600 | CD44, GNB2L1, HMGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10 | 6 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Laryngeal squamous Cell carcinoma | 4.34 × 10-5 | | CD44, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 6 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of bone cancer cell lines | 4.34 × 10-5 | −1.091 | ACTN4, CAPN2, CAV1, FN1, STMN1, VCP | 6 |
| Cell morphology | Shape change of epithelial cell lines | 4.34 × 10-5 | −1.000 | CYR61, FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, MAPK1, VIM | 6 |
| Molecular transport, protein trafficking | Nuclear transport of protein | 4.54 × 10-5 | | CALR, CSE1L, EIF5A, HSPA9, KPNB1, RAN, TNPO1, XPO1 | 8 |
| Cancer | Growth of malignant tumor | 4.65 × 10-5 | −1.175 | AHCY, AKR1B1, BSG, CACYBP, CAV1, CD44, CTSB, CYR61, EEF1A1, EZR, FASN, GNB2L1, HDGF, HMGB1, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, NPM1, PKM, PPP2CA, RHOA, RPS4X, S100A6, SQSTM1, STAT1, STMN1, TNC, TXLNA, XRCC5 | 29 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development, cellular function and maintenance, embryonic development, nervous system development and function, tissue development | Branching of neurites | 4.69 × 10-5 | −0.668 | ACTR3, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, MAP1B, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, RHOA, RTN4, SOD1 | 20 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular function and maintenance, inflammatory response | Phagocytosis of cells | 4.69 × 10-5 | −0.618 | ANXA1, ANXA5, CALR, CAPG, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, CLTC, CORO1C, EHD1, GNB2L1, HMGB1, ITGB1, MAPK1, MYH9, NPM1, PFN1, RHOA, SNX3, VIM | 20 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction | Binding of stem cells | 5.32 × 10-5 | | C1QBP, ITGB1, TLN1 | 3 |
| Tissue morphology | Collapse of epithelial tissue | 5.32 × 10-5 | | KRT18, KRT8, RHOA | 3 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Growth of focal adhesions | 5.32 × 10-5 | | FLNA, FLNB, VIM | 3 |
| Molecular transport, protein trafficking | Import of green fluorescent protein | 5.32 × 10-5 | | KPNA2, KPNB1, RAN | 3 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, hair and skin development and function | Binding of epithelial cell lines | 5.36 × 10-5 | −0.294 | ANXA2, ANXA5, CAV1, ITGB1, PPP2CA, PRMT5 | 6 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Oropharyngeal tumor | 5.36 × 10-5 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, PCNA, TUBB, TUBB4B | 6 |
| Protein degradation, protein synthesis | Catabolism of protein | 5.52 × 10-5 | 0.237 | CALR, CANX, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPNS1, CAST, CAV1, COPG1, CSTB, CTSB, FLNA, GAPDH, HSP90B1, HSPA5, HSPD1, IPO9, ITGB1, LONP1, MYH9, NACA, NPEPPS, PARK7, PDIA3, PPP2CA, PSMC4, PSMD2, SNX3, SOD1, SQSTM1, TPP1, UBE2L3, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, VCP, XPO1 | 36 |
| Cell cycle | Arrest in cell cycle progression | 5.60 × 10-5 | | C1QBP, CALR, CAV1, CD44, FASN, FKBP1A, KHDRBS1, LMNA, MAP4, MAPK1, NPM1, PA2G4, PCM1, PPM1G, PRMT5, RHOA, SFN, SSRP1, STAT1, TCP1, TNC, XRCC6, YWHAE | 23 |
| Infectious disease | Infection by flaviviridae | 5.71 × 10-5 | 0.460 | ACTR2, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARPC1B, CLTC, G3BP1, HMGB1, IFITM3, STAT1, TFRC | 10 |
| Cell cycle | G1 phase | 5.92 × 10-5 | −0.221 | CAPNS1, CDK1, CYR61, FASN, FKBP1A, FN1, GNB2L1, GPI, ITGB1, LGALS1, LMNA, MAPK1, MCM7, NASP, PPP1CA, PRKDC, PTGES3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL5, RPL7A, SPTAN1, TFRC, TMPO, YWHAG, YWHAQ | 26 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | CD30-positive peripheral t-Cell lymphoma | 6.02 × 10-5 | | TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 4 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, organ morphology | Contraction of left ventricle | 6.02 × 10-5 | 0.849 | CAPNS1, ITGB1, LMNA, RHOA | 4 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of caveolae | 6.02 × 10-5 | −1.009 | ANXA6, CAV1, PICALM, PTRF | 4 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Systemic large-cell KI-1 lymphoma | 6.02 × 10-5 | | TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 4 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Stomach tumor | 6.30 × 10-5 | | AKR1B1, ALYREF, ANXA1, CANX, CAV1, CD44, COPB2, CTNNA1, DDX39B, FKBP1A, FUS, GSTP1, HDGF, HINT1, HNRNPH1, IGF2R, IPO5, P4HB, PA2G4, RHOA, RPL22, TUBB4B, XRCC5 | 23 |
| Cell morphology, cellular function and maintenance, DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Double-stranded DNA break repair of tumor cell lines | 6.57 × 10-5 | 0.878 | KPNA2, NPM1, OTUB1, UBE2N, XRCC5, XRCC6 | 6 |
