(−)-Kunstleramide, a New Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Dienamide from the Bark of Beilschmiedia kunstleri Gamble
Abstract
:1. Introduction

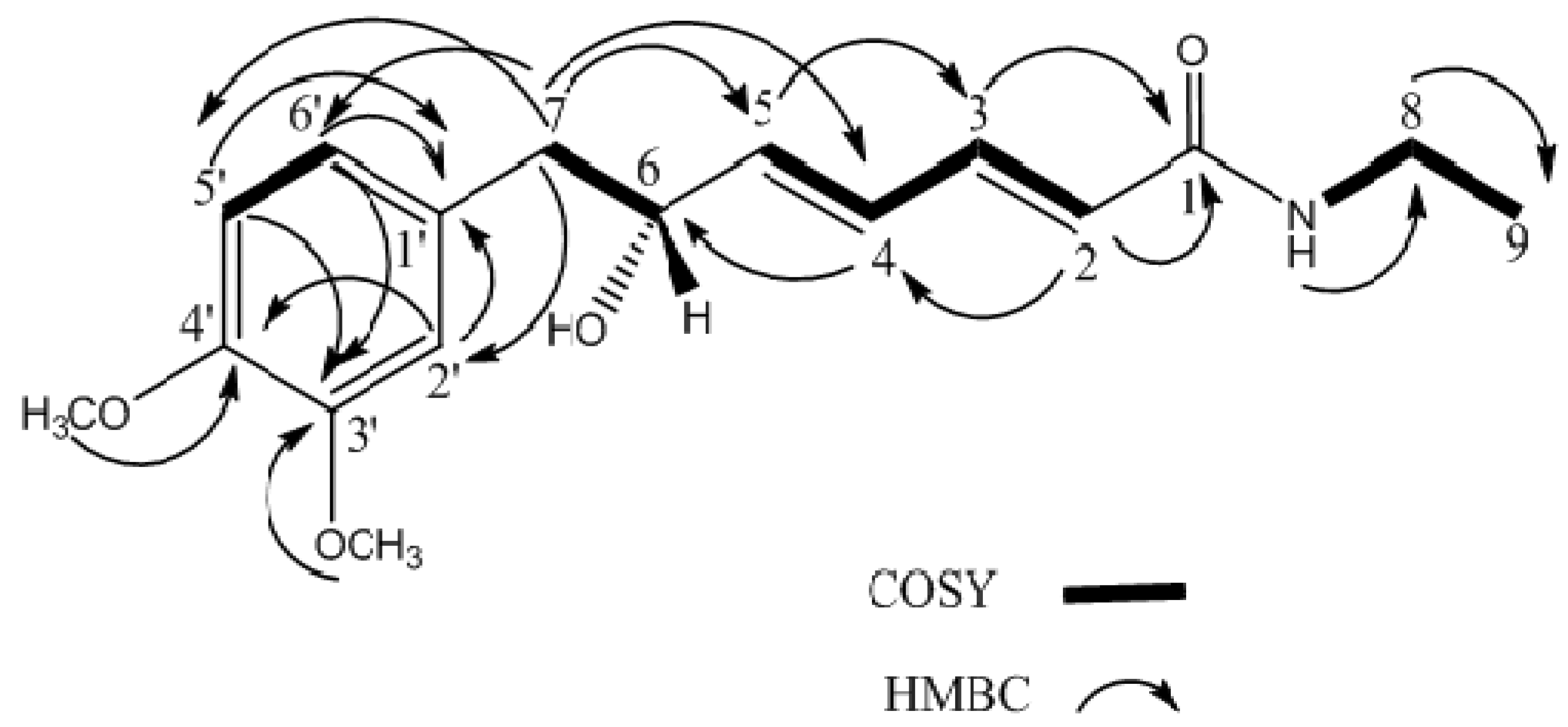
2. Results and Discussion
| Position | 1H (δH, Hz) | 13C |
|---|---|---|
| C=O | - | 165.8 |
| C-2 | 5.74, d (15.1) | 124.2 |
| C-3 | 7.15, dd (15.1, 8.9) | 140.0 |
| C-4 | 6.26, dd (15.1, 11.2) | 127.7 |
| C-5 | 6.06, dd (15.1, 5.1) | 142.3 |
| C-6 | 4.37, m | 72.6 |
| C-7 | 2.66, dd (Jβ = 13.1, 5.1),2.80, dd (Jα = 13.1, 5.1) | 43.4 |
| C-8C-9 | 3.30, q (7.4)1.10, t (7.4) | 34.614.9 |
| C-1' | - | 129.5 |
| C-2' | 6.66, d (1.8) | 112.6 |
| C-3' | - | 147.9 |
| 3’-OMeC-4'4'-OMe | 3.81, s-3.79, s | 55.9149.955.9 |
| C-5' | 6.76, d (8.2) | 111.3 |
| C-6' | 6.67, dd (8.2, 1.8) | 121.6 |
| N-HO-H | 5.43, br s 1.67, br s | -- |

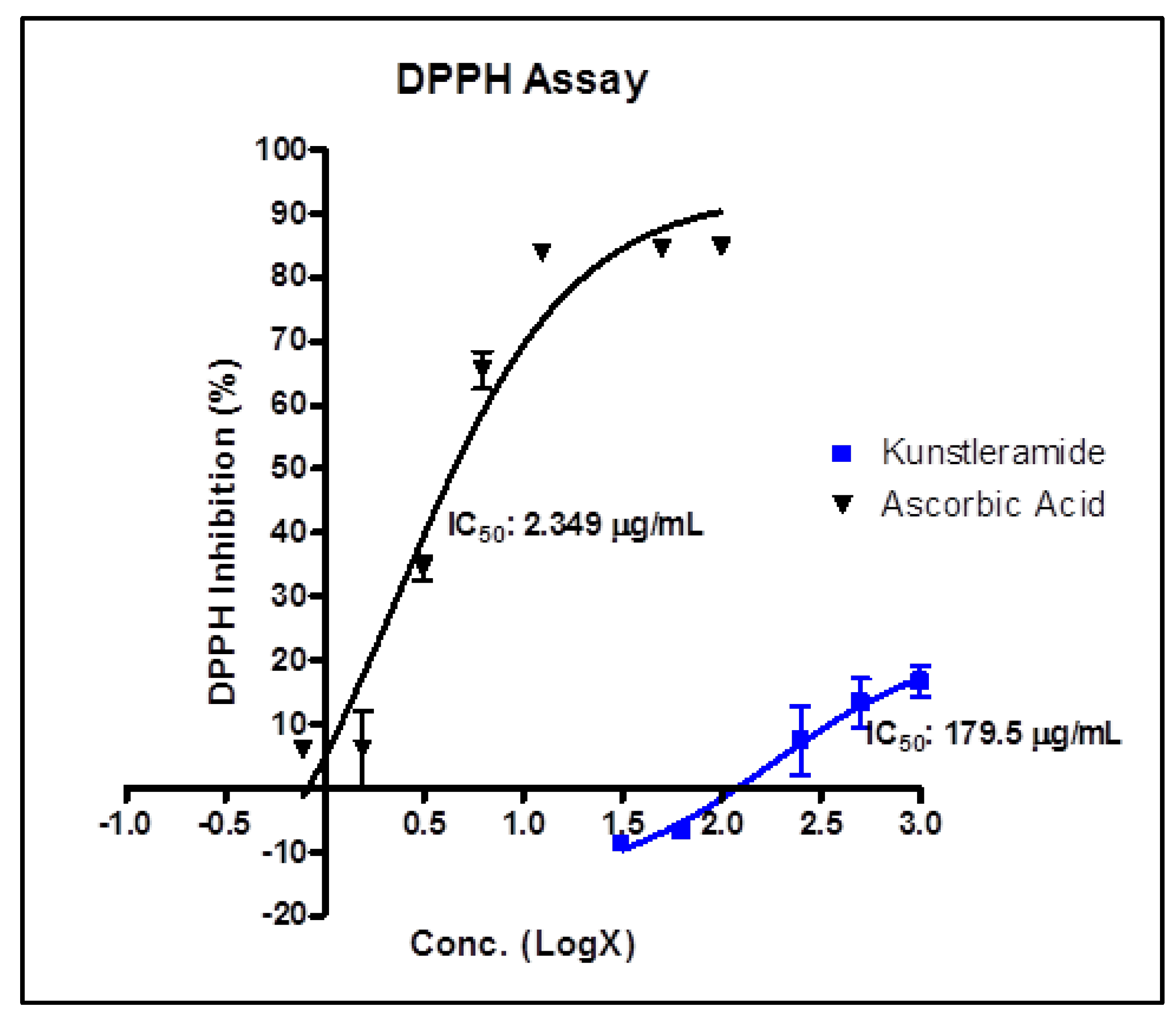
2.1. Antioxidant Activity
2.2. Cytotoxic Activity
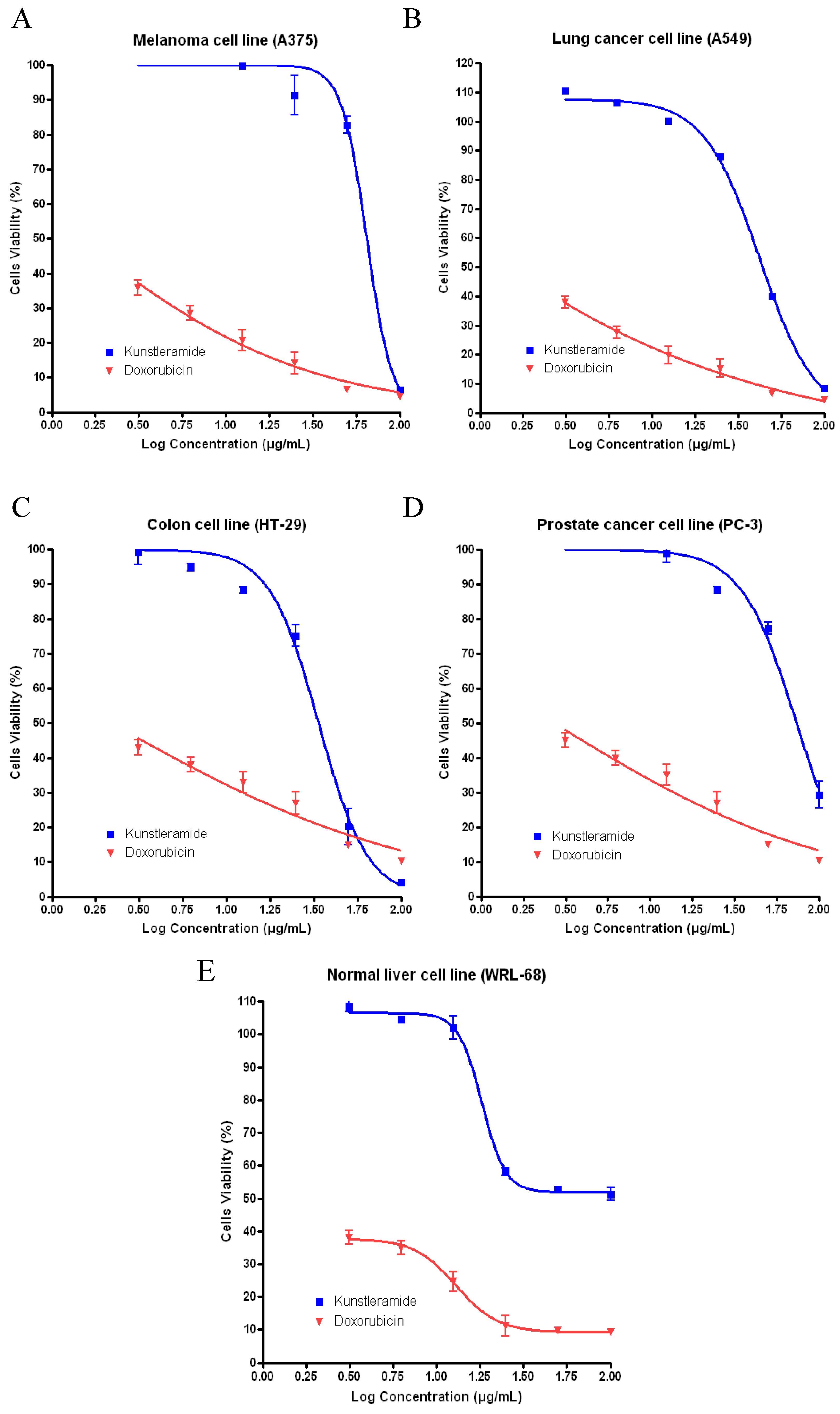
| Cell line | New Dienamide | Doxorubicin |
|---|---|---|
| A375 | 64.65 | 1.364 |
| A549 | 44.74 | 1.550 |
| HT-29 | 55.94 | 1.957 |
| PC-3 | 73.87 | 2.125 |
| WRL-68 | 70.95 | 1.731 |

3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation of Chemical Constituents
3.4. Antioxidant Assay

3.5. Statistical Analyses
3.5. Cytotoxic Activity Studies
3.5.1. Cell Culture
3.5.2. Cellular Viability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Kochummen, K.M. Tree Flora of Malaya: A Manual For Foresters; Ng, F.S.P., Ed.; Longman: Selangor, Malaysia, 1989; Volume 4, p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Pudjiastuti, P.; Mukhtar, M.R.