| Cancer | Head and neck cancer | 6.57 × 10-5 | 1.756 | ACTN1, ANXA1, ATIC, BSG, CAV1, CD44, CTTN, DDX3X, EZR, FASN, FLNA, FN1, GSTP1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HNRNPK, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA5, LDHA, LGALS1, MARCKS, MCM7, NPM1, PCM1, PKM, PLOD2, PRDX1, PRKDC, PRMT5, RPL10, SET, SF3B1, SFN, SPTBN1, STAT1, TAGLN, TNC, TUBB, TUBB4B, VIM, XRCC5, XRCC6 | 43 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Formation of actin cytoskeleton | 6.71E-05 | | CORO1C, ERP29, FLNA, FN1, ITGB1 | 5 |
| Gene expression | Transcription | 7.48 × 10-5 | 0.968 | ACTR2, ACTR3, ALYREF, BASP1, BTF3, C14orf166, C1QBP, CALR, CAND1, CAV1, CBX3, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, EEF1D, EIF2S1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUBP3, GLO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, HDGF, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HSPA8, ILF2, ILF3, IQGAP1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, LGALS1, LMNA, LRPPRC, MAPK1, MATR3, MCM7, NONO, NPM1, OTUB1, PA2G4, PARK7, PCNA, PDLIM1, PEA15, PEBP1, PFN1, PHB2, PHGDH, PICALM, PPP2CA, PRKDC, PRMT5, PTGES3, PTMA, PTRF, RHOA, RPL12, RPL6, SET, SFPQ, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, SUPT16H, TAGLN2, TMPO, TRIM28, UBE2L3, VAPA, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ | 90 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, connective tissue development and function, tissue development | Adhesion of fibroblasts | 7.57 × 10-5 | −0.896 | CD44, FN1, IGF2R, PLEC, TNC, VCL, ZYX | 7 |
| Organismal injury and abnormalities, skeletal and muscular disorders | Neurogenic muscular atrophy | 7.57 × 10-5 | | AARS, DYNC1H1, GARS, HINT1, HSPB1, LMNA, RAB7A | 7 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | DNA replication | 7.63 × 10-5 | −1.248 | CACYBP, CALR, CAV1, CDK1, HMGB1, MAPK1, MCM7, NAP1L1, NASP, NCL, NPM1, PCM1, PCNA, PEA15, SET, SSRP1, SUPT16H, TMPO, XRCC5 | 19 |
| Molecular transport | Nuclear export of molecule | 8.10 × 10-5 | | ALYREF, CALR, CSE1L, DDX39B, EIF5A, HSPA9, KHDRBS1, RAN, XPO1 | 9 |
| Organismal injury and abnormalities, renal and urological disease | Chronic kidney disease | 8.13 × 10-5 | | CDV3, DBI, EEF1B2, FDPS, FKBP1A, H3F3A/H3F3B, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, IMPDH2, MYH9, NPM1, PSMB1, PSMD2, RPL23, RPL7, TUBB, TUBB4B | 17 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of melanoma cell lines | 8.37 × 10-5 | −0.364 | ARF1, BSG, CAPN1, FLNA, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KRT8, MSN, PEBP1, PRDX2, RHOA | 11 |
| Cell death and survival | Cytolysis | 8.37 × 10-5 | 0.280 | ALDOA, ANXA1, B2M, CALR, CAV1, CD44, CD59, G6PD, GPI, HLA-A, IMPDH2, KRT18, LGALS1, PRDX1, PRDX2, PSME2, PTMA, SH3BGRL3, STAT1, STMN1 | 20 |
| Cell morphology, cellular function and maintenance | Transmembrane potential | 8.37 × 10-5 | −0.508 | ANXA6, B2M, CLIC1, CLIC4, HSPA4, HSPB1, HSPD1, IMMT, KIF5B, LDHA, LGALS1, LONP1, PARK7, PHB2, SLC25A6, SOD1, STOML2, VCP, VDAC1, YWHAE | 20 |
| Protein synthesis | Initiation of translation of protein | 8.60E-05 | | EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF4G1, EIF4H, HSPB1, RPS3A | 8 |
| Hematological disease, infectious disease | Infection by Zaire ebolavirus | 8.77 × 10-5 | −2.216 | CTSB, HSPA5, RPL18, RPL3, RPL5 | 5 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Formation of nucleus | 8.78 × 10-5 | −2.364 | CDK1, FLNA, FN1, GNAI2, LMNA, LMNB1, RAN | 7 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance, tissue development | Polymerization of microtubules | 8.78 × 10-5 | 1.141 | CAPZB, CAV1, FKBP4, MAP1B, MAPRE1, STMN1, TUBB | 7 |
| Inflammatory response | Immune response of cells | 9.25 × 10-5 | −1.018 | ANXA1, ANXA5, CALR, CAPG, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CLIC4, CLTC, CORO1C, CTSB, DNM1L, EHD1, FN1, GNB2L1, HLA-A, HMGB1, HSP90AA1, HSPB1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH9, NPM1, OTUB1, PFN1, PSME2, RHOA, SF3A1, SNX3, STAT1, TNPO1, UBE2L3, VIM | 34 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Adhesion of myeloma cell lines | 9.28 × 10-5 | | ANXA2, CD44, FN1, ITGB1 | 4 |
| Cell morphology, embryonic development | Cell spreading of embryonic cell lines | 9.28 × 10-5 | −1.067 | FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, VIM | 4 |
| Gene expression | Replication of RNA | 9.28 × 10-5 | 0.152 | G3BP1, NPM1, VAPA, YBX1 | 4 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function | Angiogenesis | 9.48 × 10-5 | −1.134 | AKR1B1, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, ATP5B, CALR, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, CTSB, CYR61, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FN1, G6PD, HADHA, HMGB1, HSP90B1, HSPB1, HSPD1, IGF2R, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10, MYH9, NCL, PDCD6, PGK1, PKM, PLEC, RHOA, RNH1, RPSA, RTN4, SPTBN1, STAT1, TNC, VCL, VIM, WARS, YWHAE, YWHAZ | 44 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Metastatic cervical cancer | 9.62 × 10-5 | | ATIC, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 6 |
| Molecular transport, protein trafficking | Nuclear export of protein | 9.62 × 10-5 | | CALR, CSE1L, EIF5A, HSPA9, RAN, XPO1 | 6 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Recurrent cervical cancer | 9.62 × 10-5 | | ATIC, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 6 |
| Cell morphology, renal and urological system development and function | Shape change of kidney Cell lines | 9.70 × 10-5 | 0.050 | ANXA2, FLNA, FLNC, FN1, ITGB1, MAPK1, RHOA, VIM | 8 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation | Proliferation of lung cancer cell lines | 1.00 × 10-4 | −1.422 | ACLY, ANXA1, ANXA2, C1QBP, CAV1, CYR61, GAPDH, H2AFY, HNRNPA2B1, ITGB1, MAPK1, NASP, PKM, PTBP1, SET, SLC25A6, SOD1, STMN1, TRIM28 | 19 |
| Cancer | Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 1.01 × 10-4 | | ATIC, FN1, HNRNPK, KRT18, SFN, SLC25A5, TNC | 7 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Degradation of DNA | 1.03 × 10-4 | −0.941 | APEX1, BSG, CAPN2, CAST, DHX9, ENO1, HNRNPA1, HSD17B10, HSPB1, KRT8, LMNA, NPM1, PPIA, RHOA, SOD1, STAT1 | 16 |
| Cellular development | Branching of cells | 1.12 × 10-4 | −1.379 | ACTR3, ANXA2, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, FN1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, MAP1B, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, RHOA, RTN4, SOD1, TNC | 24 |
| Cell morphology, embryonic development | Shape change of embryonic cell lines | 1.13 × 10-4 | −0.555 | FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, MAPK1, VIM | 5 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, organismal development | Vasculogenesis | 1.15 × 10-4 | −1.808 | AKR1B1, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, ATP5A1, CALR, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, CTSB, CYR61, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, G6PD, HADHA, HMGB1, HSP90B1, IGF2R, ITGB1, KRT1, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10, PDCD6, PKM, PLEC, PPIA, PRKDC, RAD23B, RHOA, SEPT9, SERPINH1, SOD1, SPTBN1, STAT1, TNC, VCL, VIM, WARS, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAZ | 45 |
| Cancer, cellular movement, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease, tumor morphology | Invasion of mammary tumor cells | 1.17 × 10-4 | 0.156 | CD44, CTTN, FLNA, FN1, HDLBP, ITGB1, RHOA | 7 |
| Cancer | Solid tumor | 1.21 × 10-4 | 0.779 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AIP, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, C1QBP, CACYBP, CALR, CAND1, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPRIN1, CAPZA1, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC1, CLTC, CNN3, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYB5R3, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EHD1, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, ETFA, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPR, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAFAH1B2, PAICS, PARK7, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDE6H, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLOD2, PLS3, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMB1, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PSME1, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RANBP1, RARS, RCN1, RHOA, RNH1, RPL10, RPL12, RPL21, RPL22, RPL27, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS11, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS27A, RPS3A, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3 | 387 |
| | | | | SHMT2, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM3, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TWF2, TXLNA, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, UQCRC1, VARS, VAT1, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| Cancer, cellular movement, tumor morphology | Invasion of tumor cells | 1.29 × 10-4 | −1.586 | AHCY, CAPN2, CD44, CTSB, CTTN, EZR, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, HDLBP, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, PARK7, RHOA | 15 |
| Embryonic development, organ development, organismal development, skeletal and muscular system development and function, tissue development | Formation of muscle | 1.29 × 10-4 | −0.543 | ACTA1, ACTG1, ACTN4, ANXA1, ANXA5, CALR, CAPN2, CAPZB, CAV1, FKBP1A, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, HMGB1, HSP90B1, ITGB1, KRT8, MAPK1, MYH10, MYH9, PLEC, RHOA, STIP1, UCHL1, VCL, VIM | 26 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, embryonic development | Binding of embryonic cells | 1.31 × 10-4 | | C1QBP, ITGB1, TLN1 | 3 |
| Cell death and survival, connective tissue disorders, developmental disorder, hematological disease, hereditary disorder | Hereditary nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia | 1.31 × 10-4 | | ALDOA, G6PD, GPI | 3 |