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Saidi, N.; Morita, H.; Litaudon, M.; Awang, K. (6,7-Dimethoxy-4-methylisoquinolinyl)-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-methanone, a new benzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Beilschmiedia brevipes. Molecules 2010, 15, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funasaki, M.; Lordello, A.L.; Viana, A.M.; Santa-Catarina, C.; Floh, E.I.S.; Yoshida, M.; Kato, M.J. Neolignans and sesquiterpenes from leaves and embryogenic cultures of Ocotea catharinensis (Lauraceae). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, M.P.; Rao, K.V.; Douglas, B.; Weisbach, J.A. Alkaloids of Cassytha Americana. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 2443–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Chung-hsiung, C.; Shoei-shen, L.; Chung-fang, L.; Jinn, W.; Jack, L.B. A caryachnine N-methosalt from Cryptocarya chinensis and PMR spectral characteristics of some quaternary pavine alkaloids. J. Nat. Prod. 1979, 42, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.L.B.; Xavier, C.M.; Souza, A.D.L.D.; Rabelo, D.D.M.; Batista, C.L.; Batista, R.L.; Costa, E.V.; Campos, F.R.; Barison, A.; Valdez, R.H.; et al. Acanthoic acid and other constituents from the stem of Annona amazonica (Annonaceae). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Babkock, P.A.; Segelman, A.B. Alkaloids of Lindera benzoin (L.) Blume (lauraceae), I: Isolation and identification of laurotetanine. J. Pharm. Sci. 1974, 63, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, A.; Leboeuf, M.; Moskowitz, H.; Ranaivo, A.; Bick, I.; Sinchai, W.; Nieto, M.; Sevenet, T.; Cabalion, P. Alkaloids of Cryptocarya phyllostemon. Aust. J. Chem. 1989, 42, 2243–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, M.M.V.; Prashant, V.P. Tandem acylation-cycloalkylation with cyclohexene-1-acetic acid: A new entry