| Cell morphology, endocrine system development and function, organ morphology, organismal development | Morphology of thyroid cells | 1.31 × 10-4 | | CAV1, CTSB, FN1 | 3 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Quantity of filopodia-like projection | 1.31 × 10-4 | | ACTR2, ARPC2, CAPZB | 3 |
| Amino acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Synthesis of l-serine | 1.31 × 10-4 | | PHGDH, PKM, SHMT2 | 3 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance, tissue development | Formation of actin filaments | 1.34 × 10-4 | −1.689 | ACTR3, ARF1, ARPC2, CAPN1, CAV1, CD44, CFL1, CTTN, FN1, GNAI2, GPI, ITGB1, MAPK1, NPM1, PFN1, RHOA, TNC, TPM2, TWF1, TWF2, ZYX | 21 |
| Cell cycle, cellular movement | Cytokinesis of cervical cancer cell lines | 1.34 × 10-4 | 0.218 | GNAI2, LMNA, NPM1, RHOA, SEPT7, SEPT9, SSRP1 | 7 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer | 1.34 × 10-4 | | ATIC, EIF4A1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 7 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Adhesion of hepatoma cell lines | 1.37 × 10-4 | | BSG, C1QBP, ITGB1, RHOA | 4 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, cell morphology, cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, organ morphology, organismal development, skeletal and muscular system development and function, tissue morphology | Morphology of intercalated disks | 1.37 × 10-4 | | CALR, CAPZB, PLEC, VCL | 4 |
| Cellular compromise | Stress response of cervical cancer cell lines | 1.37 × 10-4 | | CALR, HNRNPA1, HSP90B1, HSPA5 | 4 |
| Cancer | Metastatic occult primary cancer of head and neck | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, connective tissue disorders, respiratory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the ethmoid sinus | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the glottis | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the lip | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the maxillary sinus | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the oropharynx | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the supraglottis | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cellular movement, connective tissue development and function, hepatic system development and function | Migration of hepatic stellate cells | 1.43 × 10-4 | −0.218 | CD44, GNB2L1, HMGB1, LGALS1, MYH10 | 5 |
| Cancer | Recurrent occult primary cancer of head and neck | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, connective tissue disorders, respiratory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the ethmoid sinus | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the glottis | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the lip | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the maxillary sinus | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the supraglottis | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer | Unresectable occult primary cancer of head and neck | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, connective tissue disorders, respiratory disease, skeletal and muscular disorders | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the ethmoid sinus | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the glottis | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the hypopharynx | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the lip | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the maxillary sinus | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the oropharynx | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, respiratory disease | Unresectable squamous Cell cancer of the supraglottis | 1.43 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of carcinoma Cell lines | 1.48 × 10-4 | 0.447 | C1QBP, CAV1, CD44, CTTN, CYR61, HNRNPA2B1, ITGB1, LGALS1, STMN1, TAGLN2, VIM, ZYX | 12 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation | Proliferation of colon cancer cell lines | 1.48 × 10-4 | 1.556 | AHSA1, CACYBP, CALR, CDK1, CSE1L, DDX5, EIF3C, FN1, HSP90AA1, IGF2R, IPO7, NCL, PKM, RHOA, SFN, SFPQ, UBA1, XRCC5 | 18 |
| Cardiovascular disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Dilated cardiomyopathy | 1.50 × 10-4 | −0.192 | CAST, DNM1L, FKBP1A, LMNA, MYH9, PGK1, PPP1CA, SDHA, TLN1, TMPO, TPI1, VCL, VDAC1, VDAC2 | 14 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, organ morphology, organismal development, skeletal and muscular system development and function, tissue morphology | Morphology of cardiac muscle | 1.50 × 10-4 | | CALR, CAPZB, CAV1, FKBP1A, FN1, HADHA, HSP90B1, IGF2R, MAPK1, MYH10, PLEC, SPTBN1, VCL, YWHAE | 14 |