to phenanthrene alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Res. 1996, 8, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Mollataghi, A.; Hamid, A.H.A.; Awang, K.; Jamaludin, M.; Litaudon, M.; Mukhtar, M.R. (+)-Kunstlerone, a new antioxidant neolignan from the leaves of Beilschmiedia kunstleri Gamble. Molecules 2011, 16, 6582–6590. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Jamil, S.; Ibrahim, A.Z.; Read, R.W. Alkenylalamides from Piper maingayi Hk. F. Pertanika. J. Sci. Technol. 1996, 4, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, J.V.; Oliveira, A.D.; Raggi, L.; Young, M.C.M.; Kato, M.J. Antifungal activity of natural and synthetic amides from piper species. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.J.; Tsai, I.L.; Chen, I.S. Chemical constituents from the root bark of Formosan Zanthoxylum ailanthoides. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2003, 50, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Chaaib, F.; Queiroz, E.F.; Ndjoko, K.; Diallo, D.; Hostettmann, K. Antifungal and antioxidant compounds from the root bark of Fagara zanthoxyloides. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Muhammad, I.; Dunbar, D.C.; Mustafa, J.; Khan, I.A. New alkamides from maca (Lepidium meyenii). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 690–693. [Google Scholar]
- Caturla, F.; Najera, C. Lithiated (E)-N-isopropyl-5-tosyl-4-pentenamide: Synthetic applications as new δ-acyldienyl anion equivalent. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 11255–11270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Nakanishi, K. Exciton chirality method and its application to configurational and conformational studies of natural products. Acc. Chem. Res. 1972, 5, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.E. Chiroptical properties of the benzene chromophore. A method for the determination of the absolute configurations of benzene compounds by application of the benzene sector and benzene chirality rules. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1709–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blot, W.J.; Li, J.Y.; Taylor, P.R.; Guo, W.; Dawsey, S.; Wang, G.Q.; Yang, C.S.; Zheng, S.F.; Gail, M.; Li, G.Y.; et al. Nutrition intervention trials in Linxian, China: Supplementation with specific vitamin/mineral combinations, cancer incidence, and disease-specific mortality in the general population. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, N.; Rahman, A.; Uddin, N.A.; Rana, S.; Akter, R.; Chowdhury, M.A. Antioxidant, cytotoxic and antimicrobial properties of Eclipta alba ethanol extract. Int. J. Biol. Med. Res. 2010, 1, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Price, J.A.; Sanny, C.G.; Sherlin, D. Application of manual assessment of oxygen radical absorbent capacity (ORAC) for use in high throughput assay of “total” antioxidant activity of drugs and natural products. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2006, 54, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, M.K.; Naz, Q.; Ejaz, A.; Yilmaz, G.; Kan, Y.; Konuklugil, B.; Sener, B.; Choudhary, M.I. Antioxidant and anticholinesterase evaluation of selected Turkish Salvia species. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, B.; Seger, C.; Pacher, T.; Harti, M.; Hadacek, F.; Hofer, O.; Vajrodaya, S.; Greger, H. Antioxidant dehydrotocopherols as a new chemical character of Stemona species. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 2719–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayat, S.; Banerjee, S. Comparative antioxidant activities of extracts from leaves, bark and catkins of Salixa egyptiaca species. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, S.C.; Appleton, D.R.; Lee, S.T.; Lam, M.L.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Mustafa, M.R. Panduratin a inhibits the growth of A549 cells through induction of apoptosis and inhibition of NF-Kappa B translocation. Molecules 2011, 16, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for the cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, P.A.; Dos Santos, D.A.; Da Silva, M.F.; Vieira, P.C.; Fernandes, J.B.; Houghton, P.J.; Fang, R. In vitro cytotoxicity activity on several cancer cell lines of acridone alkaloids and N-phenylethyl-dienamide derivatives from Swinglea glutinosa (Bl.) Merr. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mollataghi, A.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Cheah, S.-C. (−)-Kunstleramide, a New Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Dienamide from the Bark of Beilschmiedia kunstleri Gamble. Molecules 2012, 17, 4197-4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17044197
Mollataghi A, Hadi AHA, Cheah S-C. (−)-Kunstleramide, a New Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Dienamide from the Bark of Beilschmiedia kunstleri Gamble. Molecules. 2012; 17(4):4197-4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17044197
Chicago/Turabian StyleMollataghi, Abbas, A. Hamid A. Hadi, and Shiau-Chuen Cheah. 2012. "(−)-Kunstleramide, a New Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Dienamide from the Bark of Beilschmiedia kunstleri Gamble" Molecules 17, no. 4: 4197-4208. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17044197