| Infectious disease | Infection by dengue virus 2 | 1.53 × 10-4 | 0.896 | ACTR2, AP1B1, AP2B1, ARPC1B, CLTC, IFITM3, STAT1 | 7 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Reorganization of cytoskeleton | 1.59 × 10-4 | −1.953 | ARHGDIA, CD44, CFL1, DPYSL2, EZR, FLNA, FLNC, FN1, HMGB1, MARCKS, MSN, MYH9, PLS3, RHOA, SPTAN1 | 15 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Cell-cell adhesion of tumor Cell lines | 1.62 × 10-4 | 0.128 | C1QBP, ERP29, GNB2L1, ITGB1, MAPK1, ZYX | 6 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Formation of cytoplasmic aggregates | 1.62 × 10-4 | −1.131 | CAV1, DDX6, LMNA, RHOA, SOD1, YWHAZ | 6 |
| Tissue development | Aggregation of cells | 1.65 × 10-4 | −0.939 | ACTG1, AKR1B1, BSG, CAPN1, CAST, CD44, CLIC1, CSRP1, FLNA, FN1, GNAI2, HNRNPA2B1, HSPB1, ITGB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH9, MYL12A, P4HB, PDIA3, TLN1, VCL | 22 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of fibroblast Cell lines | 1.65 × 10-4 | −0.651 | CAPNS1, CDK1, CLIC4, CYR61, DDX3X, DNM1L, EEF1A1, EIF2S1, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF6, FN1, FUS, GPI, HSPA5, HSPD1, ITGB1, RHOA, RPL10, STAT1, VIM | 22 |
| Infectious disease, reproductive system disease | Infection of cervical cancer cell lines | 1.69 × 10-4 | −2.295 | ARF1, ATP5B, CCT2, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPG1, DDX3X, DNAJA2, EIF3I, GML, H3F3A/H3F3B, HNRNPK, HNRNPU, HSPA9, MAP4, PDIA3, PDIA6, PSME2, RAB1B, RANBP1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, STIP1, TWF1, UAP1, UQCRC1, XPO1 | 28 |
| Cell cycle | Mitosis | 1.76 × 10-4 | −1.833 | BUB3, CAPN2, CCT4, CDK1, CLTC, CSE1L, CYR61, DBI, DHX9, DYNC1H1, EIF6, KPNB1, KRT18, MAPK1, MARCKS, MYH10, NUMA1, PEBP1, PPP1CA, PRMT5, PTMA, RAN, RPS24, SEPT9, STAT1, STMN1, TCP1, TNC, TUBB, YWHAE | 30 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of tumor cells | 1.76 × 10-4 | −0.843 | ACTN4, AHCY, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CTSB, CTTN, EZR, FN1, HMGB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, RHOA, S100A6, TNC, VIM | 17 |
| Cell morphology, cellular function and maintenance | Autophagy of cells | 1.77 × 10-4 | 0.609 | CAPN1, CAPNS1, CAST, DNM1L, EIF2S1, EIF4G1, FKBP1A, HMGB1, HSPA5, KRT18, PAFAH1B2, PRKDC, RAB7A, SERPINH1, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, TUFM | 18 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, organismal development | Development of blood vessel | 1.78 × 10-4 | −1.788 | AKR1B1, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, ATP5A1, CALR, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, CTSB, CYR61, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, G6PD, HADHA, HMGB1, HSP90B1, HSPB1, IGF2R, ITGB1, KRT1, LDHA, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10, PDCD6, PGK1, PKM, PLEC, PPIA, PRKDC, RAD23B, RHOA, RNH1, SEPT9, SERPINH1, SOD1, SPTBN1, STAT1, TNC, VCL, VIM, WARS, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAZ | 48 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, cell morphology | Cell spreading of endothelial cells | 1.79 × 10-4 | −1.000 | FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, VIM, YWHAZ | 5 |
| Cell morphology, renal and urological system development and function | Cell spreading of kidney Cell lines | 1.79 × 10-4 | −0.678 | FLNA, FLNC, FN1, ITGB1, VIM | 5 |
| Cell death and survival, DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Fragmentation of DNA | 1.88 × 10-4 | −0.910 | APEX1, BSG, CAPN2, CAST, ENO1, HSD17B10, HSPB1, KRT8, LMNA, NPM1, PPIA, RHOA, SOD1, STAT1 | 14 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Nasopharyngeal cancer | 1.91 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, SFN, TUBB, TUBB4B | 6 |
| Energy production, nucleic acid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry | Binding of ATP | 1.94 × 10-4 | −0.068 | MAPK1, PCNA, PTGES3, STIP1 | 4 |
| Free radical scavenging | Modification of hydrogen peroxide | 1.94 × 10-4 | −1.710 | PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, SOD1 | 4 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular assembly and organization, tissue development | Turnover of focal adhesions | 1.94 × 10-4 | −0.254 | CAV1, ITGB1, PLEC, VCL | 4 |
| Cancer, cell death and survival, tumor morphology | Cell death of tumor cells | 1.95 × 10-4 | 0.142 | ACLY, ANXA1, ANXA2, B2M, BSG, CAV1, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CTSB, CYR61, EIF3C, ENO1, FASN, GNB2L1, HMGB1, HSP90AB1, LGALS1, MAPK1, PPP2CA, RHOA, RPS3A, RTN4, SOD1 | 24 |
| Cellular function and maintenance, tissue development | Organization of muscle cells | 1.98 × 10-4 | | ACTG1, CALR, CAV1, CTNNA1, FN1, ITGB1, KRT8 | 7 |
| RNA post-transcriptional modification | Processing of rRNA | 1.98 × 10-4 | | DDX5, NPM1, RPL5, RPL7, RPS15, RPS24, RPS7 | 7 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease | Oral cavity carcinoma | 2.06 × 10-4 | | ATIC, EZR, FASN, FN1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, LGALS1, NPM1, PLOD2, RPL10, TAGLN, TNC, TUBB, TUBB4B | 15 |
| Inflammatory response | Inflammation of body cavity | 2.07 × 10-4 | 0.920 | ACTN4, ALDOA, ANXA1, ANXA5, ARHGDIA, B2M, BSG, CAV1, CD44, CYR61, DDX5, ENO1, FKBP1A, GAPDH, GSTP1, HLA-A, HMGB1, HSPA5, IMPDH2, KRT18, KRT8, LGALS1, MYH10, MYH9, P4HB, PDIA3, PDLIM1, PPIA, PPP2CA, PRDX1, PSMB1, PSMD2, SOD1, STAT1, TKT, TPI1, TUBB, YBX1 | 38 |
| Cancer | Malignant solid tumor | 2.08 × 10-4 | 0.397 | AARS, ACAT1, ACAT2, ACLY, ACTG1, ACTN1, ACTN4, ACTR2, ACTR3, AHCY, AHNAK, AKR1B1, ALDOA, ALDOC, ANXA1, ANXA2, ANXA5, AP1B1, APEX1, ARF1, ARHGDIA, ARPC2, ATIC, ATP5A1, ATP5B, B2M, BASP1, BSG, C14orf166, C1QBP, CACYBP, CAND1, CANX, CAP1, CAPG, CAPN1, CAPN2, CAPRIN1, CAPZA1, CAST, CAV1, CBX3, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8, CD44, CD59, CDK1, CFL1, CLIC1, CLTC, CNN3, COPA, COPB1, COPB2, COPE, COPG1, CORO1C, COTL1, CRIP2, CSE1L, CTNNA1, CTPS1, CTSA, CTSB, CTTN, CUTA, CYB5R3, CYC1, CYR61, DBI, DBN1, DDX1, DDX39B, DDX3X, DDX5, DHX9, DLAT, DNAJA1, DNAJA2, DNAJC8, DNM1L, DPYSL2, DYNC1H1, DYNC1I2, ECHS1, EEF1A1, EEF1B2, EEF1D, EEF2, EHD1, EIF2S1, EIF2S2, EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF3M, EIF4A1, EIF4G1, EIF4H, ENAH, ENO1, ENO2, EPRS, ESYT1, ETFA, EZR, FASN, FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, FUBP3, FUS, G3BP1, G6PD, GANAB, GARS, GCN1L1, GDI1, GDI2, GLUD1, GML, GMPS, GNAI2, GNB2L1, GPI, GSTP1, H2AFY, H3F3A/H3F3B, HADHA, HARS, HDGF, HDLBP, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C | 383 |
| | | | | HIST1H2BL, HIST2H2AC, HLA-A, HLA-B, HMGB1, HN1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPA3, HNRNPH1, HNRNPH3, HNRNPK, HNRNPL, HNRNPM, HNRNPR, HNRNPU, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPA9, HSPD1, HYOU1, IARS, IDI1, IFITM3, IGF2R, ILF2, ILF3, IMMT, IMPDH2, IPO5, IPO7, IPO9, IQGAP1, ITGB1, KHDRBS1, KHSRP, KIF5B, KPNA2, KPNA3, KPNB1, KRT1, KRT18, KRT8, KRT9, LAMB1, LASP1, LDHA, LGALS1, LMNA, LMNB1, LOC102724594/U2AF1, LONP1, LRPPRC, LRRC59, MAP1B, MAP4, MAPK1, MAPRE1, MARCKS, MARS, MATR3, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, MDH1, MDH2, MSN, MVP, MYH10, MYH9, MYL12A, NACA, NAP1L1, NAP1L4, NASP, NCL, NNMT, NONO, NPEPPS, NPLOC4, NPM1, NSFL1C, NUMA1, OLA1, P4HB, PA2G4, PABPC1, PAFAH1B2, PAICS, PCBP1, PCBP2, PCM1, PCMT1, PCNA, PDCD6, PDE6H, PDIA3, PDIA4, PDLIM1, PDXK, PEA15, PFKP, PFN1, PGAM1, PGD, PGK1, PGM1, PHGDH, PICALM, PKM, PLEC, PLOD2, PLS3, PPIA, PPM1G, PPP1CA, PPP2CA, PPP2R1A, PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX5, PRKCSH, PRKDC, PRMT5, PRPF19, PSMA1, PSMB1, PSMC1, PSMC4, PSMD2, PSME1, PTBP1, PTMA, PTRF, PUF60, PYGB, PYGL, QARS, RANBP1, RARS, RCN1, RHOA, RNH1, RPL10, RPL12, RPL22, RPL27, RPL4, RPL5, RPL7, RPL7A, RPL8, RPLP0, RPN1, RPN2, RPS11, RPS12, RPS2, RPS24, RPS27A, RPS3A, RPS5, RPS7, RRBP1, RTN4, S100A6, SDHA, SEPT9, SERBP1, SERPINH1, SF3A1, SF3B1, SFN, SFPQ, SH3BGRL3, SHMT2, SLC25A3, SLC25A5, SLC38A2, SND1, SOD1, SPTAN1, SPTBN1, SSRP1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, STOML2, SYNCRIP, TAGLN, TALDO1, TARS, TCP1, TFRC, TLN1, TMPO, TNC, TNPO1, TPI1, TPM2, TPM3, TPM4, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8, TWF2, TXLNA, TXNDC5, UAP1, UBA1, UBE2N, UBXN4, UCHL1, UQCRC1, VARS, VAT1, VCL, VCP, VIM, VPS35, WARS, WDR1, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAE, YWHAG, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ, ZYX | |
| Cell cycle | M phase of cervical cancer Cell lines | 2.10 × 10-4 | 0.218 | GNAI2, LMNA, MCM7, NPM1, RHOA, SEPT7, SEPT9, SSRP1 | 8 |
| Cardiovascular system development and function, organismal development, tissue morphology | Morphology of cardiovascular tissue | 2.11 × 10-4 | | ARHGDIA, CALR, CAPZB, CAV1, CD44, CLIC4, FKBP1A, FN1, HADHA, HSP90B1, IGF2R, MAPK1, MYH10, PLEC, SPTBN1, VCL, YWHAE | 17 |
| Cell cycle | Interphase of tumor cell lines | 2.11 × 10-4 | 1.067 | ANXA2, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, FASN, ITGB1, LGALS1, MCM7, NASP, NPM1, PDCD6, PTGES3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL5, RPL7A, SFN, SPTAN1, STAT1, TCP1, TFRC, YWHAG, YWHAQ | 23 |
| Infectious disease | Replication of retroviridae | 2.19 × 10-4 | 0.989 | ANXA5, BTF3, CAV1, DDX5, DHX9, IFITM3, PLIN3, PPIA, PRDX1, PRDX2, RAB11A, TMPO | 12 |
| Cell morphology | Sprouting | 2.22 × 10-4 | −1.379 | ACTR3, ANXA2, BASP1, CAPNS1, CAPZB, CAV1, CSRP1, CYR61, DBN1, DNM1L, DPYSL2, EZR, FN1, HMGB1, HNRNPK, ITGB1, MAP1B, NNMT, PDIA3, PFN1, RHOA, RTN4, SOD1, TNC | 24 |
| Connective tissue disorders, developmental disorder, hereditary disorder | Marfan’s syndrome | 2.22 × 10-4 | | ALDOC, FLNA, MYH10, TAGLN, VCL | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Metastatic squamous cell cancer of the hypopharynx | 2.22 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cellular function and maintenance | Pinocytosis | 2.22 × 10-4 | −1.000 | ACTN4, CAV1, EZR, NCL, RHOA | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the hypopharynx | 2.22 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Cancer, gastrointestinal disease, respiratory disease | Recurrent squamous cell cancer of the oropharynx | 2.22 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 5 |
| Embryonic development, tissue morphology | Morphology of visceral endoderm | 2.23 × 10-4 | | DHX9, ITGB1, MAPK1, MYH9, RAB7A, SERPINH1 | 6 |
| Cellular movement | Cell movement of lung cancer cell lines | 2.26 × 10-4 | 0.276 | C1QBP, CAV1, CD44, FN1, HNRNPA2B1, ITGB1, STMN1, VIM, YBX1, ZYX | 10 |
| Cellular movement | Migration of cancer cells | 2.28 × 10-4 | −0.743 | AHCY, CAV1, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CTSB, EZR, FN1, HMGB1, IQGAP1, ITGB1, RHOA, S100A6, TNC, VIM | 15 |
| Cell cycle | Arrest in interphase of tumor cell lines | 2.29 × 10-4 | | ANXA2, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, FASN, ITGB1, LGALS1, PDCD6, PTGES3, RHOA, RPL23, RPL5, RPL7A, SFN, SPTAN1, TCP1, TFRC, YWHAG | 18 |
| Cellular function and maintenance | Engulfment of tumor cell lines | 2.48 × 10-4 | 0.222 | ANXA1, CAV1, CD44, CLTC, EZR, GNB2L1, ITGB1, NCL, PFN1, RHOA, SFPQ, VIM | 12 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, tissue development | Detachment of cells | 2.52 × 10-4 | 0.851 | ANXA1, ANXA5, CAPN2, FLNA, FN1, ITGB1, MAPK1, RHOA, TLN1 | 9 |
| Cell morphology, cell-to-Cell signaling and interaction | Morphology of intercellular junctions | 2.52 × 10-4 | | B2M, CALR, CAPRIN1, CAPZB, CAV1, LGALS1, PLEC, VCL, YWHAG | 9 |
| Gene expression, protein synthesis | Initiation of translation of mRNA | 2.53 × 10-4 | | EIF3B, EIF3C, EIF3I, EIF4G1, EIF4H, HSPB1, RPS3A | 7 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, connective tissue development and function, tissue development | Attachment of fibroblast Cell lines | 2.57 × 10-4 | | FN1, IPO9, ITGB1 | 3 |
| Cell morphology | Cell spreading of fibrosarcoma cell lines | 2.57 × 10-4 | | FLNA, FLNB, ITGB1 | 3 |
| Organ morphology, skeletal and muscular system development and function | Contraction of airway smooth muscle | 2.57 × 10-4 | | CAV1, GNAI2, RHOA | 3 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Formation of nuclear envelope | 2.57 × 10-4 | | CDK1, LMNA, RAN | 3 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | Metabolism of fructose-1, 6-diphosphate | 2.57 × 10-4 | | ALDOA, ALDOC, PFKP | 3 |
| Cancer, endocrine system disorders, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Metastatic ovarian tumor | 2.57 × 10-4 | | HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1 | 3 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation | Outgrowth of breast cancer Cell lines | 2.57 × 10-4 | | CYR61, FN1, ITGB1 | 3 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance, protein trafficking | Sequestration of g-actin | 2.57 × 10-4 | | PFN1, TWF1, TWF2 | 3 |
| Cell cycle | Abnormal cell cycle | 2.58 × 10-4 | | CAV1, H3F3A/H3F3B, HSPB1, PRDX1, RBM3, STAT1, TMPO, YWHAE | 8 |
| Cellular movement, connective tissue development and function | Migration of fibroblasts | 2.64 × 10-4 | 0.975 | CAPNS1, CAV1, CYR61, EHD1, FLNB, FN1, MAPK1, MYH10, PLEC, STMN1, VCL, ZYX | 12 |
| Developmental disorder, hematological disease, hereditary disorder, organismal injury and abnormalities | Diamond-blackfan anemia | 2.66 × 10-4 | | RPL5, RPS10, RPS24, RPS7 | 4 |
| Organismal injury and abnormalities, renal and urological disease | Minimal change nephrotic syndrome | 2.66 × 10-4 | | ACTN4, FKBP1A, IMPDH2, PDLIM1 | 4 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, renal and urological disease | Transitional cell bladder cancer | 2.66 × 10-4 | | GSTP1, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1 | 4 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Growth of microtubules | 2.72 × 10-4 | −1.710 | MAP4, MAPRE1, MYH9, SSRP1, STMN1 | 5 |
| Cell death and survival | Apoptosis of cerebral cortex cells | 2.84 × 10-4 | 0.050 | CAPN1, CAST, CDK1, HSPA5, MAP1B, P4HB, PEA15, RPS3, SOD1, YWHAB | 10 |
| Cell death and survival, renal and urological system development and function | Cell viability of kidney cell lines | 2.85 × 10-4 | −0.378 | ANXA5, CAV1, EZR, HNRNPU, HSP90B1, HYOU1, PPIA, VDAC1 | 8 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, renal and urological system development and function | Binding of kidney cell lines | 2.85 × 10-4 | 0.055 | ANXA2, BSG, CAV1, ITGB1, PPP2CA, PRMT5, RPSA | 7 |
| Molecular transport, RNA trafficking | Transport of mRNA | 2.85 × 10-4 | | ALYREF, DDX39B, EIF5A, FUS, KHDRBS1, U2AF2, XPO1 | 7 |
| Gene expression | Transcription of RNA | 2.90 × 10-4 | 1.084 | ACTR2, ACTR3, ALYREF, BASP1, BTF3, C14orf166, C1QBP, CALR, CAND1, CAV1, CBX3, CD44, CDK1, CSE1L, CYR61, DDX3X, DDX5, EEF1D, EIF2S1, ENO1, FKBP1A, FLNA, FN1, FUBP3, GLO1, GSTP1, H2AFY, HDGF, HEXB, HINT1, HIST1H1C, HMGB1, HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2B1, HNRNPK, HSPA8, ILF2, ILF3, IQGAP1, KHDRBS1, KPNA2, LGALS1, LMNA, LRPPRC, MAPK1, MATR3, MCM7, NONO, NPM1, OTUB1, PA2G4, PARK7, PCNA, PDLIM1, PEA15, PEBP1, PFN1, PHB2, PHGDH, PICALM, PPP2CA, PRKDC, PRMT5, PTGES3, PTMA, PTRF, RHOA, RPL6, SET, SFPQ, SQSTM1, SSRP1, STAT1, TMPO, TRIM28, UBE2L3, VAPA, XPO1, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1, YBX3, YWHAB, YWHAH, YWHAQ, YWHAZ | 86 |
| Cancer, endocrine system disorders, respiratory disease | Small cell lung cancer | 2.99 × 10-4 | | ENO2, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, HSPD1, PDCD6, TUBB, TUBB4B, YWHAE | 9 |
| Cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, embryonic development, organ development, organismal development, skeletal and muscular system development and function, tissue development | Formation of muscle cells | 3.04 × 10-4 | −1.408 | ACTA1, ACTG1, ACTN4, CALR, CAPZB, FLNC, FN1, HMGB1, HSP90B1, ITGB1, KRT8, MYH10, PLEC, UCHL1 | 14 |
| Cellular assembly and organization | Quantity of actin filaments | 3.14 × 10-4 | −0.570 | CFL1, FN1, GNB2L1, MARCKS, PLEC, RHOA, SPTAN1, TMOD3 | 8 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Repair of DNA | 3.18 × 10-4 | −0.335 | APEX1, CDK1, DDX1, FUS, HMGB1, HNRNPU, KPNA2, NPM1, OTUB1, PCNA, PRKDC, PRPF19, RAD23B, TRIM28, UBE2N, VCP, XRCC5, XRCC6, YBX1 | 19 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction | Binding of leukemia cell lines | 3.20 × 10-4 | 0.415 | ANXA2, ANXA5, CD44, HLA-A, ITGB1, NCL, TNC | 7 |
| Molecular transport, RNA trafficking | Export of RNA | 3.20 × 10-4 | −1.974 | ALYREF, DDX39B, EIF5A, KHDRBS1, RAN, U2AF2, XPO1 | 7 |
| Cancer, hematological disease, immunological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Large-cell KI-1 lymphoma | 3.20 × 10-4 | | HMGB1, PSMB1, PSMD2, TUBB, TUBB4B, TUBB6, TUBB8 | 7 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Organization of microtubules | 3.20 × 10-4 | −1.000 | DPYSL2, GAPDH, MAPRE1, NUMA1, PCM1, RRBP1, TUBB | 7 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Metastatic breast cancer | 3.25 × 10-4 | | FDPS, FKBP1A, FLNA, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, STAT1, TUBB, TUBB4B | 9 |
| Immunological disease, inflammatory disease, inflammatory response, organismal injury and abnormalities, renal and urological disease | IGA nephropathy | 3.31 × 10-4 | | ACTN4, IMPDH2, PDLIM1, PSMB1, PSMD2 | 5 |
| Cellular movement, hematological system development and function, immune cell trafficking | Cell rolling of granulocytes | 3.47 × 10-4 | 0.000 | ANXA1, CD44, CTTN, GNAI2, ITGB1, TLN1 | 6 |
| DNA replication, recombination, and repair | Conformational modification of DNA | 3.47 × 10-4 | | HMGB1, MCM4, MCM6, MCM7, NCL, SSRP1 | 6 |
| Cancer | Locally advanced malignant tumor | 3.47 × 10-4 | | ATIC, FKBP1A, HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1, TUBB4B | 6 |
| Organismal survival | Viability | 3.53 × 10-4 | −1.671 | B2M, GNAI2, MAP1B, PFN1, PRKDC, RAN, TKT, VCL, XRCC5 | 9 |
| Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, skeletal and muscular system development and function, tissue development | Adhesion of smooth muscle cells | 3.56 × 10-4 | | CYR61, FN1, ITGB1, RHOA | 4 |
| Cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Quantity of lamellipodia | 3.56 × 10-4 | 0.000 | ACTR2, ARPC2, ENAH, TPM3 | 4 |
| Cell morphology | Shape change of leukemia Cell lines | 3.56 × 10-4 | | FN1, ITGB1, MAPK1, TNC | 4 |
| Cardiovascular disease, organismal injury and abnormalities | Primary cardiomyopathy | 3.58 × 10-4 | | LMNA, PGK1, SDHA, TPI1, VCL, VDAC1, VDAC2 | 7 |
| Cellular growth and proliferation | Formation of cells | 3.63 × 10-4 | −2.209 | ACTA1, ACTG1, ACTN4, ANXA2, ARHGDIA, B2M, BSG, CALR, CAPZB, CD44, CTTN, DNAJA1, EEF1D, EHD1, ENAH, EZR, FLNA, FLNB, FLNC, FN1, HEXB, HMGB1, HSP90B1, HSPA4, ITGB1, KRT18, KRT8, LGALS1, MAPK1, MYH10, MYH9, NPEPPS, PAFAH1B2, PEBP1, PLEC, PLS3, PRDX4, RAD23B, RANBP1, RHOA, RPL22, SFN, SOD1, SQSTM1, STAT1, STIP1, STMN1, TCP1, UCHL1, XRCC6, YBX3 | 51 |
| Cancer, organismal injury and abnormalities, reproductive system disease | Uterine leiomyoma | 3.74 × 10-4 | | ALDOA, CYR61, DDX6, HSD17B10, HSP90AB1, IQGAP1, KPNA3, MDH1, MYH10, NPEPPS, PCNA, RPL27, RPS15, SF3A1, TNC, TWF1, VCP, ZYX | 18 |
| Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance | Reorganization of actin cytoskeleton | 3.78 × 10-4 | −2.219 | ARHGDIA, CFL1, DPYSL2, EZR, FLNA, FLNC, FN1, MYH9, PLS3, RHOA, SPTAN1 | 11 |
| Cancer | Stage 3 cancer | 3.78 × 10-4 | | ATIC, CAV1, CBX3, CCT3, FKBP1A, FN1, KRT8, MAPK1, PCNA, TUBB4B, TUBB6 | 11 |
| Cancer, tumor morphology | Progression of tumor | 3.83 × 10-4 | −0.342 | ANXA1, ANXA2, BSG, CAV1, CD44, EZR, FASN, FUS, GSTP1, HMGB1, STAT1, TNC, YWHAZ | 13 |